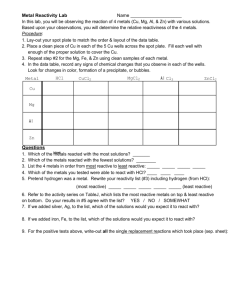
Reactions of metals Reactive metals + acid … How metals react with acid tell you about their reactivity... Metal + Acid → Salt + Hydrogen • Some metals react with acids to produce a salt and a hydrogen gas. • You can use the reactions of different metals with dilute acid to work out how reactive they are. • The more reactive the metal is, the faster the reaction will go – very reactive metals (e.g. sodium) react explosively. • You can carry out a practical to investigate the differences in reactivity of a variety of different metals by using their reaction with acids. • Set up 3x boiling tubes and fill them with equal volumes of dilute hydrochloric or dilute sulfuric acid. • Place the pieces of magnesium, zinc and iron in separate test tubes – make sure that the size and shape of the metal pieces is the same. • The speed of the reaction is indicated by the rate at which the bubbles of hydrogen are given off. • The hydrogen is confirmed by the burning splint test. The magnesium should give the loudest ‘squeaky pop’ as it has the most vigorous reaction producing the most hydrogen gas. KS3: Reacting metals with dilute acid: • Metals above hydrogen in the reactivity series will react with acid to make a salt and hydrogen. • The metals below hydrogen in the reactivity series do not react with acids. • The reaction becomes less and less exciting as you go down the series. • All acids contain hydrogen so the hydrogen here comes from the acid. More reactive metals react more violently… Potassium React violently with dilute acids (likely to explode) Sodium Calcium Magnesium React fairly well with dilute acids. Aluminium Zinc Iron Lead Copper Do not react with dilute acids. Silver Gold The lower the reactivity, the less likely it is for a reaction to happen. Zinc + Sulfuric acid → Zinc sulfate + hydrogen The zinc takes the place of the hydrogen in the reaction as it is more reactive than the hydrogen. Sodium + hydrochloric acid acid → sodium chloride + hydrogen The sodium takes the place of the hydrogen in the reaction as it is more reactive than the hydrogen. Metals + water… The reactions of metal and water also shown the reactivity of the metals. Metal + Water → Metal hydroxide + Hydrogen (Or: less reactive metal + steam → metal oxide + Hydrogen) Very reactive metals like potassium, sodium, lithium and calcium will all react vigorously with water. The amount of energy given out by the reaction increases the reactivity of the metal. The reaction with potassium gives out enough energy to ignite hydrogen. Less reactive metals like magnesium, zinc and iron won’t react much with cold water, but they will react with steam. You could show this in the lab using the experiment… Copper will not react with either water or steam.