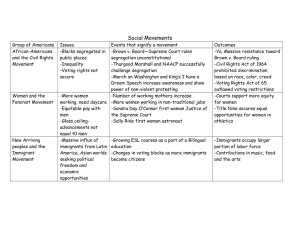
Really good Netflix movies/shows that compliment these topics - The Trial of the Chicago 7 - 13th - When They See Us - Teach Us All - Fruitvale Station - I Am Not Your Negro - Who Killed Malcolm X Civil Rights Vocabulary Segregation - the separation of public and private facilities, opportunities for movement, and institutions by race. Segregation laws are the cornerstone of the Jim Crow era South which lasted from the 1870s to 1964. - De Jure segregation--legally stipulated segregation, i.e. whites only schools. - De Facto segregation-- “of fact.” segregation resulting from conditions not stipulated by law, i.e. segregation - De Jure segregation is upheld as constitutional in Plessy vs. Ferguson (1864) under the “separate but equal doctrine” Tripartite system of domination -- three aspects of domination: economic, political, social (personal). Proletariat -- the working class, mass of workers whose labor Ideology -- the ruling belief structure that justifies given organization of society. The Issues that spurred the Civil Rights movement from the 1950s to the 1970s - Jim Crow -- De jure segregation across the South and de facto across much of U.S. Exclusion from public institutions, education, - Voting Rights -- Widespread across the South, Fannie Lou Hamer, Medger Evers, MLK - Economic domination -- marginalization, red-lining, predatory lending, misappropriation, exploitation - Across the country - Police Brutality -- Northern cities -- Lynching much of the country (Malcom X) - Vietnam War -- disproportionate drafting of Black men to fight in Vietnam NAACP Founded in 1909 in NYC by white progressives and Black intellectuals including W.E.B. Du Bois and Ida B. Wells. Early focus on anti-lynching, reversing disenfranchisement of blacks in the South, desegregating the federal government and permitting Blacks to fight in WWI NAACP Efforts - Used legal, court, and policy action to address racial inequality, violence, and injustice. - Emmitt Till is lynched in 1955, photographs in Jet magazine set of a nationwide wave of anti-lynching sentiment - “Racism is not getting worse; it is getting filmed”. Resonates still today with Police Brutality - - NAACP steps up its membership efforts in the South and is met with white supremacist resistance. NAACP is labeled communist and subversive leading to its banning or suppression across the South. 1962 -- NAACP field secretary, Medgar Evers, is assassinated by white supremacists in Jackson, Mississippi. NAACP and Brown vs. Board of Ed. - Overturns Plessy v Ferguson (separate but - NAACP and their attorney Thurgood Marshall wage a legal battle that resulted in the Supreme Court cases: Brown vs. the Board of Education of Topeka Kansas 1954 (Brown I) - So called Brown II 1955 limited the scope of enforcing Brown I--state must end segregation with “all deliberate speed” - This approach emphasized integration of black students into segregated white schools. But was largely unsuccessful. By 1964 1 in 85 North Carolinian Black students were in integrated school. - Not until 1971, with Swann v. Charlotte-Mecklenburg Board of Ed., does Supreme Court mandate busing. - Respond to economic Jim Crow. Boycotts used Black Boycotts -Segregation on buses and the refusal of Black passengers was widespread across the South. -- In the North many bus companies refused to hire Black drivers--Milwaukee, Chicago, St. Louis --First boycott is in Baton Rouge in 1953 --Most famous boycotts in Montgomery, AL (Rosa Parks); Tallahassee, FL; Birmingham, AL: 1955-6 --Organizational activity takes place through Black churches. Students Nonviolent Coordinating Committee - Young people, nonviolent, direct action - Sit-ins, voter registration drives Malcolm X - “It looks like 1964 will be the year of the ballot or the bullet” Important figures of the Civil Rights Era - Fannie Lou Hamer - Medgar Evers - Martin Luther King Jr. - Stokely Carmichael - Black Panthers - Bobby Seale, Huey P Newton, Eldridge Cleaver - Angela Davis Black Nationalism - Black control and ownership within black communities. - Inspired by international decolonial movements -- African, Asian, Latin American - Connects the oppression of African Americans to colonial power