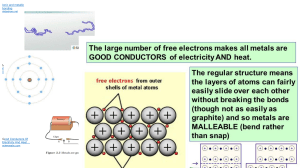
Name : ………….………………………….. ( ) Class : ………………… Date : ……./……./……. Department of Science 2019 S3 Chemistry EOY Revision - Kinetic Particle Theory, Elements Mixtures and Compounds, Separation Techniques, Chemical Bonding 1. Kinetic Particle Theory (a) Describe the movement and arrangement of particles in the solid, liquid and gaseous states: Solid: ......................................................................................................................................... Liquid: ....................................................................................................................................... Gas: ........................................................................................................................................... (b) The graph below shows the heating curve obtained by heating an unknown substance Temperature / °C F 161 D E Time / s 0 -51 B C A (i) Explain any changes in the movement of particles from A to B. ............................................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................................. 1 (ii) Explain why the temperature remains constant from B to C and D to E. ............................................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................................. (ii) Deduce if the unknown substance heated was pure. Explain your answer. ............................................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................................. (c) A drop of ink is added separately to a glass of cold and hot water. State and explain the expected observations and differences, if any. ............................................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................................. (d) The following experiment was set up to investigate the movement of gaseous ammonia and gaseous hydrogen chloride. Direc7on%of% movement%of% ammonia%gas% Direc7on%of% movement%of% hydrogen%chloride%gas% Co#on%wool%soaked%with% hydrochloric%acid% Sealed%glass%tube% Co#on%wool%soaked%with% aqueous%ammonia% Gaseous ammonia and hydrogen chloride react to form a white solid. (i) Write a chemical equation for the reaction that occurred. ............................................................................................................................................................. (ii) (iii) Use a cross to indicate the position that the white solid will form in the sealed glass tube. Explain your answer in (d)(ii). ............................................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................................. 2 2. Elements, Compounds, Mixtures (a) State if the following six substances are elements, mixtures or compounds. If the substance is a mixture, identify if it is a mixture of elements/compounds. Substance 1: Substance 2: This is a _______________________________ This is a _______________________________ Substance 3: Substance 4: This is a _______________________________ This is a _______________________________ Substance 5: Substance 6: This is a _______________________________ This is a _______________________________ 3 (b) Use the following Venn Diagram to organise the similarities and differences that exist between elements, mixtures and compounds. ELEMENT COMPOUND MIXTURE 3. Separation Techniques (a) State the scientific basis of the following separation methods and what type of mixtures they can be used to separate. separation method scientific basis of separation method type of mixtures that method can be used to separate (e.g: solid-solid, solidliquid, liquid-liquid etc.) Distillation Fractional Distillation Paper chromatography 4 Use of a separating funnel Use of a separating funnel Filtration + crystallisation Filtration + crystallisation Filtration + evaporation to Filtration + dryness evaporation to dryness Sublimation Sublimation (b) Paper chromatography was used to determine the purity of a sample. The chromatogram produced showed the presence of two A and B.the A locating was used. (b) Paper chromatography was usedspots, to determine purity ofagent a sample. The chromatogram produced showed the presence of two spots, A and B. A locating agent was used. 4.0 cm solvent front 12 cm B A 5.4 cm starting line (i) Urine sample Chromatogram Calculate the Rf values for A and B. (i) Calculate the Rf values for A and B. (ii) Explain why a why locating agentagent was used. (ii) Explain a locating was used. ............................................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................................. 5 5 (iii) Deduce and explain if the sample was pure. ............................................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................................. (c) (i) Label all parts of the fractional distillation set-up below and add in any missing apparatus. (ii) State the purpose of the following apparatus: Glass beads in the fractionating column: ............................................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................................. Condenser: ............................................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................................. Thermometer: ............................................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................................. 6 4. Chemical Bonding (a) Given the following keywords, complete the Summary table on the next page. Keywords for describing structure: • giant molecular structure • simple molecular structure • giant metallic lattice structure • giant ionic lattice structure Keywords for stating the type of chemical bonding: • covalent bonding (sharing of electrons) • ionic bonding (transfer of electrons) • metallic bonding Keywords for describing forces of attraction in chemical bonding: • strong electrostatic forces of attraction • strong covalent bonds • weak van der Waals’ forces of attraction OR intermolecular forces of attraction Keywords for stating types of partlcles involved chemical bonding: • metal cations and sea of delocalised electrons • molecules • atoms • oppositely charged ions 7 Summary Table – Structure, bonding and physical properties of matter ionic compounds covalent substances metallic solids structure type of bonding present type of particles involved in bonding Example: Calcium nitride description of structure and bonding for specific example(s) Example: Nitrogen . Example: Diamond Example: Calcium Example: Graphite physical properties 8 (b) Complete the following table with the dot-and-cross diagrams for the ionic and simple covalent substances as well as the structure to show metallic bonding in metallic solids. ionic compounds calcium nitride simple covalent substances nitrogen carbon dioxide metallic solids calcium 9 (c) The structures of some substances are provided below. (i) Identify the structure and type of bonding present in the above substances. Deduce and explain if they have high or low melting and boiling points. substance structure and type of bonding high/ low meling point? explanation A B C D E F 10 (ii) Which structure(s) can conduct electricity in the solid state? Explain your answer. ............................................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................................. (iii) Which structure(s) can only conduct electricity in the liquid state? Explain your answer. ............................................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................................. (iv) Which structure(s) cannot conduct electricity in all states? Explain your answer. ............................................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................................. 11