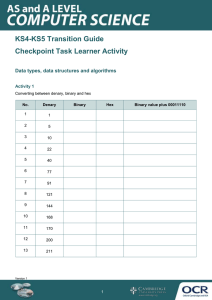
COMPUTER SCIENCE Binary Put these into Size Order – 30secs Data Storage Capacities bit (a single 0 or 1 is a binary digit) 8 bits = 1 byte 1024 bytes = 1Kb 1024 Kilobytes = 1Mb 1024 Megabytes = 1Gb 1024 Gigabytes = 1Tb Learning Objectives To understand that computers use the binary alphabet to represent all data and instructions. Understand the terms bit, nibble, byte, kilobyte, megabyte, gigabyte and terabyte Success Criteria ALL— will be able to state what binary is. MOST— will be able to explain how computers use binary and do simple binary conversions. SOME— will create a spreadsheet that automatically works out denary number from a given binary number. Rank these types of data storage in size RAM Hard Drive How Computers Work – Binary! Computers are made up of complicated hardware that stores and processes data. If you break a computer down into its most basic components you have millions of circuits that either allow electricity to flow, or not. Imagine a whole row of light switches that you can switch on and off in different combinations to mean different things. Each switch is either on or off. It only has two states. That is why everything stored in a computer can be stored as a series of 1s and 0s. This is called binary. CPU / Processor/ Chip The CPU is the brain of the computer – it tells the computer what to do and when. Has millions of tiny switches that can either be: on or off 1 or 0 Denary System 0 , 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 We use a number system that uses 10 different numbers. (Base 10 number system) This is called the Denary System. However computers don’t understand this as they only understand 0’s and 1’s. on or off Denary System 243 3 units Denary System 243 4 tens 4 * 10 = 40 Denary System 243 2 hundreds 2 * 100= 200 Denary System 2 hundreds 4 tens 3 units 2 * 100= 2004 * 10 = 40 243 Binary Computers understand binary which is a Base 2 number system as it only has two numbers: 0 and 1 Binary The position of numbers in binary is also important. Calculating denary number 1: Denary 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 Binary 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 (1 * 1) = 1 Binary The position of numbers in binary is also important. Calculating denary number 3: Denary 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 Binary 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 (1 * 2) = 2 (1 * 1) = 1 Binary The position of numbers in binary is also important. Calculating denary number 6: Denary 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 Binary 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 (1 * 4) = 4 (1 * 2) = 2 Binary The position of numbers in binary is also important. Calculating denary number 37: Denary 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 Binary 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 (1 * 32) = 32 (1 * 4) = 4 (1 * 1) = 1 Binary Can you work out how to write the denary number 115 in binary? Denary 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 Binary 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 64 32 16 2 1 Binary Can you work out how to write the denary number 255 in binary? Denary 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 Binary 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 Tip – Always use 8 bits for binary! So far we have only looked at numbers using eight columns. This is an 8-bit number, or a byte. 00000011 is binary for 3 but so is 11. You do not need the leading zeros for it to be a valid number but we tend to write groups of 8 bits because computers usually store data in bytes. Binary Task Work out the following numbers in binary: Number 165 117 61 224 39 139 170 186 255 223 84 Binary Binary Task - Answers Work out the following numbers in binary: Number Binary 165 10100101 117 01110101 61 00111101 224 11100000 39 00100111 139 10001011 170 10101010 186 10111010 255 11111111 223 11011111 84 01010100 Extension Can you create a spreadsheet that will automatically work out the denary number from the binary you type in (or vice versa?) Validate it so you can only enter a 0 or 1 Review What is binary? Explain this as if you are explaining this to someone who knows nothing about it. HW Complete the “Binary” questions on the VLE (it’s Learning).