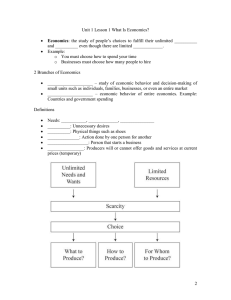
KORBEL FOUNDATION COLLEGE, INC. . Purok Spring Uno, Brgy. Morales, Koronadal City Contact No. 887-2051 Subject: Applied Economics Semester: 2nd (1st Term) Grade: ______ Module: 1(1–2) I. OBJECTIVES: 1. The learners should define basic terms in applied economics. 2. The learners should identify the basic economic problems of the country. 3. The learners should explain how applied economics can be used to solve economic problems. II. PRE-ASSESSMENT: ACTIVITY 1: Read and comprehend the text below and answer or discuss the questions at the end of the text. In October 2016, President Rodrigo Duterte outlined a long-term economic development plan entitled AmBisyon Natin 2040. This plan outlines a vision of the country’s economic development in the year 2040, and is the basis for the Philippine Development Plan (PDP) 2017-2022 drafted by the National Economic and Development Authority (NEDA). It is expected to be the guiding template for succeeding development plans until 2040. The following are the main goals for economic development from the PDP 20172022. The Filipinos’ vision for the Philippines in 2040 is a prosperous, predominantly middle-class society where there are equality of opportunities and poverty has been eradicated. It will be a society where people live long and healthy lives with a higher life expectancy at birth of 80 years. Longevity will be enhanced by the ability of individuals and communities to withstand natural as well as man-made shocks and disasters. With smarter and more innovative people, the country in 2040 is also envisioned to be a major player in the global knowledge economy, producing innovative products and processes that are used to make high-quality goods and services at competitive prices. The Philippines will be a high trust, more caring and peaceful society where human security is assured and government enjoys the people’s trust because it is clean, efficient, and service-oriented. High trust will also prevail between the private sector and the government, as well as between and among peoples. Overall, a high-trusty society will facilitate official and business transactions, and smooth interpersonal relations. On the kind of life they want for themselves, Filipinos want a life that is strongly rooted, comfortable, and secure; matatag, maginhawa at panatag. The terms “strongly rooted, comfortable, and secure” used to describe the life envisioned by Filipinos by 2040 reveal middle-class aspirations. They include home ownership, a steady source of income to support family and self, college education for the children, a motor vehicle, stable finances to cover daily needs and contingencies, savings for retirement, and time for vacation and travel. There is also a strong family orientation that underlies the preferences as reflected in the choice of living and working in the same locality, the desire for adequate spaces that allow for activities with family and friends, and the desire for access to convenient and affordable transportation for occasional visits to family and friends, among other reasons. The same value is reflected in the importance attached to education. Nearly every Filipino family considers college education a requisite to a decent job and so aspires to have the children complete a college degree. The desired lifestyle requires a monthly family income of at least P120,000 for a family of four valued in 2015 prices in the National Capital Region. With the right policies, improvements in productivity and efficiency can more than triple the gross national income per capita of the country in 25 years. This will allow the majority of Filipinos to enjoy a middle-class standard of living. Without reforms, however, per capita income can only double over a period of 25 years. Page 1 of 6 KORBEL FOUNDATION COLLEGE, INC. . Purok Spring Uno, Brgy. Morales, Koronadal City Contact No. 887-2051 From the above text discuss the following questions. You can answer in Illonggo, Cebuano, Filipino or English Language. 1. What are the major Goals of the PDP 2017-2022? ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 2. Do you believe that these goals are attainable? Which of these goals do you consider to be attainable by 2022? By 2040? Why? ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 3. What economic concepts or theories, in your view, are the bases in formulating these goal? ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 4. Make a list of economic terms used in the text. How are these terms significant to development? ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ Page 2 of 6 KORBEL FOUNDATION COLLEGE, INC. . Purok Spring Uno, Brgy. Morales, Koronadal City Contact No. 887-2051 III. DISCUSSIONS: LESSON 1: REVISITING ECONOMICS AS SOCIAL SCIENCE What is Economics? Economics refers to the effective management of scarce economic resources to satisfy unlimited human wants and needs. It is a social science that studies the means by which individuals, groups, and societies produce, distribute, and consume product and services. From the definition of economics, we can derive the following basic economic concepts: 1. Scarcity (Scarce) – is the fundamental concept of economics. It refers to the limitation of resources, particularly economic resources such as land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship. 2. Economic Resources – are the factors used in producing goods or providing services. In other words, they are the inputs that are used to create things or help you provide services. Economists divided these factors into four major categories: a. Land – refers to all natural resources that exist without man’s intervention. It encompasses all things derived from the forces of nature such as air, water, forests, vegetation, and minerals. The payment for land is called rent. b. Labor – refers to human inputs such as manpower skills that are used in transforming resources into different products that meets our needs. The payment for labor is called wages and salaries. c. Capital – is a man-made factor of production used to create another product. Examples are machinery and equipment used in manufacturing companies. The payment for capital is interest. d. Entrepreneurship – is the factor od production that integrates land, labor and capital to create new products. An entrepreneur is an individual who makes the decisions with regard to production and utilizing the other factors of production. 3. Needs – is defined as things that are desired which are essential for human survival. 