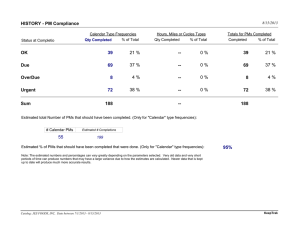
EU MDR Post-Market Surveillance Best Practices for Medical Device Regulatory, Compliance & Quality Specialists Jon Gimbel, Ph.D. – Executive Director – Regulatory & Quality Solutions (R&Q) Agenda ▪ PMS Requirements ▪ PMS Planning ▪ PMS Reporting ▪ Now What? ▪ Q&A CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 2 Post-Market Surveillance – Definition ▪ MDR Article 2 Section 60: ▪ ‘post-market surveillance’ means all activities carried out by manufacturers in cooperation with other economic operators to institute and keep up to date a systematic procedure to proactively collect and review experience gained from devices they place on the market, make available on the market or put into service for the purpose of identifying any need to immediately apply any necessary corrective or preventive actions CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 3 Post-Market Surveillance – Requirements ▪ MDR Article 83: ▪ For each device, manufacturers shall plan, establish, document, implement, maintain and update a post-market surveillance system in a manner that is proportionate to the risk class and appropriate for the type of device ▪ The post-market surveillance system shall be suited to actively and systematically gathering, recording and analyzing relevant data on the quality, performance and safety of a device throughout its entire lifetime, and to drawing the necessary conclusions and to determining, implementing and monitoring any preventive and corrective actions CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 4 PMCF – Requirements ▪ MDR ANNEX XIV Part B ▪ PMCF shall be understood to be a continuous process that updates the clinical evaluation…and shall be addressed in the manufacturer's postmarket surveillance plan. ▪ When conducting PMCF, the manufacturer shall proactively collect and evaluate clinical data from the use in or on humans of a device which bears the CE marking…with the aim of ▪ confirming the safety and performance throughout the expected lifetime of the device ▪ ensuring the continued acceptability of identified risks and of detecting emerging risks on the basis of factual evidence CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 5 Post-Market Surveillance – Article 83(3) ▪ The goal of the PMS system is to: ▪ Update risk management, labeling, and clinical evaluation ▪ Identify need for corrective, preventative, or field safety corrective actions ▪ Improve the usability, performance, and safety of the device ▪ Contribute to the PMS of other devices ▪ Detect and report trends which may impact the benefit-risk analysis, health or safety CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 6 Post-Market Clinical Follow -Up – Annex XIV ▪ The goal of PMCF is to proactively collect and evaluate clinical data from use of device with aim of: ▪ Confirming safety & performance throughout device’s expected lifetime ▪ Identifying previously unknown / monitoring known side effects ▪ Identifying and analyzing emergent risks ▪ Ensuring continued acceptability of benefit-risk ratio ▪ Identifying possible system misuse or off-label use of device CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 7 PMS Plan PMCF PMCF Plan Plan Legend Updated annually (Class IIb & III) Updated every 2 years (Class IIa) Submitted to NB via electronic system (Class III) Made available to NB and by request to CA (all other classes) CER Updated based on PMS and PMCF as needed Updated at least annually if the device carries significant risk or is not yet well established Updated very 2 – 5 years otherwise SSCP Publicly Available Published by NB on EUDAMED PMCF Evaluation Report Updated when necessary Updated annually (Class III & Implantables) Class I Clinical Development Plan All Classes CEP PSUR Class III & Implantables Technical Documentation Class IIa/b & III Documentation requirements Clinical Technical PMS PMCF PMS Report Updated when necessary Available to CA on request CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 8 Report frequencies Class I CER Clinical Evaluation Report PMS Report Post Market Surveillance Class IIa Class IIb Class III After receiving PMS information with potential to change current evaluation At least annually if the device carries significant risk or is not yet well established Every 2 – 5 years if device is not expected to carry significant risks and is well established Ref: MEDDEV 2.7/1 Rev 4 Clause 6.2.3 When necessary Ref: MDR Art. 85 N/A PSUR Periodic Safety Update Report N/A When necessary and at least every 2 years Ref: MDR Art. 86(1) PMCF Evaluation Report Post-Market Clinical Follow-up When needed and according to the PMCF Plan (Ref. MDR Annex XIV Part B) If implantable, at least annually Ref MDR Art. 61(11) Otherwise, when needed and according to PMCF plan (Ref. MDR Annex XIV Part B) At least annually Ref: MDR Art. 61(11) N/A N/A unless device is implantable If implantable, at least annually Ref: MDR Art. 61(11) At least