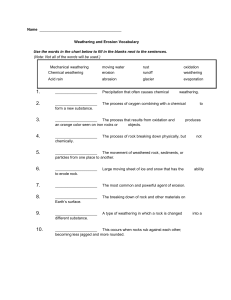
Name: Date: Reference: Use your weathering chart, classroom notes and in your textbook. Per: __ Background: Weathering includes both mechanical and chemical weathering. Mechanical weathering is any process that breaks up rock without changing its chemical composition. Chemical weathering is any process in which water, air or other substances react with the minerals in the rock and change the chemical composition. Directions: Decide if the weathering process is mechanical (M), chemical (C) or both (B). Then, indicate the type of weathering (agent of weathering). Question #1 has been completed for you as an example. ___ ____________ 1. Lichen grows on the surface of rocks, producing pits in the rocks. ___ ____________ 2. The wedging of tree roots along cracks in granite outcrops. ___ ____________ 3. Limestone dissolved away producing an underground cave. ___ ____________ 4. Minerals that contain iron turn yellowish brown indicating the formation of rust. ___ ____________ 5. This type of weathering includes repeated freezing and thawing of water that cracks rocks. ___ ____________ 6. Water, salt and oxygen on car fenders and panels is this type of weathering. ___ ____________ 7. Rocks that have been carried by streams and have become smaller and more rounded. ___ ____________ 8. Feldspar mixed with water until it disolves, producing clay minerals. ___ ____________ 9. A boulder field is created at the base of Pike’s Peak. ___ ____________ 10. Independence Rock in Wyoming, Half dome in Yosemite, and granite outcrops in Central Minnesota all show signs of weathering because the outer parts of the rock are peeling off in layers. ___ ____________ 11. Sulfur dioxide and nitric oxide are formed as a result of burning fossil fuels. ___ ____________ 12. A large piece of basalt has a pine tree growing through it. ___ ____________ 13. Rocks crack because of repeated expansion and contraction. 1 Part I. Complete the chart below Cause/Specific type of Weathering Kind of Weathering Description 1. _____________________ Mechanical Rock particles carried by wind and water wear away rock 2. _____________________ Chemical Freezing and thawing Carbon dioxide 5. ______________________ 6. ______________________ Plant growth 3. ______________________ 4. ______________________ Plants produce this as they grow causing minerals in rocks to decay Breaks rock by wedging rocks apart Combines with water in the atmosphere to form carbonic acid Weathers marble and limestone Chemical Mechanical Causes movements such as landslides that further break down rocks Roots pry apart cracks in rocks 7. ______________________ Combines with iron to produce rust Oxygen 9. _______________________ 8. _______________________ Chemical Formed in factories and cars an a result of burning fossil fuels—creates acid rain Part II. Completion 1. How are chemical and mechanical weathering alike? 2. How are chemical and mechanical weathering different? Part III. Matching 3. _____water a. This gas, when mixed with water, causes iron to rust 4. _____oxygen b. This is caused by pollution 5. _____carbon dioxide c. It is the most important factor in several types of weathering 6. _____living organisms d. This is the main “ingredient” in making carbonic acid 7. _____acid rain e. Lichens are one example of …... 2