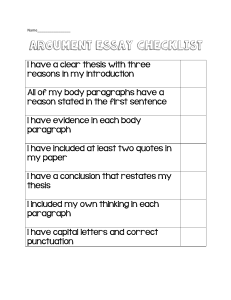
Introduction (Hook)--Opening sentence(s) o (Background) o engages the reader & introduces the topic essential information for the reader to understand the main idea—context (who, when, where), brief history, importance Thesis Forecast (can be included in thesis) Body (PEE+C/T) Topic sentence Explanation/Analysis Example (Explanation of the example) Conclusion (Transition) Conclusion Summary Intensified Insight o opinion, lesson, prediction, call for an action… ⚠️ 1. proofread verb tense, spelling, punctuation 2. One paragraph, one main idea (SPECIFIC) a. Completely explain each point making before going on to the next one b. Topic Sentence i. State it clearly ii. Keep it simple & short, connect to the forecast iii. Each topic sentence relates to the thesis statement c. Using one Example (specific people and events) & Explain the Example d. Conclusion/Anchor 3. Bridging Transition a. comes before the topic sentence of the 2nd paragraph/the end of the 1st paragraph b. paragraph unity i. connect paragraphs smoothly ii. “not only, but also……”/ “A is indeed……, but not at the expense of B.” 4. Ideas’ Order a. From smallest to biggest Introduction 1. Definition a. Coin own definition to suit the topic 2. Leading Question a. Interesting, thought-provoking b. “Have (you) ever wondered whether……?” c. “What would (you) do if (you)……?/What do (you) think would have happened if……?” d. “Would/Do/Will/Is/Are/How much/How important……?” e. “Can we really (afford)……?” 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. f. "Children always find something new interesting, don't they?” Related Quotation Narrative Alluring Description /Imagery a. Creating a picture in the reader’s mind can make him or her feel connected to your writing. Surprising Fact Common Misconception Dialogue Metaphor/Simile Conclusion 1. Summary a. Repeats the main arguments that have been presented in the essay 2. Thesis Restatement a. Rewording of the thesis statement (final emphasis) b. Not a word-by-word repetition 3. Closing by Return a. Close the essay by commenting on some aspect of the introductory paragraph 4. Call to Action a. Asks the reader to take a particular action on an issue b. definite & clear 5. Answer to the Question Syntax Variation 1. 以主句开始整句话 a. Those who are about to graduate from university may feel under increasing pressure, because of the soaring unemployment rate. 代词 b. To find a decent and well-paid job seems to be increasingly difficult for the undergraduate. 不定式 c. Finding a satisfying career is no easy task for most undergraduates. 动名词 2. 以状语(时间、地点、目的、频率、表达情感态度的副词、连接副词等)开始整句 话 a. b. c. d. e. f. In contemporary society, Inevitably On a global scale From linguistic perspectives Through this way As/When/Whether 3. 一些搭配 a. b. c. d. e. f. g. With/Without There is (no doubt that) / It is (commonly believed that) While + Ving……; ……, whereas / while / whilst Xxx (year) has witnessed …… Despite (that) / Even though / Although/ Nevertheless, ……, yet Apart from / Besides ……/ …… alongside……/……, along with 4. 以倒装句型开始整句话 a. Not only……but also…… i. Not only could the acquisition of a foreign language promote the children’s intelligence development, but also it could stimulate their interest on study and enrich their knowledge scope. b. Only by……can sb. be i. Only by valuing life, uniting each other, and enhancing mutual trust across the countries can we be calmer while facing life's uncertainty. 5. 强调句 a. it is A that …… 6. 条件句 a. If……