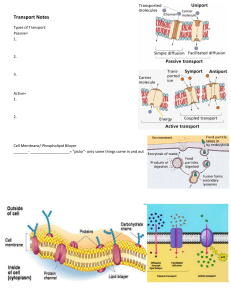
1.3. Membrane Structure 1. ____________ _______ A. _________ of Phospholipids i. A _____ head (___________) ii. composed of a ________ and a _________ molecule ___ _________ tails (___________) compose of _____ ____ (hydrocarbon) chains Phospholipids are ___________ (contain both ___________ and __________ regions) B. ___________ in membranes i. _____________ arrange into a _______ ii. The ___________ tail regions → face _______/are ________ from the surrounding _____ ______ iii. The ___________ head regions → associate with the _________ and _____________ ______ C. __________ of the Phospholipid Bilayer i. The _______ held together by weak ___________ ____________ between the _____ ii. Hydrophilic / hydrophobic layers restrict the _______ of many __________ iii. __________ _____________ can move within the bilayer, allowing for ________ ________ and ___________ iv. This fluidity allows for the ___________ ________ and _________ of membranes (___________/__________) 2. Membrane Proteins Phospholipid bilayers are embedded with ________, which may be either ___________ ___________ attached to the membrane A. ________ proteins ___________ attached to the membrane Typically, _____________ (span across the bilayer) __________ proteins ___________ attached by ____________ interactions Associate with ___ surface of the membrane _________ of membrane proteins i. _____ _____ of a membrane protein Localized according to ________ _________ (___________) amino acids ii. _____ (___________) amino acids Are located __________ Face _______ solution _____________ proteins (________ proteins) B. Associate ________ with the _____ _______ Typically adopt ___ of two ________ __________ ______ _______ / _______ _______ ____ _______ (common in _______ proteins) Membrane Protein Structures i. ________ Proteins _______ ___________ ___________ _______ ______ _______ ____________ _________ _________ ii. __________ Proteins C. _______, _________, ____________ (carriers) _________ of Membrane proteins i. _________ ii. iii. May function as _______ for cellular ______________ _________ vi. Responsible for ___________ _________ and ______ _________ ___________ v. Fixing to membranes _________ _________ pathways _________ iv. Serve to _______ and ____ two cells together _______ __________ points for ____________ and _____________ matrix ____________ 3. ____________ (channel proteins) Function as _________ for _______ hormones Cholesterol A _________ of animal cell __________ Functions to maintain _________ and __________ _________ ______ in _____ cells The plasma membranes are surrounded and supported by a rigid ____ ____ made of cellulose Cholesterol is an ___________ molecule → has both ___________ and ___________ regions Cholesterol’s ________ group ___________ Aligns towards the _________ _____ of phospholipids The _________ of the molecule (steroid ring and hydrocarbon tail) ___________ Associates with the ____________ _____ Phospholipids bilayers are _____ A. Phospholipids are in ________ movement relative to one another ___________ of Cholesterol with _____ ____ _____ Cholesterol interacts with the _____ ____ _____ of phospholipids to ________ the properties of the membrane __________ the outer surface of the membrane → reducing ________ Makes the membrane ____ _________ to very small water-soluble molecules that would otherwise freely cross ________ phospholipid _____ → prevent _______________ of the membrane Helps ______ __________ proteins by forming ____ _______ _____ _____ capable of _________ the protein 4. Fluid-Mosaic Model Cell membranes are represented according to a ____________ model ______ The phospholipid bilayer is _______ and __________ phospholipids can move position ______ The phospholipid bilayer is _____ with proteins, resulting in a ______ of components A. Structure of the Plasma Membrane (Fluid-Mosaic) B. __________ of the Plasma Membrane _____________ Form a _______ with _________ _____ facing outwards and fatty acid tails facing inwards 5. ___________ Found in ______ cell membranes Improve _________ and reduce ________ ________ May be either ________ (transmembrane) or __________ Serve a _______ of roles Membrane models i. ________ ___ ______ model (1935) The _____ model that attempted to describe the position of ________ within the bilayer Proposed a model whereby ___ ______ of protein _______ a _______ phospholipid bilayer Described as a ____________ ________ The lipid layer was __________ between two _______ layers The ____ ________ seen under microscope were identified as representing the _______ layers (_______) Problems with the ____________ ________ model It assumed all membranes were of a _______ _________ and would have ________ _____________ _____ It assumed all membranes would have ___________ ________ and ________ surfaces It did not account for the ____________ of certain substances (did not recognize the need for ___________ pores) The ___________ at which membranes solidified did not _________ with those expected under the proposed model ii. Falsification Evidence Membrane proteins were discovered to be _________ in water (indicating ___________ surface) and varied in ____ Such proteins would not be able to form a _______ and __________ layer around the outer surface of a membrane Fluorescent antibody tagging of membrane proteins showed they were ______ and ___ _____ in place Membrane proteins from two different cells were tagged with red and green, fluorescent markers respectively When the two cells were _____, the markers became _____ throughout the membrane of the fused cell This demonstrated that the membrane proteins _____ ____ and did not form a ______ layer (as per Davson-Danielli) Freeze fracturing was used to split open the membrane and revealed _________ _____ surfaces within the membrane These rough surfaces were interpreted as being _____________ proteins, demonstrating that proteins were not ______ _________ to the outside of the membrane structure iii. New model _______________ model Proposed by Seymour Singer and Garth Nicolson in 1972 Proteins were ________ within the _____ _______ rather than existing as separate layer Known as the ____________ model