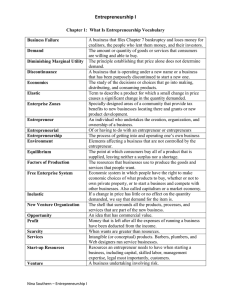
ENTREPRENEURIAL BEHAVIOUR Clarisse Kae Castillo MKTMGT-3201 18-55469 Mary Grace De Claro 18-57342 Michael Mendoza 18-53454 Chapter 1 and 2 The Nature and Importance of Entrepreneurs I. Learning Objectives ❖ Explain the definition of entrepreneurship ❖ Explain the process of entrepreneur ❖ Entrepreneurship in 17th to late 20th Century ❖ Explain Entrepreneur as an innovator ❖ Decisions for a potential Entrepreneur ❖ To understand the types of start-up ❖ Role of entrepreneurship in Economic Development ❖ To know the essentials of the three mechanism: The government Intrapreneurship or Entrepreneurship ❖ The Overall objectives for a Course in Entrepreneurship ❖ To know the Qualities and Attitudes of an Enrepreneur ❖ Who are The Future of Entrepreneurship II. Materials Needed ❖ cellphone/tablet/laptop ❖ notebook ❖ Paper 1 ENTREPRENEURIAL BEHAVIOUR III. Discussion Topic 1 The reporter discussed the chapter 1 of the course subject which is The Nature and Importance of Entrepreneur. The reporter discussed the definition of entrepreneur which is the individual who takes risk and create something new, aside that, the process of creating something new and assuming the risk and reward which is requires the creation process, the devotion of the necessity effort and time, it involves also the necessary risks, and reward for being an entrepreneur. The reporter also discussed the process of entrepreneur. The first process are the entrepreneur must have an idea that can be used for financial gain that is usually centered on a product and services. Second, entrepreneurs must identify the opportunity, they look for needs and wants of the consumer, third is matching idea to the opportunity. The entrepreneur must select the most feasible ideas among all the choices that gain profit. And lastly, Exploiting the opportunity, In order to gain profit the entrepreneur must take advantage it. The reporter also discussed the development of entrepreneur theory and terms. In this topic the reporter knew of what and who is the entrepreneur during early and middle ages. The presenter also discussed the philosopher of entrepreneur which is include Richard Cantillon, Jean-baptiste say, Francis walker, Joseph Schumpeter, David McClellend, Peter Drucker, Albert Shapero, Karl vesper, Gifford Pinchot, and Robert Hisrich. Topic 2 Entrepreneur in 17 th 18 th 19 th and 20 th Century So we all know that entrepreneur have many definitions. So once again entrepreneur is a person who organizes and operates a business or businesses, taking on greater than normal financial risks in order to do so. 17 th Century The connection of the risk with entrepreneurship developed in the 17th century. An entrepreneur was a person who entered into a contract with the 2 ENTREPRENEURIAL BEHAVIOUR government to perform a service or to supply stipulated products. –The CONTRACT PRICE was fixed. Resulting profit or losses were of the entrepreneur’s. John law, a Frenchman was one of the entrepreneur in that period in 17th century. John Law, a Frenchman established a ROYAL BANK (later on developed as franchise) 9And last, Richard Cantillon: RISK-TAKER (a noted economist of 1700’s & founder of the term Entrepreneurship.) 18 th Century In the 18th century, the person with capital was differentiated from the one who needed capital. The entrepreneur was distinguished from the capital provider. One reason for this differentiation was the industrialization occurring throughout the world. Many inventions developed during this time. Like, Eli Whitney was an American inventor best known for inventing the cotton gin. Inventor Tomas Edison: was unable to finance invention himself. 19 th and 20 th Century In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, entrepreneurs were frequently not distinguished from managers and were viewed mostly from an economic perspective. The entrepreneur organizes and manages an enterprise for personal gain. Middle of 20th Century –Entrepreneur as an INNOVATOR - Andrew Carnegie is one of the best examples of this definition. Because, Carnegie, who descended from a poor Scottish family, made the American Steel Industry one of the wonders of the industrial world. And, He made the American steel industry one of the wonders of the industrial world, preliminary through his unremitting competitiveness rather than hisinventiveness or creativity. Entrepreneur as an innovator The entrepreneur is commonly seen as an innovator, a source of new ideas, goods, services, and business/or procedures. As an entrepreneur why they need to innovate? Because the purpose of them is to continuously grow and renew an enterprise with new or better products, more efficient processes, or enhanced business. And as you can see Entrepreneurs play a key role in any economy, using the skills and initiative necessary to anticipate needs and bring good new ideas to market. 