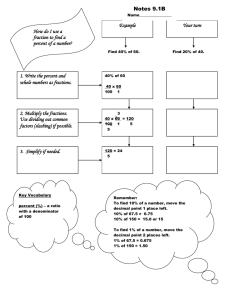
Key Concepts Summary - Order of Operations & Fractions 1. Basic scientific calculator functions: addition (+), subtraction ( -), multiplication ( x, *, .), division (/, ÷), exponents (4 n), roots (√), inverse (1/x, x -1), negative numbers (-n) 2. The order of operations are a. Parentheses i. Fraction lines: treat numbers above and below fraction line as if in parentheses b. Exponents and roots c. Multiplication and division d. Addition and subtraction e. If there is a tie, then read left to right 3. The top number of a fraction is called the numerator. 4. The bottom (down) number of a fraction is called the denominator. 5. Proper fraction – number less than 1 6. Improper fraction - number greater than 1 7. Equivalent fractions – represent the same number Preparing for College Mathematics Instructor: Jason Novak Key Concepts Summary - Order of Operations & Fractions 8. Like fractions – different fractions with the same denominator 9. Mixed number – sum of whole number and a proper fraction 10. To reduce a fraction (find lowest terms) we can cancel out common factors. a. Lowest terms – simplest fraction in set of equivalent fractions b. Cancel – divide top and bottom by SAME number 11. To change a mixed number to an improper fraction, multiply the whole number by the denominator and add it to the numerator. 12. When multiplying proper or improper fractions, first reduce and then multiply across. 13. When multiplying a whole number by a fraction, first change the whole number to the numerator over 1 and then multiply across. 14. To divide proper or improper fractions, invert the divisor (use reciprocal) and multiply. a. Reciprocal – invert numerator and denominator 15. When multiplying or dividing mixed numbers, you must first change the mixed numbers to improper fractions before multiplying across. 16. We find the least common denominator (LCD) of two or more fractions by finding the least common multiple of the denominators. Preparing for College Mathematics Instructor: Jason Novak Key Concepts Summary - Order of Operations & Fractions a. Calculator Method: i. Write down a few multiples of the larger denominator ii. Test each multiple until you find one that is exactly divisible by the smaller denominator 17. To build equivalent fractions, first find the LCD, and then find how many times the denominator must be multiplied to get the LCD. Finally multiply the numerator by this number. 18. To add fractions with the same denominators, you get the sum’s numerators by adding the two numerators, while the sum’s denominator is the original denominator. 19. To add or subtract proper or improper fractions with different denominators, a. first find the LCD, b. then build up the fractions i. so that denominator = LCD c. finally add the two fractions. 20. To add mixed numbers, separately add the whole number parts and the fractional parts. If the sum of the fractional parts produces an improper fraction, change the improper fraction to a mixed number. Then add the mixed number to the whole number sum. Preparing for College Mathematics Instructor: Jason Novak