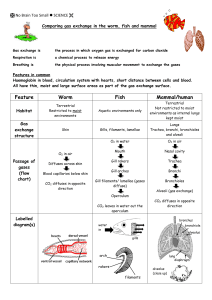
How gas is exchanged in fish 1. The gills are the gas exchange surface in fish. 2. Water (containing O ) enters the fish through its m_____ and passes out 2 through the g____. As this happens, O diffuses from the water into the 2 blood in the gills and Carbon Dioxide CO diffuses from the blood into 2 the water 3. Each gill is made of lots of thin plates called gill f_______, which give a big s______ a____ for exchange of gases. 4. The gill filaments are covered in lots of tiny structures called l________, which increase the surface area even more. 5. The lamellae have lots of blood c_______ to speed up d______. 6. They also have a thin layer of cells to m_____ the distance gases have to diffuse. 7. B_____ flows through the lamellae in one direction and water flows over in the opposite direction. This maintains a large c_________ g______ between the water and the blood. 8. The concentration of O__________ O in the water is always 2 h_________ than that in the blood, so as much O as possible diffuses 2 from the water into the blood. Oxygen, higher, gills lamellae, mouth, filaments, Blood, surface area, capillaries, minimise, diffusion concentration gradient How gas is exchanged in fish 1. The gills are the gas exchange surface in fish. 2. Water (containing O ) enters the fish through its m_____ and passes out 2 through the g____. As this happens, O diffuses from the water into the 2 blood in the gills and Carbon Dioxide CO diffuses from the blood into 2 the water 3. Each gill is made of lots of thin plates called gill f_______, which give a big s______ a____ for exchange of gases. 4. The gill filaments are covered in lots of tiny structures called l________, which increase the surface area even more. 5. The lamellae have lots of blood c_______ to speed up d______. 6. They also have a thin layer of cells to m_____ the distance gases have to diffuse. 7. B_____ flows through the lamellae in one direction and water flows over in the opposite direction. This maintains a large c_________ g______ between the water and the blood. 8. The concentration of O__________ O in the water is always 2 h_________ than that in the blood, so as much O as possible diffuses 2 from the water into the blood. Oxygen, higher, gills lamellae, mouth, filaments, Blood, surface area, capillaries, minimise, diffusion concentration gradient