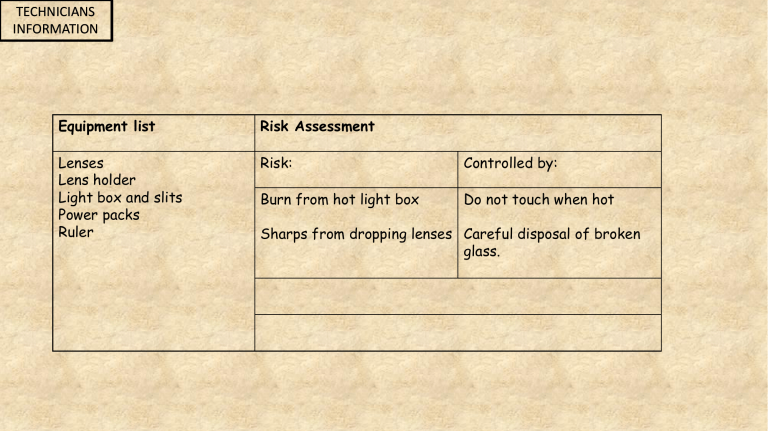
TECHNICIANS INFORMATION Equipment list Risk Assessment Lenses Lens holder Light box and slits Power packs Ruler Risk: Controlled by: Burn from hot light box Do not touch when hot Sharps from dropping lenses Careful disposal of broken glass. Lesson SP5c: Lenses Specification Extract Separates P5.5P: Use ray diagrams to show the similarities and differences in the refraction of light by converging and diverging lenses P5.6P: Explain the effects of different types of lens in producing real and virtual images P5.4P: Relate the power of a lens to its focal length and shape RISK ASSESSMENT 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. What is the normal? Describe diffuse reflection? State the law of reflection Describe specular reflection? Why do we see a green leaf as green? Where do we measure the angle of incidence from? Why will a light ray slow down and change direction? Draw a ray of light passing through a glass block? Why do we use colour filters? A filter is blue, what happens to white light as it hits the filter? 1. A line at right angles to the glass block or mirror. 2. Light reflecting off an uneven surface, light will not obey the law of reflection, loss of detail. 3. The angle of incidence = the angle of reflection. 4. Light reflecting off a smooth surface, light obeys the law of reflection, no loss of detail. 5. Only green light is reflected, the rest is absorbed. 6. The incident ray to the normal. 7. It enters a more dense medium. 8. Correct drawing. 9. To produce different lighting effects, stage, cinema. 10. Only blue light passes through the rest is reflected. Lenses and Images Learning Objectives Describe the refraction of light by converging and diverging lenses Describe real and virtual images Relate the power of a lens to its shape Increasing power The power of a lens describes how large the angle of refraction is as the light refracts through the lens. The larger the refraction, the thicker the lens is, the more powerful the lens. Two types of lens Converging Lens convex Diverging Lens concave Why do we call it a Converging lens? Why do we call it a Diverging lens? A clue it is to do with light rays Refraction of light through a diverging lens A diverging lens, the focal point is the point from which the waves seem to be coming from after passing through the lens. Refraction of light through a converging lens The focal point is where the rays of light meet after refraction. The focal length is measured from the point to the middle of the lens. With your ray boxes see how light behaves through the different lenses What happens to the light when it refracts through this combination Focal length of a lens • Lets see if we can focus an image • You will need • Lens holder • Ray box • Powerpack • Ruler • Screen • Different lenses Set up equipment as shown. Move screen back and too until a clear crisp image is formed. Bulb in ray box Lens > > Ray box Lens holder Screen Focal length of a lens • Using the keywords write how you find the focal length of a lens. Image Lenses and Images Learning Objectives Describe the refraction of light by converging and diverging lenses Describe real and virtual images Relate the power of a lens to its shape Two types of images can be created A virtual image is one from which the light rays appear to come but don’t actually come from that image like in a mirror. A real image is the image formed where the light rays are focussed http://www.gcsescience.com/pwav27.htm Image size and position Object is at 2 focal lengths Image is inverted Image is the same size Image is real Object is at 1 focal lengths No image is formed Image size and position Object is between 1 & 2 focal lengths Image is inverted Image is made bigger Image is real Image size and position Object is at 2 focal lengths Image is inverted Image is the same size Image is real Image size and position Less than one focal length Image right way up Image is smaller Virtual image formed Lenses and Images Learning Objectives Describe the refraction of light by converging and diverging lenses Describe real and virtual images Relate the power of a lens to its shape x > > Quick Quiz 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Draw the rays of light through a diverging lens What is a virtual image How do you find the focal length of a lens If the object is at 1 focal length describe the image Give two factors which will increase the power of a lens Draw light rays through a converging lens Label the focal length and focal point



