Contract Law Elements: Offer, Acceptance, Revocation, Rejection
advertisement

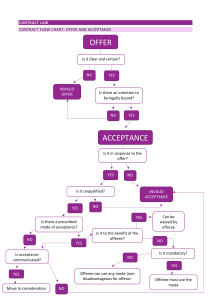
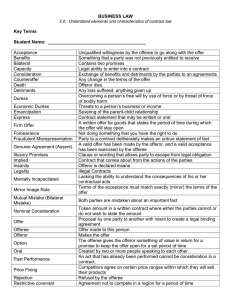
ELEMENTS OF COMMON LAW CONTRACT FORMATION CONTRACT ELEMENT OFFER ACCEPTANCE REVOCATION Section 36 Restatement REJECTION Section 38 Restatement DEFINITION LEGAL EFFECT Manifestation of willingness to enter into a bargain, so made as to justify another person in understanding that his assent to that bargin is invited and will conclude it Acceptance of an offer is a manifestation of assent to the terms thereof made by the offeree in a manner invited or required by the offer. Annulment or cancellation of a statement, document, or offer not yet accepted, or cancellation of a contract by the parties to it. For example, a person can revoke a will or revoke an offer to enter into a contract, and a government agency can revoke a license. If offer made, then it just takes an acceptance to have a K. Transfers liability. Effective upon receipt Terms of offer are accepted, and acceptor assumes liability Effective upon sent (mailing) a : a refusal to accept an offer b : a refusal to accept nonconforming goods as performance of a contract (1) An offeree’s power of acceptance may be terminated by Rejection or counteroffer by the offeree, or Lapse of time or, Revocation by the offeror, or Death or incapacity of the offeror or offeree (1) An offeree’s power of acceptance is terminated by his rejection of the offer, unless the offeror has manifested a contrary intention. TIME WHEN EFFECTIVE NOTES ELEMENTS OF COMMON LAW CONTRACT FORMATION COUNTER-OFFER Section 39 restatement A counteroffer functions as both a rejection of an offer to enter into a contract, as well as a new offer that materially changes the terms of the original offer. Because a counteroffer serves as a rejection, it completely voids the original offer. This means that the original offer can longer be accepted. However, added modifications do not necessarily mean that a party made a counteroffer. Instead, these added modifications may create a conditional acceptance, depending on the changed terms (2) A manifestation of intention not to accept an offer is a rejection unless the offeree manifests an intention to take it under further advisement (1) A counter offer is an offer made by an offeree to his offeror relating to the same matter as the original offer and proposing a substituted bargain differing form that proposed by the original offer. (2) An offeree’s power of acceptance is terminated by his making of a counteroffer unless the offeror has manifested a contrary intention or unless the counter offer manifests a contrary intention of the offeree ELEMENTS OF COMMON LAW CONTRACT FORMATION and the applicable law. Alternatively, requests for modifications may not constitute a new offer at all, but may instead be mere negotiation.