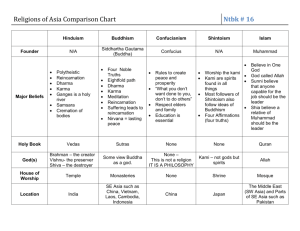
What is Yoga? A method of training designed to lead to the union with Brahman Origins of Hinduism Believe it was the Aryans who settled in India that developed Hinduism Vedas- Collection of hymns and religious ceremonies Upanishads –book explaining how to unify Brahman and Atman Brahman- a form of ultimate reality one seeks to join after death Atman – the individual self, known after enlightenment, “the World Soul” Early form of Hinduism too complex an idea for common Indians Developed more “human-like” gods and goddesses 3 Chief Gods Brahma the Creator Vishnu the Preserver Shiva the Destroyer Gods and Goddesses give every day people a means to seek salvation and a means to gain everyday things needed in life Main Hindu Ideas Reincarnation – the belief that the individual soul is reborn in a different form after death Karma – the force generated by a person’s actions that determines how the person will be reborn in the next life Dharma – “divine law” requires that all people do their duty in life All 3 ideas are connected in such that one must follow their dharma in life (duties) in order to achieve good karma. If you achieve good karma, you will achieve more success in your next life Origins of Buddhism Appeared in Northern India in the 6th century B.C.E. Founder was named Siddhartha Gautama (a.k.a. the Buddha or “Enlightened One”) Was raised in wealth, a sheltered life One day discovered the pain of illness, sorrow of death, and the effects of old age Gave up his royalty to find the end of suffering in the world Reached enlightenment while meditating under a tree (Bodhi Tree) Buddhist Beliefs Denied reality of the material world Pain, poverty, and sorrow that afflict human beings are caused by their attachments to the things of this world Once people let go of their worldly cares; pain and sorrow can be forgotten After that, then comes bodhi, or wisdom Achieving wisdom is a key step to achieving nirvana: the ultimate reality – the end of the self and the reunion with the Great World Soul Teachings of Siddhartha Eightfold Path Right view – we nee to know the 4 Noble Truths 2. Right intention – we need to decided what we really want 3. Right speech – we must seek to speak truth and to speak well of others 4. Right action – The Buddha gave 5 precepts: “Do not kill. Do not steal. Do not lie. Do not be unchaste. Do not take drugs or drink alcohol.” 1. 5. 6. 7. 8. Right livelihood – we must do work that uplifts our being Right effort - The Buddha said “those who follow the Way might well follow the example of an ox that arches through the deep mud carrying a heavy load. He is tired, but his steady, forwardlooking gaze will not relax until he comes out of the mud” Right mindfulness – we must keep our minds in control of our sense “all we are is the result of what we have thought.” Right concentration – we must meditate to see the world in a new way. Buddhist Ideas Siddhartha accepted idea of reincarnation and dharma Rejected the caste system All people could reach nirvana as a result of their good behavior ○ Appealed to downtrodden peoples at the lower end of the social scale Rejected idea of gods Forbade his followers to worship either his person or his image after death People view Buddhism as a philosophy instead of religion After his death, followers traveled throughout India spreading his message. Temples sprang throughout the countryside and Buddhist monasteries were established Confucianism Founded by Confucius, 551-479 BCE The Analects are a collection of Confucius sayings Helped to form social order in China Belief that humans are good, not bad Respect for elders Code of politeness (still used in Chinese society today) Emphasis on education Ancestor worship 5 Key Relationships Daoism (Taoism) Founded by Laozi (Lao-tzu) in China Stressed the Yin and Yang Simple life in harmony with nature Don’t stress material things Live a humble life No laws or government ○ “the best government is one that governs the least” Helped to form Chinese culture and values Yin and Yang 2 forces the Chinese believe need to remain in balance ○ Can’t have one without the other Legalism Chinese philosophy during the Han Dynasty that all people are evil and the government should punish all those who break the law (STRICT) Jainism Founded in India Believed in Ahimsa (non-injury) Avoid hurting others Strict vegetarians Filters their water Sweep their path as they walk ○ Don’t injure unseen creatures Believes in reincarnation Buddhism Hinduism