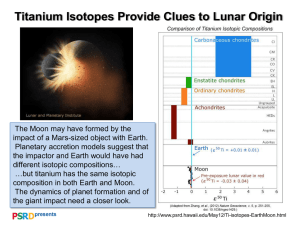
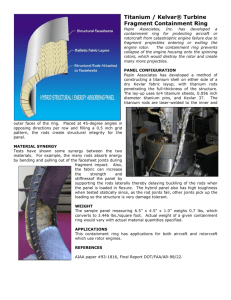
HW 3 Name: Bharatsai Alla 1) What are titanium implants? Titanium advantages and disadvantages? Ans: Titanium implants are implants made of titanium material. They are mainly used for dental purpose. Titanium dental implants are surgically implanted directly into the patient’s jawbone. This allows the implant post to remain firmly anchored in place, as the bone fuses to it over time. Essentially, an titanium implant mimics the function of a natural tooth root. In contrast, subperiosteal implants are positioned above the jawbone, but underneath the gum tissue. As you might expect, subperiosteal implants are not nearly as durable or strong as titanium implants. [1] Fig from reference 1 Dental implants have a few main parts. The implant itself, often called the post, is implanted into the jawbone. An abutment screws on top of the implant. The third main component is the crown, which is the white part that looks like a natural tooth. It encases the entire post and abutment. [1] (reference 1) Advantages: • The ability to ossify Titanium integrates with the bone tissue in a process called osseointegration, which means that it essentially becomes a part of the bone. [2] • • Strong and light Titanium is extremely strong but lighter than even gold alloys, making it perfect for patients who need a comfortable, secure dental restoration.[2] • • Low thermal conductivity This reduces the risk of pain or irritation associated with dramatic temperature changes.[2] • The success rate of titanium dental implants is an incredibly high 95 percent. Most dental implants can remain in place for the remainder of a patient’s life. Individual or multiple implants can be used to support crowns, bridges, or dentures for a secure, lasting, aesthetic tooth restoration options.[2] • • 2) Disadvantages: Titanium dental implants can cause corrosion and wear. Particles and ions of titanium and titanium alloy components due to corrosion and wear can be deposited in surrounding tissues, and inflammation reactions can occur.[3] One of the causes of implant failure can be attributed to allergic reactions to titanium. There have been reports of hypersensitive reactions such as erythema, urticaria, eczema, swelling, pain, necrosis, and bone loss due to titanium dental implants [3] MAGEC rods: MAGEC rods are used to treat certain types of early onset scoliosis (EOS). MAGEC stands for Magnetic Expansion Control. Growing rods have been used to treat scoliosis for many years. Here’s how traditional growing rods and MAGEC rods differ: [4] • • Traditional growing rods are placed into a child’s back during surgery. Because children grow so quickly, the rods need to be lengthened about every six months. Each time the rods are lengthened surgery is needed.[4] The MAGEC system combines traditional growing rods with new magnet technology. MAGEC rods are put into a child’s back during surgery one time. After that, they can be lengthened in clinic using a remote control and powerful magnets. This allows a child to grow without needing repeat surgeries.[4] The goal with any growing rod is to stop the spinal curve from progressing. Another goal is to straighten the spine.[4] A MAGEC rod is made with magnets and a motor inside the rod that allow it to extend. A remote control used outside of the body contains powerful magnets that “talk to” the magnets within the rod. The doctor use the remote. The remote makes the rod longer or shorter as needed.The MAGEC system is most often used in children with scoliosis under age 8.Children typically have the rods removed when they are 10 to 12 years old. [4] 3) Pedicle screws and trajectory Pedicle screw fixation was designed to provide immediate stability, rigid immobilization and short fixation without sacrificing additional motion segments required by other forms of fixation. Knowledge of biomechanics offers the opportunity to predict and avoid surgical constructs that may lead to hardware failure and poor clinical outcomes.[5] Vertebral fixation system comprises anchorage components (screws, hooks, wires and cables), longitudinal components (rods, plates), transversal connectors and accessories (staples). Pedicle screws are penetrating implants that provide bending and pullout resistance.[5] Fig 2: Components of screw and biomechanical features [5] The trajectory of the pedicle screw also has an influence on the screw pullout resistance. A straightforward screw trajectory has a beneficial effect on the pullout resistance5 as well as the screw convergence. Convergence of pedicle screws by 30° in the coronal plane can increase pullout strength by 28.6% [6] References: [1] https://www.oralsurgeonsofsandiego.com/blog/2017/06/a-closer-look-at-titanium- implants/#:~:text=Titanium%20dental%20implants%20are%20those,of%20a%20natural %20tooth%20root. [2] http://www.southbaydentalstudio.com/titanium-dental-implants-and-theiradvantages.html [3] Kim, K.T., Eo, M.Y., Nguyen, T.T.H. et al. General review of titanium toxicity. Int J Implant Dent 5, 10 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40729-019-0162-x [4] https://www.cincinnatichildrens.org/health/m/magec-rods [5] https://www.wheelessonline.com/issls/section-11-chapter-9-pedicle-screw-fixationand-design/ [6] Wray S, Mimran R, Vadapalli S, Shetye SS, McGilvray KC, Puttlitz CM. Pedicle screw placement in the lumbar spine: effect of trajectory and screw design on acute biomechanical purchase. J Neurosurg Spine. 2015;22(5):503-510.