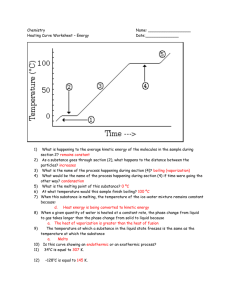
Phases of Matter: Solid matter that has definite volume and shape. The molecules are packed together tightly and move slowly. Liquid matter that has definite volume but not shape. Since the molecules of a liquid are loosely packed and move with greater speed, a liquid can flow and spread. Gas matter that has no definite volume or shape. Molecules of a gas are so loosely arranged and move so rapidly that they will fill their container. Phase Change Descriptions: Melting the change from solid to liquid. Freezing the change from liquid to solid. Vaporization the change from liquid to gas. Evaporation vaporization from the surface of a liquid. Boiling vaporization from within as well as from the surface of a liquid. Condensation the change from gas to liquid. Fill in the phase changes in the blanks provided. 3 4 The graph was drawn from data collected as a substance was heated at a constant rate. Use the graph to answer the following questions. At point A, the beginning of observations, the substance exists in a solid state. Material in this phase has _______________ volume and _____________ shape. With each passing minute, _____________ is added to the substance. At point B, the temperature of the substance is ______°C. The solid begins to _______________. At point C, the substance is completely _________________ or in a ___________ state. Material in this phase has _______________ volume but not shape. The energy put to the substance between minutes 5 and 9 was used to convert the substance from a ___________ to a ___________. This heat energy is called the latent heat. Between 9 and 13 minutes, the added energy increases the _____________________ of the substance. During the time from point D to point E, the liquid is ___________________________. By point E, the substance is completely in the __________ phase. Material in this phase has _____________ volume or shape. The energy put to the substance between minutes 13 and 18 converted the substance from a ___________ to a ___________ state. This heat energy is called the latent heat. Beyond point E, the substance is still in the ______________ phase. Which of these three substances was likely used in this phase change experiment ? __________________________ Substance Bolognium Unobtainium Foosium Melting point 20 °C 40 °C 70 °C Boiling point 100 °C 140 °C 140 °C 1. Vaporization is the change from: a. liquid to gas. b. solid to liquid. c. gas to solid. d. solid to gas to solid. e. gas to liquid. 2. The change from gas to liquid is called: a. boiling. b. condensation. c. distillation. d. melting. 3. How many phase changes have latent heat that is gained ? _______ 4. How many phase changes have latent heat that is lost ? ______ 5. What are the 2 examples of the phase change from liquid to gas? ________________________________ ________________________________ 6. How many phases are there ? _________ 7. How many phase changes did we list in the chart ? ________ Use the above graph for the following 4 questions. 8. During which interval of the graph is a phase change occurring ? a. A to B b. E to F c. C to D d. D to E 9. During which interval does water get heated ? a. A to B b. E to F c. C to D d. D to E c. C d. D e. B c. C d. D e. B 10. At what point does vaporization end ? a. A b. E 11. At what point does melting start ? a. A b. E 12. You cannot see water vapor. a. true b. false 13. List the phases from greatest to least energy. ______________________________________ _____________________________________ _______________________________________ e. sublimation.