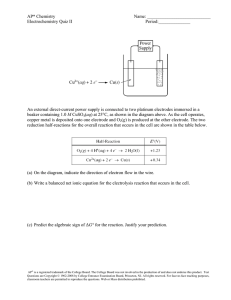
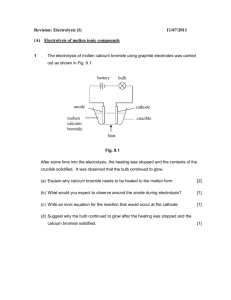
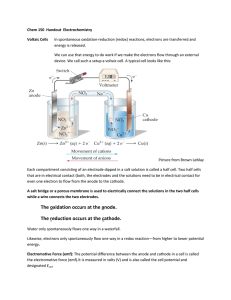
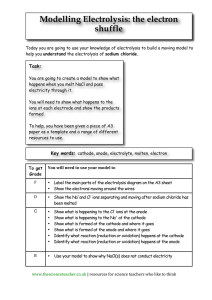
1 1 What are the products at the electrodes when dilute sulfuric acid is electrolysed using inert electrodes? anode cathode A hydrogen oxygen B oxygen hydrogen C sulfur oxygen D sulfur dioxide hydrogen [1] [Total: 1] 2 Electricity is passed separately through concentrated hydrochloric acid, concentrated aqueous sodium chloride and dilute sulfuric acid. In which rows are the electrolysis products correctly named? A cathode product anode product 1 concentrated hydrochloric acid hydrogen chlorine 2 concentrated aqueous sodium chloride sodium chlorine 3 dilute sulfuric acid hydrogen oxygen 1, 2 and 3 B 1 and 2 only C 1 and 3 only D 2 and 3 only [1] [Total: 1] 3 Which reactions could take place at the anode during electrolysis? A − 2H2O(I) + O2(g) + 4e 1 4OH (aq) 2 2Cl (aq) 3 Cu (aq) + 2e 4 2H (aq) + 2e − Cl 2(g) + 2e 2+ 1 and 2 + − − B − − Cu(s) H2(g) 1 and 4 C 2 and 4 D 3 and 4 [1] 2 [Total: 1] 4 The diagram shows a simple cell. voltmeter V copper electrode zinc electrode electrolyte Which statement about the process occurring when the cell is in operation is correct? A Cu B Electrons travel through the solution. C The reaction Zn D The zinc electrode increases in mass. 2+ ions are formed in solution. 2+ Zn − + 2e occurs. [1] [Total: 1] 3 5 When concentrated hydrochloric acid is electrolysed, gases P and Q are formed. P Q concentrated hydrochloric acid platinum electrodes – + What are P and Q? P Q A chlorine hydrogen B chlorine oxygen C hydrogen chlorine D hydrogen oxygen [1] [Total: 1] 4 6 The diagram shows the apparatus used for the electrolysis of molten sodium bromide. R + – S U T What does the term electrolysis mean? .................................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................. [1] [Total: 1] 7 A student electrolyses aqueous copper(II) sulfate using the apparatus shown. power supply + – carbon electrodes aqueous copper(II) sulfate Oxygen gas forms at the positive electrode (anode). (a) Describe what the student observes at the negative electrode. ........................................................................................................................................... [1] (b) Give two other observations which the student makes during the electrolysis. 1......................................................................................................................................... 2......................................................................................................................................... [2] [Total: 3] 5 8 The table gives information about the products of the electrolysis of two electrolytes. Platinum electrodes are used in each case. (a) Give two reasons why platinum is suitable to use as an electrode. 1......................................................................................................................................... 2......................................................................................................................................... [2] (b) Complete the table. electrolyte observation at the anode (+) name of product at the anode (+) concentrated aqueous potassium chloride aqueous copper(II) sulfate observation at the cathode (−) name of product at the cathode (−) bubbles of colourless gas bubbles of colourless gas [6] [Total: 8] 9 Magnesium is manufactured by the electrolysis of molten magnesium chloride. The negative electrode is made of iron. Suggest a non-metal which could be used for the positive electrode. Give a reason for your answer. .................................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................. [2] [Total: 2] 6 10 A student electrolyses aqueous copper(II) sulfate using the apparatus shown. power supply + – carbon electrodes aqueous copper(II) sulfate Oxygen gas forms at the positive electrode (anode). Write an ionic half-equation for the reaction at the negative electrode (cathode). Include state symbols. .................................................................................................................................................. [3] [Total: 3] 11 12