Carbohydrates: Biochemistry Lecture - Sugars, Structure, & Classification
advertisement

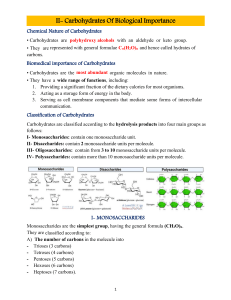
General Biochemistry III lecture Carbohydrates - Sugars Glucose glycogen galactose ribose/deoxyrabose Lactose intolerance Diabetes mellitus Disorders Galactosemia Glycogen storage disease Classification of Carbohydrates Monosaccharides Disaccharides Polysaccharides Oligosaccharides Monosaccharides (Classification according to the number of carbon atoms) Trioses (3C) Tetroses (4C) Pentoses (5C) Hexoses (6C) Heptoses (7C) Monosaccharides (Classification according to the type of the functional group) Aldoses Ketoses Polyhydric alcohols (polyols) Trioses Glyceraldehyde (Glycerose) Dihydroxyacetone • L and D stereoisomers are defined by the position of hydrogen and hydroxyl towards the carbon atom that is just before the final alcohol group; L D • This isn’t the same as optical isomerism. Tetroses D-Erythrose D-Threose Pentoses D-Ribose D-Deoxyribose D-Xylose D-Arabinose • Isomers differing as a result of variations in configuration of the hydrogen and hydroxyl atoms to the chiral carbon atoms, instead the one that is just before the final alcohol group (CH2OH) are known as epimers. D-Ribulose D-Xylulose Hexoses D-Glucose D-Galactose D-Mannose D-Fructose Cyclic structures and Anomers Furan D-Glucofuranose Pyran D-Glucopyranose D-Ribofuranose D-Deoxyribofuranose D-Fructofuranose D-Fructopyranose Anomers Anomeric carbon atom α-D-Glucopyranose Anomeric carbon atom β-D-Gluopyranose Polyols Sugar Alcohols Monosaccharide+Monosaccharide Monosaccharide+ Non Carbohydrate compoun Glycosides O-glycans • • • • • N-Glycans Methanol Glycerol Sterol Phenol Adenine Aminosugars α-D-glucosamine α-D-galactosamine Disaccharides Polysaccharides Homopolysaccharides • • • • • Glycogen Starch Cellulose Chitin Inulin Heteropolysaccharides • • • • • Hyaluronic acid Chondroitin sulfate Heparin Heparansulfate Dermatan sulfate Hyaluronic acid Chondroitin sulfate Heprain Thank you for your attention