annually Ref: MDR Art. 61(11) SS&CP Summary of Safety & Clinical Performance CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com N/A N/A At least annually Ref: MDR Art. 86(1) 9 Typical PMS / PMCF activities Reactive PMS, e.g., - Complaints - FSCAs / Recalls - Incident reports / MDRs Pro-Active PMS / PMCF, e.g., - PMCF studies - Registry studies - Retrospective Record Review - Focus groups - Surveys Literature / Database Reviews CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 10 Typical PMS / PMCF activities Reactive PMS, e.g., - Complaints - FSCAs / Recalls - Incident reports / MDRs Annex III: The PMS plan shall address the collection [of]…technical literature, databases and/or registers CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q Pro-Active PMS / PMCF, e.g., - PMCF studies - Registry studies - Retrospective Record Review - Focus groups - Surveys Literature / Database Reviews RQTeam.com Annex XIV PMCF: General methods…such as…screening of scientific literature;… 11 PMCF – MEDDEV 2.12/2 PMCF studies ▪ A precondition for placing a product on the market is that conformity to the relevant Essential Requirements has been demonstrated ▪ Limitations to pre-market clinical data ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ duration of pre-market clinical investigations number of subjects and investigators involved heterogeneity of subjects and investigators versus general medical practice ability to detect rare complications after wide-spread or long term use ▪ Clinical data obtained from PMS and PMCF studies are ▪ not intended to replace the pre-market data necessary to demonstrate conformity ▪ critical to updating the clinical evaluation and ensuring long term safety and performance of devices placed on the market CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 12 PMCF – MEDDEV 2.12/2 PMCF studies ▪ Circumstances that may justify PMCF studies include, for example ▪ Innovative, novel device ▪ Significant changes ▪ High product related risk; High risk anatomical locations; High risk target populations; Severity of disease/treatment challenges ▪ Questions of ability to generalize clinical investigation results; Verification of safety and performance of device when exposed to a larger and more varied population of clinical users ▪ Unanswered questions of long-term safety and performance; Continued validation of the expected life of the product; Emergence of new information on safety or performance; Results from any previous clinical investigation or PMS activities; Risks identified from the literature or other data sources for similar marketed devices ▪ Identification of unstudied subpopulations; Interaction with other medical products or treatments ▪ Where CE marking was based on equivalence. CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 13 PMCF – MEDDEV 2.12/2 PMCF studies ▪ PMCF studies may not be required when ▪ The medium/long-term safety and clinical performance are already known from previous use of the device ▪ Other appropriate PMS activities would provide sufficient data to address the risks ▪ PMCF study plans should include include: ▪ clearly stated research questions, objectives and related endpoints ▪ scientifically sound design with an appropriate rationale and statistical analysis plan ▪ a plan for conduct according to the appropriate standards ▪ a plan for an analysis of the data and for drawing appropriate conclusions CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 14 PMCF – MEDDEV 2.12/2 PMCF studies ▪ NB shall ▪ verify that the manufacturer has appropriately considered the need for PMCF based on the clinical evaluation and the characteristics of the medical device ▪ verify that PMCF is conducted when clinical evaluation was based exclusively on clinical data from equivalent devices ▪ assess the appropriateness of any justification presented by a manufacturer for not conducting a specific PMCF plan ▪ assess the appropriateness of the proposed PMCF plan ▪ verify that the clinical evaluation is being actively updated with PMCF data CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 15 Notes on Justifying Not Performing PMCF ▪ Unlikely to work on high risk devices ▪ Exception, not the rule ▪ Where device is being discontinued (monitoring end of lifetime of device) ▪ Common Specifications exist and exempt PMCFs ▪ Performance standards exist for the device and good data exists on real life use for the lifetime of the device ▪ Lower risk devices (Class I) ▪ Need sufficient clinical data ▪ Tip: May be better to use low-level proactive activities (like literature searches) rather than attempt to justify CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com MDR Definitions: PMS Activities carried out…to proactively collect and review experience gained from devices… MDR Article 86: Class IIa, IIb, III PSUR requires main findings of the PMCF MDR Article 61(4): Class III and implantable Clinical investigations shall be performed, except if…modified device…and clinical evaluation of marketed device is sufficient…In this case the notified body shall check that the PMCF plan is appropriate and includes post market studies to demonstrate the safety and performance of the device. 