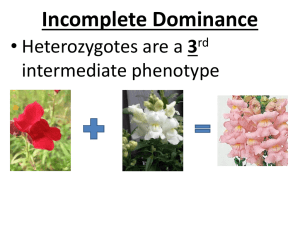
Mendelian and Human Genetics Mastery Test Review Fill in the blank using the options provided below: different dihybrid dominant Gregor Mendel heterozygous homozygous monohybrid recessive same ___________ _________ is said to be the father of genetics due to his early studies on garden pea plants. Mendel performed two types of crosses. ________________ crosses are performed between two parents that differ in only one trait, and ______________ crosses are performed between parents that differ in two traits. Mendel started each cross with true-breeding parents. We now refer to these parents as having a genotype that is _________________ because both alleles are the ________. In each cross Mendel noted that one trait would disappear in the F1 generation, only to reappear unchanged in the F2 generation. The trait that always appeared in the F1 hybrids he referred to as the __________________ trait while the trait that disappeared in the F1 generation he called the _________________ trait. The F1 hybrids have a genotype called _____________________ because they have two ____________________ alleles. Using the traits listed below fill in the chart provided and answer the questions. R = red flowers Y = yellow peas I = inflated B = black fur F = freckles W = widow’s peak Trait Flower color Fur color Freckles r = white flowers y = green peas I = constricted b = brown fur f = no freckles w = no widow’s peak Homozygous Homozygous dominant Heterozygous recessive genotype genotype genotype Dominant phenotype Recessive Phenotype 1. If you cross two pea plants that are both heterozygous for yellow peas, what phenotypic ration would result in the offspring? 2. What are the genotypes if one parent is homozygous dominant for black fur and the other has brown fur? 3. If you cross one parent that is heterozygous for inflated pods and the other has constricted pods, what genotypic ratio would result in the offspring? 4. If a man heterozygous for freckles marries a woman who has no freckles, what are the chances their children would have freckles? 5. If a man heterozygous for a widow’s peak marries a woman who is also heterozygous for a widow’s peak, what are the possible offspring phenotypes and the likelihood of each? Fill in the blank using the options provided below, use 46 twice: 1 22 44 46 autosomes extra gender meiosis missing monosomy nondisjunction pairs trisomy Down’s Syndrome Turner Syndrome XY Y X XX In humans chromosomes exist in ______ in each body cell. Each human has ____ pairs of autosomes for a total of ____ and ___ pair of sex chromosomes, resulting in ____ total chromosomes. The sex chromosomes determine the __________, or sex of the individual and are designated as the ___ or ___ chromosome. Human males have the sex genotype ______ and human females have the sex genotype _____. ___________________ are the other 22 pairs of chromosomes that are not sex chromosomes. Normal __________, gamete formation, and fertilization ensure that each human ends up with exactly ____ chromosomes. Sometimes during meiosis chromosomes fail to separate properly through a process called __________________________ and gametes result in having an ___________ or a _____________chromosome. If these gametes containing too many or too few chromosomes are fertilized the resulting zygote will have an extra chromosome, called _______________, such as ___________________________ or Trisomy 21. If they are missing a chromosome it is called _____________________, such as _____________________________ or Monosomy X. Fill out the chart below: Human Trait Inheritance Pattern Cystic fibrosis Simple dominance XH = normal Xh = hemophilia Hemophilia Color Blindness Blood Type Skin Color Alleles Sex-linked A B O Do not have to know alleles for this trait. 6. Using the alleles (R) = red flowers and (r) or (R’) = white flowers, explain or demonstrate how the results would be different if the trait were controlled by incomplete dominance vs. codominance. 7. If a colorblind father marries a woman who is a carrier, what are the chances of them having a colorblind child? 8. This pedigree shows a trait that is (autosomal/sex-linked) (dominant/recessive). 9. What is the relationship between individuals I-2 and III-3? a. mother and daughter b. father and son c. grandmother and granddaughter d. grandfather and grandson 10. If the trait in the above pedigree is hemophilia, assign genotypes to the following individuals: I-1: _________ II-2: __________ III-2: __________ 11. This pedigree shows a trait that is (autosomal/sex-linked) (dominant/recessive). 12. What is the relationship between individuals I-1 and II-2? a. mother and daughter b. father and son c. grandmother and granddaughter d. grandfather and grandson 13. If the trait in the above pedigree is cystic fibrosis, assign genotypes to the following individuals: I-1: _________ I-2: __________ II-2: __________ II-3: __________