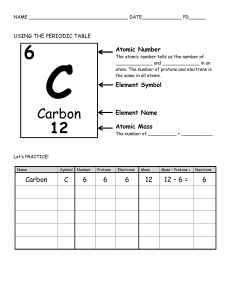
Atomic structure An atom is the smallest part of an element that can exist. Atoms consist of three basic particles: Protons Neutrons Electrons The nucleus (center) of the atoms contains the protons (positively charged) and the neutrons (uncharged) The outermost regions of the atom are called electron shells and contain The electrons (negatively charged). Each element has a certain number of protons and neutrons, which makes it easy to differentiate them. This is how atoms are arranged in the periodic table. Why do atoms have no electric charge? (Electrically neutral) Atoms contain charged particles but atoms have no overall electric charge. They are Neutral. This is because in any atom the number of protons is the same as the number of electrons. Examples: A Helium atom is made up of: 2 protons (positively charged) 2 electrons (negatively charged) 2 neutrons Hydrogen atom 1 proton (positively charged), 1 electron (negatively charged) and no neutrons. Arranging the electrons Electrons occupy shells (energy levels) Each shell can hold a maximum number of electrons: 1st shell can hold up to 2 electrons 2nd shell can hold up to 8 electrons 3rd shell can hold up to 8 electrons The outer most shell can never carry more than 8 electrons Electrons fill the shells that are closest to the nucleus first The maximum number of shells is 7 Mass number(Nucleon number): is the number of neutrons and protons inside the atom. . Atomic number: is the number of protons . this is also the same as the number of electrons), each element have a specific number of protons in fact the number of protons determine who the element is. number of neutrons = mass number – atomic number N.B The periodic table is arranged in increasing atomic number not mass number. Be Protons: Electrons: Neutrons: ……. ……. ……. N ……. ……. ……. O ..…. ……. …….. Ne …….. …….. ……. Li ……. …….. ……..