16 Notes on Sufficient Data and PMCF Activities Needed ▪ Need sufficient data in the clinical evaluation ▪ Manufacturer justifies the level of clinical evidence necessary ▪ Level of clinical evidence depends on device intended purpose ▪ Should establish specific and measurable outcome parameters ▪ PMCF needs to collect relevant data, e.g., ▪ Registries outcome parameters should align with manufacturers parameters of interest ▪ Literature searches need to provide relevant articles ▪ Should justify type and sample size of the PMCF activity CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 17 Notes on Sufficient Data and PMCF Activities Needed ▪ Need sufficient data in the clinical evaluation ▪ Manufacturer justifies the level of clinical evidence necessary ▪ Level of clinical evidence depends on device intended purpose ▪ Should establish specific and measurable outcome parameters ▪ PMCF needs to collect relevant data, e.g., Article 2: Clinical Benefit positive impact of a device…expressed in terms of a meaningful, measurable, patient-relevant clinical outcome(s)… ▪ Registries outcome parameters should align with manufacturers MDCG 2019-9: SSCP Give a description of the documented clinical parameters of interest benefits for patients with relevant and specified clinical outcome measures, and the success rate for ▪ Literature searches need to provide relevant articles achieving the outcome measures. Annex XIV: Clinical Evaluation Plan …shall include…a detailed description of intended clinical benefits to patients with relevant and specified clinical outcome parameters; ▪ Should justify type and sample size of the PMCF activity CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 18 Notes on Sufficient Data and PMCF Activities Needed ▪ Need sufficient data in the clinical evaluation ▪ Manufacturer justifies the level of clinical evidence necessary ▪ Level of clinical evidence depends on device intended purpose ▪ Should establish specific and measurable outcome parameters ▪ PMCF needs to collect relevant data ▪ Registries outcome parameters should align with manufacturers parameters of interest ▪ Literature searches need to provide relevant articles ▪ Should justify type and sample size of the PMCF activity CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 19 Key dates, requirements, and limitations EUDAMED Delay EU MDR DOA 26-May 2020 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 MDR Only Class I Devices (except IS/IM) MDR Only - Requires MDR Compliant QMS Class IR Devices All Other devices Existing devices with valid MDD Cert(s) Or Class Ir (No significant design changes) QMS No New devices until QMS is compliant Notified Bodies start to be designated for MDR certification UDI on Class III Labels 26-May-2021 New Date of Applicability CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q Last MDD Certificate Valid 26-May-2024 UDI Data in EUDAMED RQTeam.com UDI on Class II Labels 26-May-2023 Registration in EUDAMED 11/2023 Sell Thru MDR Only UDI on Class I Labels 26-May-2025 20 May 26, 2020 (2021) Checklist ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ Execute all pending design changes through change management Issue DoC before May 26th for all MDD transition devices Update Vigilance, PMS, PMCF Procedures Confirm agreements with your Economic Operators include MDR requirements (e.g. complaints, registration in EUDAMED, communications) ▪ Implement Trending of Complaint Data (severity and frequency) ▪ Create PMS/PMCF plans; schedule reports ▪ Finish application process for MDR NB support and sign contract CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 21 Agenda ▪ PMS Requirements ▪ PMS Planning ▪ PMS Reporting ▪ Now What? ▪ Q&A CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 22 WHAT DOCUMENTS ARE REQUIRED? Risk Management Clinical Evaluation Plan Clinical Development Plan Post Market Surveillance Plan Post Market Clinical Follow-Up Plan CONFIDENTIAL, © 2017 R&Q • • • • • Requirements requiring clinical data support Intended purpose & target population Clinical benefits with clinical outcome parameters Methods for examining clinical safety Parameters for benefit-risk acceptability and intended purpose • Clinical Development Plan • Planned progression of investigations • Exploratory (e.g., first-in-man, feasibility, pilot studies) • Confirmatory (e.g. pivotal investigations) • Post Market Clinical Follow-Up (PMCF) Plan • Milestones • Potential acceptance criteria WHAT DOCUMENTS ARE REQUIRED Risk Management Clinical Evaluation Plan Clinical Development Plan Post Market Surveillance Plan Post Market Clinical Follow-Up Plan CONFIDENTIAL, © 2017 R&Q • Proactive & systematic process to collect any information • Methods & processes to assess collected data • Indicators/threshold values to be used for reassessment of benefit-risk analysis and risk management • Methods to communicate with competent authorities, notified bodies, economic operators and users • Methods & tools to investigate complaints/experience collected in the field • Effective tools to trace & identify devices which may need corrective actions • A PMCF plan or justification of why it is not applicable • General methods (ex. gathering of clinical experience gained, feedback from users, screening of scientific literature) • Specific methods (ex. evaluation of suitable registers, PMCF studies) • Reference to relevant parts of CER and Risk Management • Specific objectives to be addressed • Detailed & justified time schedule for PMCF activities Example Process Flow CEP LSPs PMS Plan PMS Data LSRs PMS Report SME Review, Update, & Finalize CER PMCF Plan PMCF Data PMCF Report Risk Management Documentation / Technical Documentation CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com SSCP 25 Example Process Flow CEP LSPs CER PMS Plan PMS Data PMS Report PMCF Plan PMCF Data PMCF Report SSCP SME Review, Update, & Finalize Risk Management Documentation / Technical Documentation CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 26 Agenda ▪ PMS Requirements ▪ PMS Planning ▪ PMS Reporting ▪ Now What? ▪ Q&A CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 27 REPORT REQUIREMENTS Technical Documentation SS&CP (Class III & implantables) CER PMS Report (Class I) PMCF Eval. Report • • • • • • • • • PSUR (Class IIa, IIb, and III) • • • • • CONFIDENTIAL, © 2017 R&Q Manufacturer + SRN Device + UDI-DI Intended purpose, indications, contra-indications, and target population Descriptions, previous variant(s), differences, accessories, other products intended to be used in combination Possible diagnostic or therapeutic alternatives Harmonized Standards / Common Specifications Summary of the CER + PMCF Suggested profile and training for users Information on residual risk, undesirable effects, warnings & precautions Results of clinical evaluation including • Scientific literature • Clinical investigations Qualifications of evaluator Alternative treatment options Demonstrated device equivalence if applicable PMCF Evaluation Report REPORT REQUIREMENTS Technical Documentation SS&CP (Class III & implantables) CER PMS Report (Class I) CONFIDENTIAL, © 2017 R&Q PMCF Eval. Report • PMCF analysis results • Corrective & preventative actions identified through PMCF • Summary of analysis of PMS data • Corrective & preventative action description PSUR (Class IIa, IIb, and III) • • • • • Summary of analysis of PMS data Corrective & preventative action description Conclusions of the benefit-risk determination Main findings of the PMCF Information on amount of device usage Legend Example Process Flow CEP LSPs PMS Plan PMS Data LSRs PMS Report SME Review, Update, & Finalize CER PMCF Plan PMCF Data PMCF Report Risk Management Documentation / Technical Documentation CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q Clinical Technical PMS PMCF RQTeam.com SSCP 30 Art. 85 and 86 post-market surveillance reports – elements ▪ PMS report ▪ PSUR ▪ Results of the PMS plan ▪ Description of preventative and corrective actions taken CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q ▪ Results of the PMS plan ▪ Description of preventative and corrective action ▪ Benefit-risk determination ▪ PMCF findings ▪ Sales volume ▪ Size and characteristics of the user population ▪ Usage frequency RQTeam.com 31 Art. 85 and 86 post-market surveillance reports – elements ▪ PMS report ▪ PSUR ▪ Results of the PMS plan ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ Complaints and trends Incidents FSCAs Literature Databases Registries Info on similar devices PMCF, if applicable ▪ Description of preventative and corrective actions taken CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com ▪ Results of the PMS plan ▪ Description of preventative and corrective action ▪ Benefit-risk determination ▪ PMCF findings ▪ Sales volume ▪ Size and characteristics of the user population ▪ Usage frequency 32 ▪ PSUR ▪ Sales volume / usage ▪ Complaints ▪ Incident reports, MDRs ▪ FSCA, recalls ▪ CAPA ▪ Database reviews ▪ Registry reviews ▪ Literature reviews ▪ PMCF findings CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q Legend Art. 85 and 86 PMS reports – data packets Clinical Technical PMS PMCF Complaint data Sales / Usage Data Literature review for device Misuse / OffLabel Use Data Incident reports, MDRs Database review for device Literature review for similar devices Misuse / OffLabel Use Data Recalls / FSCA Database review for similar devices PMCF findings CAPA data RQTeam.com 33 ▪ PMCF report: ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ Proactive feedback Literature review Registry review PMCF studies, registries Data for similar devices Standards, CSs, guidance docs Proactive feedback, e.g., surveys Legend ANNEX XIV(B) PMCF – data packets