4. Wants – is defined as things that are desired but are not essential for human survival. ACTIVITY 2: Classify the following items if it is included in each of the four major categories of economic resources. Write Land, Labor, Capital, and Entrepreneurship. ITEMS Example: Equipment 1. A factory used in production 2. Unrefined Gold 3. Lumber 4. Copper 5. A bulldozer at a construction site 6. Expertise of a foreman 7. A cash register at a clothing store 8. Water 9. An oven at a bakery 10. Skills of factory workers 11. Gasoline 12. Baker’s Skills 13. A delivery equipment 14. Expertise of an engineer 15. Rice field CATEGORIES Capital Page 3 of 6 KORBEL FOUNDATION COLLEGE, INC. . Purok Spring Uno, Brgy. Morales, Koronadal City Contact No. 887-2051 The Basic Economic Questions Since the scarcity of resources is central to the study of economics, it is necessary to properly allocate these resources to meet people’s unlimited needs and wants. This process of allocation answers three economic questions: 1. What to produce? A society determines the kind and quantity of products it will produce depending on what the consumers want to buy or are willing to pay for. 2. How to produce? A society decides who will produce goods and what process of production will be used. Goods may be produced by corporations, small business-owners, or the government itself. The process of producing goods may be addressed depending on the costs and the availability of resources needed. 3. For whom to produce? This question revolves around the issue of who will benefit from the goods and services produced. This depends on the distribution of wealth in a particular society. Therefore, a consumer who has the capacity to pay for certain goods and services are more likely to benefit than those who cannot afford them. The Economic Systems The answers for above questions are influenced by the structure of a society’s economic system. An economic system is characterized by the type of institution responsible for the management and allocation of resources used in the production of goods and services. Mainly, there are three known economic systems: 1. Market Economic System – is an economic system where all of the economic resources are owned by private entities. 2. Command Economic System – is an economic system where all of the economic resources are owned by the government. 3. Mixed Economic System – is an economic system where all of the economic resources are owned by both private entities and government. Decision Making and Rationality Decision making is an important aspect of economics. It is determining how individuals or group of individuals will behave given certain changes in the economy. Economics use the concept of rationality to predict the actions of people. Rationality is defined as the assumption that individuals are consistent and logical in their decision making, and that they seek an outcome that is most beneficial to them. Economists assumes that individuals make decisions rationally and that it is possible to predict certain behavioral outcomes. The rationality test is one means of illustrating the concept of rationality. For example, if a person prefers mango over banana, and banana over guava, then it is highly likely that he or she prefers mango over guava. Opportunity cost and Trade-off Opportunity cost refers to the cost of giving up an alternative when making a choice. When resources are scarce or limited, consumers are compelled to choose how to manage them efficiently and decide how much of their wants or needs will be satisfied and how much of them will be left unsatisfied. Once the choice is made, you can no longer go back and undo such choice. This is called a trade-off. A trade of occurs when an individual has made a choice, thereby sacrificing all other alternative choices. Page 4 of 6 KORBEL FOUNDATION COLLEGE, INC. . Purok Spring Uno, Brgy. Morales, Koronadal City Contact No. 887-2051 LESSON 2: ECONOMICS AS APPLIED SCIENCE What is applied economics? Applied economics is the application of economic theory and economic tools in realworld situations. The primary concern of applied economics is to address problems and bring about economic development. Economic development as the sustained elevation of an entire society and social system toward a better and more humane life. Development is defined by the following core values: 1. Sustenance refers to ensuring that society is able to provide for basic needs like food, shelter, health, and protection. 2. Self-esteem refers to self-respect, reputation, pride and acknowledgement. 3. Freedom involves providing for a wide variety of choices for societies as well as minimizing external limitations. In the Philippines, NEDA defines economic development based on a framework of inclusive growth, the generation of employment, and reduction of poverty. The eradication of unemployment and poverty is vital in improving the economic conditions of the country and ensuring economic development. Aspects of economic Study and Analysis Economic study and analysis requires the application of certain economic concepts and tools to understand various economic issues and problems. Positive and Normative Economics Positive Economics is a principle in economic analysis which describes what exists and how things work. It strives to give an objective description of state of things. Normative Economics, meanwhile, focuses on the outcome of economic behavior, evaluates and makes judgements, and proposes courses of action. Look at the following examples of positive and normative statements: Positive: “Taxes enable the government to provide services to the people.” Negative: “The government should levy more taxes so it can provide more services to the people.” These two principles are vital tools in studying economics. Economics apply them to come up with conclusions that will be used to design economic policies and theories. Theories and Models A theory is a proposition about certain related variables that explains a certain phenomenon. It proposes a general principles regarding a phenomenon which is deeded possible or scientifically acceptable. Economic theories seek to explain economic phenomena and processes, and often proposes a model. A model is a framework or representation of significant principles and describes how variables are related. Economic models are used by economists to determine the relationships among elements in an economy, apply principles in varied scenarios, me predictions, and propose solutions. Models also provide a means to visualize the variables being analyzed. Models can include graphs, diagrams, or mathematical formulae. Assumptions in economics 1. Rationality 2. Profit maximization 3. Perfect information 4. Ceteris paribus “all things being equal” Page 5 of 6 KORBEL FOUNDATION COLLEGE, INC. . Purok Spring Uno, Brgy. Morales, Koronadal City Contact No. 887-2051 Fallacies in Economics Fallacies refers to errors in judgment or conclusions due to faulty reasoning. The following are some fallacies that are encountered in economic analysis. 1. 2. 3. 4. IV. Failure to hold things constant under ceteris paribus. Post hoc fallacy. Fallacy of composition. Sweeping generalization. ASSESSMENT Answer or discuss the following questions. Answers can be written in Illonggo, Cebuano, Filipino or English Language. 1. Classify your belongings as either needs or wants. List them in the table below and include an explanation why you consider it as needs or wants. (Minimum of five objects) OBJECT CLASSIFICATION EXPLANATION 2. What was the most significant “trade-off” or opportunity cost you have incurred in your life? What lessons have you learned from this experience? ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 3. How can Economics help guide our country toward development? ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ “Huwag ituring na ang pag-aaral ay isang tungkulin, sa halip ito ay isang nakakainggit na oportunidad na matuto” Page 6 of 6