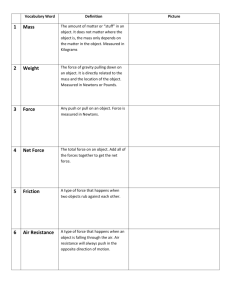
Name Date Class Newton’s Laws of Motion Understanding Main Ideas Answer the following questions in the spaces provided. Use a separate sheet of paper if you need more room. 1. Newton’s second law of motion describes the relationship among force, mass, and acceleration. Write the equation. Acceleration = Net force Mass 2. How does the diagram at the right illustrate Newton’s third law of motion? Newton’s third law of motion says that if an object, such as a foot, exerts a force on another object, such as a soccer ball, the second object (the soccer ball) exerts a force of equal strength in the opposite direction on the first object (the foot). If the statement is true, write true. If the statement is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. 3. True If you increase the force on an object, its acceleration increases. 4. Increases If you increase the mass of an object, its acceleration decreases. 5. 27 newtons is needed. To accelerate a 3 kg skateboard at 9 m/s2, a force of 3 newtons 6. Mass The amount of inertia an object has depends on its speed. Building Vocabulary Write a definition for the term on the lines below. 7. inertia An object’s resistance to a change in its motion. Name Date Class Newton’s Laws of Motion If the statement is true, write true. If the statement is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. 1. Unbalanced Newton’s first law of motion states that an object will not experience a change in motion unless acted upon by a(n) balanced force. 2. True To increase acceleration of an object, you reduce its mass or increase the applied force. 3. Opposite Newton’s third law of motion states that if one object exerts a force on another object, then the second object exerts a force of equal strength in the same direction. 4. Inertia Resistance to change in motion is called stasis. 5. Do Not Action and reaction forces acting in opposite directions do cancel out because they act on different objects. 6. Equal weaker force. If you lean against a wall, the wall pushes back on you with a(n) Fill in the blank to complete each statement. 7. Newton’s second law of motion states that an object’s acceleration depends on its mass and on the net force acting on it. 8. Acceleration is measured in meters per second per second (m/s2) . 9. Force is measured in a unit called the accept newtons or kilograms times meters per second (kg × m/s2) . 10. The smaller the mass of an object, the less its inertia.