Clinical Technical PMS PMCF Literature review for device Misuse / OffLabel Use Data Literature review for similar devices Misuse / OffLabel Use Data Registry review for device Misuse / OffLabel Use Data Registry review for similar devices PMCF studies Standards and CSs CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 34 Legend Data for CER LSRs PMS Report PMCF Report CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q Literature review for similar devices Literature review for device Misuse / OffLabel Use Data Complaint data Recalls / FSCA Database review for device CAPA data Incident reports, MDRs Sales / Usage Data Database review for similar devices Misuse / OffLabel Use Data Proactive feedback, e.g., surveys Registry review for device Misuse / OffLabel Use Data PMCF studies, Registries Registry review for similar devices Standards and CSs RQTeam.com Clinical Technical PMS PMCF CER 35 Legend Data for CER LSRs PMS Report PMCF Report CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q Literature review for similar devices Literature review for device Misuse / OffLabel Use Data Complaint data Recalls / FSCA Database review for device CAPA data Database review Misuse / OffIncident reports, Sales / Usage for similar Label Use Data MDRs Data devices - Provides summary and evaluation of all clinical data to demonstrates conformity to GSPRs 1 and 8 Proactive- Includes conclusions regarding alignment between the Registry review Misuse / Offfeedback, e.g., clinical data, risk management and labeling for device Label Use Data surveys - Determines need for PMS / PMCF PMCF studies, Registries Registry review for similar devices Clinical Technical PMS PMCF CER Standards and CSs RQTeam.com 36 Legend Example Process Flow CEP LSPs PMS Plan PMS Data LSRs PSUR SME Review, Update, & Finalize CER PMCF Plan PMCF Data PMCF Report Risk Management Documentation / Technical Documentation CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q Clinical Technical PMS PMCF RQTeam.com SSCP 37 Process Flow - - Includes experts from quality, risk management, regulatory, engineering / product development, clinical, etc… Confirms conclusions and determines action items Benefits - Facilitates integration of different areas - Provides documentation of decisions - Enables experts to align on actions - Allows actions to be integrated into CER CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q PMS Plan / Report SME Review PMCF Plan / Report Update Risk Docs CER, SSCP Final Review & Sign IFU RQTeam.com 38 Notes on Risk Management, Complaints, and Clinical Data Alignment ▪ Risk management vs clinical studies and literature articles ▪ Risk occurrence definitions do not typically match adverse event rates in clinical studies ▪ Harms are not always clearly listed in risk management file ▪ Risk management vs complaints ▪ Complaint coding and adverse event reports are typically not categorized to make it easy to compare to the hazard analysis ▪ At a minimum, ▪ Need to determine whether risks identified are covered in the risk management file and residual risks are covered in the IFU ▪ Compatibility matrix may be useful that lists clinical risks identified and where they can be found in the risk management file and IFU CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 39 Notes on Coding Complaints ▪ Coding with IMDRF terms is a mandatory requirement for reportable incidents (MIR Form v7.2) ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ IMDRF 'Medical device problem codes’ (Annex A) IMDRF 'Health Effect' terms and codes (Annex E, F) IMDRF ‘Cause Investigation' terms and codes (Annex B, C, D) IMDRF Component codes (Annex G) ▪ Form also requires IMDRF codes for identifying similar incidents ▪ IMDRF 'Medical device problem’ (Annex A) ▪ IMDRF ‘Investigation finding' (Annex C) Note: Can use in-house codes instead during transition ▪ These codes may be useful for organizing complaints CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 40 Vigilance Implementation Challenges and Solutions Challenges Recommendations Coding of complaints per IMDRF codes Changing classification/coding of complaints on intake to match reporting form Using legacy data to establish trending limits Allow different rules for new product launches when there is insufficient data to establish good baseline values Consider linking to risk management expected levels Complaint data allows for trending quantity of complaints but not severity of complaints Coding of complaints can aid in distinguishing between severities of adverse events Misalignment of labeling, risk, PMS data which requires extra reports Conduct an integrated review of all data sources to ensure residual risks are appropriately captured in the labeling CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 41 Agenda ▪ PMS Requirements ▪ PMS Planning ▪ PMS Reporting ▪ Now What? ▪ Q&A CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 42 PMS – Common NB findings ▪ Notified body findings and