3 ENTREPRENEURIAL BEHAVIOUR Types of start-up 1. Lifestyle firm 2. Foundation Company 3. High Potential Venture image. To succeed, a startup must pay close attention to and focus on those aspects of the business that are within its control, aspects that can be revised, tweaked and improved as circumstances change and as the business develops and grows over time. Next, 1.Lifestyle Firm: Privately held Modest growth Limited money devoted to R&D Grow after several years to 30 or 40 employees Annual revenues of about $2 million Exists primarily to support owners Little opportunity for significant growth and expansion 2.Foundation Company: Created for R&D Grows in 5 to 10 years from 40 to 400 employees $10 million to $20 million in yearly revenues Rarely goes public Draws the interest of private investors only 3.High Potential Venture: Receives the greatest investment, interest and publicity. Rapid growth. After 5 to 10 years could employ about 500 employees Revenues are $20 million to $30 million. Also called Gazelles. Role of entrepreneurship in Economic Development It involves initiating and constituting change in the structure if business and society (i-e innovation). Entrepreneurship is the primary factor in the growth of economies. Each new business launched has an impact on an economy and affect people around it. An entrepreneur is first of all someone who has new ideas, who creates and innovates to solve a problem. An entrepreneur embraces change and tries to maximize profits while innovating. And supporting entrepreneurship in a motivating, innovating and stimulating environment will result in economic development. It should be the primary concern of decision-makers, which also 4 ENTREPRENEURIAL BEHAVIOUR have the responsibility to lead and channel entrepreneurship projects through sectors that are part of the development strategy. Product – Evaluation process: The process through which innovation develops and commercializes through entrepreneurial activity, which in turn stimulates economic growth. Iterative (Repeating)synthesis: The critical point in the product-evaluation process is the intersection of knowledge and recognized social need, which begins the product development phase. This point is called iterative synthesis. Ordinary innovations: New products have little uniqueness and technology. Topic 3 The reporter discussed the essence of three mechanisms in the level of technology. First is The government as innovator the one who is conduit for commercializing the results of the synthesis of social need and technology. This is frequently called technology transfer. Though the govt. has the financial resources to transfer technology but it faces the following problems: It lacks business skills, Bureaucracy and red tape Second is Intrapreneurship or Entrepreneurship which bridges the gap between science and the marketplace because they can use science to the business. the reporter also tackle the Overall objectives for a Course in Entrepreneurship where it Act as a positive force in economic growth, understand the relative strengths and weaknesses of different types of enterprises, it will help entrepreneurs to fulfill their personal needs, assess the student’s own entrepreneurial skills, bridge the gap between innovation and the marketplace, know alternative methods for identifying and evaluating business opportunities and the factors that support and inhibit creativity, increase national income by creating new jobs, know the general correlates of success and failure in innovation and new venture creation, understand the aspects of creating and presenting a new venture business plan and the last know how to identify, evaluate and obtain resources. The reporter also discussed the qualities and attitudes an entrepreneur must possess. and lastly The Future of Entrepreneurship, how will it continue in the future. 5 ENTREPRENEURIAL BEHAVIOUR IV. Conclusions The nature and importance of entrepreneur are also key to effective and efficient, thus, and by having all the topics that have been discussed, from the definition of entrepreneur to role of entrepreneurs in economic development, the reporters can say that those learning’s will imply knowledge to them that they can use as a tool when they were already at the actual battlefield of doing or being part of the business. But they can not only wait for their time to be there just to practice what they have acquired in this course. So, to wrap it up, this course, particularly this chapter, has been more than successful in achieving its objectives. As the lesson ended, the listeners were able to identify the role of entrepreneur in business that they were only seeing before, and up until now. As future entrepreneurs they know what will do and their functions in business. This course is showing effectiveness in imparting its agenda to the target audiences, which are the listeners and the reporters themselves as well. V. References http://abmalik.weebly.com/uploads/1/0/3/3/10333801/chapter_1_and_2.ppt 6