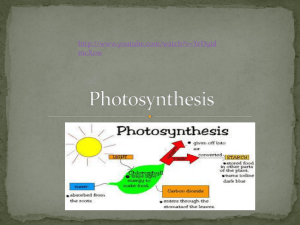
Photosynthesis Explained: Matter & Energy Transformations
advertisement

Carbon: Transformations in Matter and Energy Environmental Literacy Project Michigan State University Plants Unit Activity 4.4 Explaining How Plants Make Food: Photosynthesis 1 Plants make their own food Materials for growth: Biosynthesis Food To Cells Energy: Cellular respiration 2 Constructing explanations Consider the following as you construct your explanation: • Evidence from the investigation • What you learned from the molecular modeling activity • Three Questions Handout 3 Comparing Ideas with a Partner • Compare your explanations for each of the Three Questions. – How are they alike? – How are they different? • Check your explanation with the middle- and right-hand columns of the Three Questions handout. • Consider making revisions to your explanation based on your conversation with your partner. 4 The Matter Movement Question Where are atoms moving from? Where are atoms moving to? 5 Which atoms and molecules move so that plants can do photosynthesis? water carbon dioxide oxygen glucose 6 How do glucose water, carbon dioxide, and oxygen move for a plant leaf to photosynthesize? water carbon dioxide oxygen glucose 7 Matter Movement CO2 Do you have: • an arrow showing carbon dioxide or CO2 going into the plant’s leaf cell? 8 Matter Movement CO2 H2 O Do you have: • an arrow showing water or H2O going into the plant’s leaf cell? 9 Matter Movement CO2 H2 O Glucose Do you have: • an arrow showing glucose or C6H12O6 leaving the plant’s leaf cell? 10 Matter Movement CO2 H2 O O2 Glucose Do you have: • an arrow showing oxygen or O2 leaving the plant’s leaf cell? 11 The Matter Change Question How are atoms in molecules being rearranged into different molecules inside a potato cell during photosynthesis? 12 Plants make glucose from carbon dioxide and water in their leaves. 13 What happens inside the leaf cell as it photosynthesizes? Chemical change 14 Matter Change What is the name of the chemical change that allows cells to make food? Photosynthesis Write the chemical equation for this change: 6 CO2 + 6 H2O C6H12O6 + 6 O2 15 Matter Change What molecules are carbon atoms in before the chemical change? Carbon dioxide or CO2 What molecules are carbon atoms in after the chemical change? Glucose or C6H1206 Chemical Change What other molecules are needed? Water or H2O What other molecules are produced? Oxygen or O2 16 Energy Change What forms of energy go into this chemical change? Light energy What forms of energy come out of this chemical change? Chemical energy 17 Matter Movement What happens to glucose made by photosynthesis? Glucose moves from a plant’s leaves to all of its cells. 18 Drawing arrows to show matter movement for photosynthesis • Blue arrows: Carbon dioxide enters the plant’s leaves from the air (along with water from the soil through the plant’s roots and stem • Green arrows: Sugar moves from leaves to all plant cells 19 Telling the Whole Story Question: How does a cell in the potato plant get food to a cell in its root? Matter movement: Carbon dioxide and water enter into the cell. Matter change: Carbon dioxide and water react resulting in glucose and oxygen. Energy change: The light energy of the sun is converted into chemical energy that is stored in the high energy C-C and C-H bonds of glucose. Matter movement: Glucose and oxygen leave the cell. The glucose is transported to other cells in the plant, including root cells. 20 Exit Ticket • 4.4 ET, available in canvas now • Download, edot, and return the 4.4 Explainer Tool about how Plants get energy to move and function 21