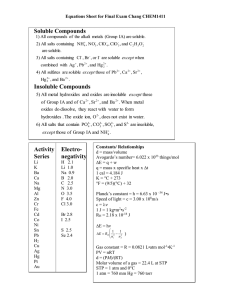
***When writing the formula for an acid, add enough H atoms to neutralize the anion’s charge. Common Polyatomic Ions Formula H2PO4C2H3O2HSO3HSO4HCO3- NO2CrO42CNOHClOClO3PO33NH4+ BrO3CNS- Name Dihydrogen Phosphate Acetate Hydrogen Sulfite Hydrogen Sulfate Hydrogen Carbonate (Bicarbonate) Nitrite Chromate Cyanide Hydroxide Hypochlorite Chlorate Phosphite Ammonium Bromate Thiocyanate Formula HPO42C2O42SO32SO42CO32- Name Hydrogen Phosphate Oxalate Sulfite Sulfate Carbonate NO3Cr2O72SiO32MnO4ClO2ClO4PO43S2O32IO3- Nitrate Dichromate Silicate Permanganate Chlorite Perchlorate Phosphate Thiosulfate Iodate Prefixes For Molecular Compounds Number Prefix Number Prefix 1 2 3 4 5 Common Metals With More Than One Charge **Chromium and Manganese may have even more possible charges. Ion 1+ Cu Cu2+ Fe2+ Fe3+ Pb2+ Pb4+ Sn2+ Sn4+ Cr2+ Cr3+ Mn2+ Mn3+ Co2+ Co3+ Stock System Copper (I) Copper (II) Iron (II) Iron (III) Lead (II) Lead (IV) Tin (II) Tin (IV) Chromium (II) Chromium (III) Manganese (II) Manganese (III) Cobalt (II) Cobalt (III) Classic System Cuprous Cupric Ferrous Ferric Plumbous Plumbic Stannous Stannic Chromous Chromic Manganous Manganic Cobaltous Cobaltic 3+ HexaHeptaOctaNonaDeca- Activity Series of Metals (listed in order of reactivity – most active at the top) Metals Lithium Potassium Barium Calcium Sodium Magnesium Aluminum Zinc Iron Nickel Tin Lead Hydrogen* Copper Mercury Silver Gold Halogens Fluorine (F2) Chlorine (Cl2) Bromine (Br2) Iodine (I2) Symbol Li K Ba Ca Na Mg Al Zn Fe Ni Sn Pb H Cu Hg Ag Au **Metals from Li to Na will replace H from acids AND water; from Mg to Pb they will replace H from ONLY acids. Solubility Rules *Soluble compounds dissolve in water and are therefore aqueous (aq); insoluble compounds do not dissolve and are therefore solids (s). 2+ Rules for Naming Acids Naming Format Anion Anion Example Ending ClClO2ClO3- 6 7 8 9 10 *Elements that appear above others in the table will replace them in a single replacement reaction (they are more likely to be oxidized). 1+ Metals with a single possible charge include Al , Zn , and Ag Hydrochloric Acid Chlorous Acid Chloric Acid MonoDiTriTetraPenta- -ide -ite -ate Acid Example HCl HClO2 HClO3 *Remember, acids formed from anions ending in -ide or –ate’s become acids ending in –ic; those from anions ending in –ite become acids ending in –ous. **Oxyacids are NOT named with the “hydro” prefix. All compounds containing alkali metal cations and ammonium are soluble. All compounds containing NO3-, ClO3-, ClO4-, and C2H3O2anions are soluble. All chlorides, bromides, and iodides are soluble except those containing Ag+, Pb2+, Hg22+ All sulfates are soluble except those containing Hg22+, Pb2+, Sr2+, Ca2+, or Ba2+ cations. All hydroxides are insoluble e xcept compounds of the alkali metals Ca2+, Sr2+, and Ba2+ cations. All compounds containing PO43-, S2-, CO32-, and SO32anions are insoluble except those that contain alkali metals or NH4+.