observations ▪ Please provide complaints, sales, and the complaint rate per year separately for EU and the ROW ▪ Please provide information on any CAPAs associated with vigilance activities ▪ The search for vigilance did not include any international databases. Only the FDA MAUDE database was searched ▪ There is no explanation why the complaint rate is acceptable ▪ Suggestions and tips ▪ Consider searching at least one international database ▪ Provide PMS data for at least the last 3-5 years by year ▪ Consider adding a justification for why the complaint rate is considered acceptable instead of just stating that it is low CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 43 International databases Recalls / FSCAs • FDA recalls database (US) https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfd ocs/cfRES/res.cfm • BfArM Field Corrective Actions (Germany) https://www.bfarm.de/SiteGlobals/Forms/Suche /EN/kundeninfo_Filtersuche_Formular_en.html • MHRA Alerts and Recalls (UK) https://www.gov.uk/drug-device-alerts • SWISSMEDIC (Switzerland) https://fsca.swissmedic.ch/mep/#/ • ANSM (France) https://ansm.sante.fr/content/search?SearchTex t=device • Health Canada Recall (Canada) Recall • TGA Recall (Australia) https://www.tga.gov.au/recall-actions-database CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q Incidents / Adverse Events • FDA MAUDE database (US) https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/c fMAUDE/search.CFM • BfArM Recommendations (Germany) https://www.bfarm.de/EN/MedicalDevices/RiskInfor mation/Recommendations/_functions/_node.html • MHRA Alerts and Recalls (UK) https://www.gov.uk/drug-device-alerts • Health Canada Medical Device Incidents (Canada) https://hpr-rps.hres.ca/mdi_landing.php • TGA DAEN (Australia) https://apps.tga.gov.au/prod/DEVICES/daenentry.aspx RQTeam.com 44 PMS / PMCF Plan – Common NB findings ▪ Please provide a proactive PMS/PMCF Plan that is in line with the safety and performance objectives ▪ MDR excerpts ▪ For implantable and class III devices based on equivalence, “the notified body shall check that the PMCF plan is appropriate and includes post market studies to demonstrate the safety and performance of the device.” ▪ “The clinical evaluation…shall be updated throughout the life cycle of the device concerned with clinical data obtained from…implementation of the…PMCF plan…and the post-market surveillance plan ▪ MEDDEV 2.7/1 rev 4 excerpts ▪ “the notified body assesses the...PMS plan and PMCF plan…” CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 45 PMS / PMCF Plan – Recommendations ▪ Ensure that a MDR compliant PMS plan and PMCF plan is created and referenced in the CER ▪ Refer to MDCG 2020-7 and -8 and GHTF MEDDEV 2.12/2 rev.2 ▪ Keep in mind…clinical data obtained from PMS and PMCF studies are ▪ Not intended to replace the pre-market data necessary to demonstrate conformity ▪ Intended to monitor clinical performance and safety throughout the expected lifetime of the device, e.g., ▪ Uncertainties regarding medium and long term performance ▪ Safety under wide-spread use ▪ Monitor residual risks such as undesirable side-effects and rare complications ▪ If PMCF is not conducted, ensure a sound justification based on data is provided. Consider elements in MEDDEV 2.12/2. ▪ Ensure the PMS/PMCF aligns with the objectives of the clinical evaluation and is statistically sound CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 46 PMS audit ready ▪ MDD Audit before May 26, 2020 ▪ Increased focus on PMCF and clinical evidence ▪ Companies (small and large) have lost CE marking due to lack of adequate PMCF (class IIa to class III devices). ▪ When you get a finding, you need to take it seriously ▪ Limited opportunities to respond (3 rounds of questions and then done) ▪ Don’t waste your first-round (and second round) response by trying to dress up a non-compliant plan CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 47 PMS audit ready ▪ MDR Audit or MDD Audit after May 26, 2020 ▪ Requires PMS and PMCF Plans for all products ▪ Specific to the product and the risk ▪ Expect to provide sample as part of the EU MDR NB application process ▪ Tip: Don’t put your strategic products at risk with a less than robust PMS/PMCF plan. ▪ PMS Reports or PSURs ▪ They have been asked for in EU MDR audits ▪ If samples available, this has been adequate ▪ If samples are not available, have been able to show plan and timeline for completion without getting a finding ▪ Tip: Creating a sample report will help define whether the plans are executable. Data that should be readily available sometimes takes different forms requiring modifications to the plans or data collection systems. CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 48 Agenda ▪ PMS Requirements ▪ PMS Planning ▪ PMS Reporting ▪ Now What? ▪ Q&A CONFIDENTIAL © 2020 R&Q RQTeam.com 49 Thank you! Visit our website to… WATCH on-demand webinars and panel discussions. SUBSCRIBE to our Resources Blog. BEGIN a conversation.