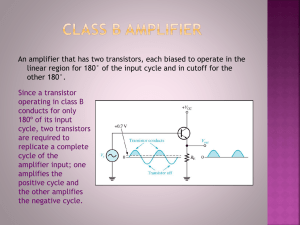
10 W Audio Amplifier Circuit using Op-Amp and Power Transistors Made by Fatma 10 Watt Audio Amplifier Circuit using Op-Amp and Power Transistors Amplifiers: The device which is mostly used to increase the current, voltage and power of a signal is called amplifier. We used amplifiers mostly in audio equipment, in broadcasting and in wireless communication. They are termed as power amplifiers or weak signal. They are consider as the backbone of analog electronic. Power amplifier which is usually the segment of audio electronics is used to maximize the amplitude of the given input signal. The voltage of the signal is increase by operational amplifier in sound electronics but it can’t give the current which is needed to run a load. In this project report I have built a 10 W amplifier using 8Ω impedance speaker attached to it. For this purpose an operational amplifier with two extra power transistors are used in order to get the 10 W output. Components used: In order to design the 10 W audio amplifier circuit on Proteus I have used the following components: Components Quantity 12V Rail to Rail power supply with +/-12V 1 LF351 IC with 8 pin IC Base 1 TIP122 Transistor 1 TIP127 Transistor 1 8Ω 10 Watt speaker 1 4.7kΩ Resistor 2 250Ω Resistor 2 47kΩ Resistor 1 10pF Capacitor 1 0.82uF Capacitor 1 3.2kΩ Resistor 1 Construction Topology for Amplifiers: The power amplifier is mostly used at the end stage or last stage just before the load in an amplifier system. The block diagram shows the topology which is mostly used by sound amplifier. Figure 1 shows block diagram of sound amplifier From the block diagram you can see that power amplifier is directly attached to the load in the last stage. The signal is mostly corrected before the power amplifier with the help of pre amplifiers and voltage controls amplifiers. On the other hand just before the power amplifier we can also add the tone controller if there is a need to control the tone. Amplifier Load: The load driving capacities and the load of the amplifiers are the major feature in the design of audio amplifier. For power amplifier, loud amplifier is a chief load. The output of the power amplifier is totally depends on the load impedance. Therefore the stability and the efficiency of the power amplifiers are badly effected by adding an improper load Due to huge load, loud speakers mostly act as inductive load or resistive load. As the power amplifier supply AC output therefore the speaker’s impedance contribute a major role in transferring the power properly. We should be very careful about the speaker and amplifier ratings, efficiency and impedance of a speaker because different variety of speakers are present in the market i.e. 4Ω, 8Ω, 16Ω and 32Ω. The 4Ω and 8Ω speakers are mostly used because they are cheap in rates and easily available. Also remember that the amplifiers having 5 W, 6 W, 10 W or even more is the RMS (Root Mean Square) wattage, supplied by the amplifier to a specific load in continuous operation. Circuit Diagram of 10 W audio amplifier: Figure 2 shows circuit diagram of 10 W audio amplifier Explanation: The circuit diagram of 10 W audio amplifier is quite simple. For power amplification I used two power transistors and the LF 351 is used to amplify the voltage signal. Power supply is used to deliver the power to the 8Ω loud speaker with the help of two transistors. In this circuit I have used TIP 127 to provide the power amplification on the positive peak and to provide the power amplification on the negative peak signal I have used TIP 122. The reason for this is as the sinusoidal wave change the polarity therefore TIP 127 and TIP 122 are used. The two major components in this circuit are TIP 127 and TIP 122. These two transistors are identical in pair having 100V Collector Emitter Sustaining Voltage @ 100 mA. Both of the two ICs provide high DC Current gain i.e. hFE= 2500 typically. Figure 3 shows T0-220B package Both of the two transistors are available in this package. For perfect head transfer this package is crucial and is useful to fit with a heatsink. I have connected the base of these two transistors with 250Ω resistor. The collector junction of both transistors are used to measure the amplified output. Testing the 10 W Amplifier Circuit: In order to check the output of circuit I have also used proteus simulation. For this purpose I have used virtual oscilloscope to measure the output. To power the circuit I have used +/-12V DC and the input sinusoidal signal. For this purpose I attach the channel A of oscilloscope having yellow line with the output against 8Ω load while the channel B of oscilloscope having blue line is attach with the input sinusoidal signal as shown in figure 2. Figure 4 shows the output of the difference between the given input sinusoidal signal and the amplified output signal. Figure 4 shows difference between the input and amplified output signal I have also measured the output wattage. As discuss above that amplifier wattage is mostly depends on the speaker efficiency and impedance, amplifier efficiency, design topologies and total harmonic distortions etc. Therefore I can’t calculate all the above possible factors which effect the amplifier wattage. The main reason is that the real life circuit is totally different than the simulation circuit because a lot of factors are required to consider while testing or measuring the output. Calculation of Amplifier Wattage: I have used a very simple formula to measure the wattage of the amplifier. Amplifier Wattage= W = V2 / R For measuring the output wattage I have connected the AC voltmeter across the output of the circuit as shown in figure 5. The voltage signals shown in the meter are peak to peak AC voltage. I have provided a low frequency of about 45Hz to the input sinusoidal signal. The reason is that amplifier deliver more current to the load at low frequency and AC voltmeter measure the AC voltage properly. Figure 5 shows AC voltmeter is connected across the load The AC voltmeter measured +8.59V AC as shown in figure 6. Figure 6 shows AC voltmeter measurement Therefore we can easily calculate the output at 8Ω load of power amplifier by using the formula: Amplifier Wattage = V2 / R Amplifier Wattage = (8.59 V)2 / 8Ω Amplifier Wattage = 9.23 W (Which is approximately equal to 10 W) Things to Remember while designing 10 W Amplifier You should remember the following points in mind while designing the 10 W power amplifier. Properly connect the heatsink with power transistors. You should use larger heatsink because it provides good result. For better output result you should use audio grade rated box type capacitors. In order to decreases or eliminates the noise coupling try to make the pre-amplifier as short as possible.