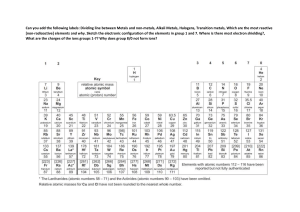
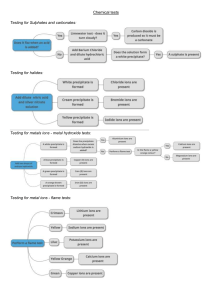
LANDAU SCHOOL ACADEMIC YEAR 2020-2021 SPRING MIDTERM PREPARATION YEAR 6 SCIENCE BIOLOGY Pollination ● Flowering plants use flowers for sexual reproduction. ● Gamete - sex cell. Each pollen grain contains male gamete. ● Pollination - the transfer of pollen from an anther to a stigma. ● Insect - pollinated plants have petals, but wind pollinated do not. ● Ovaries - produce egg cells. ● Cross - pollination - when pollen is transferred from one plant to a different plant of the same species. ● Plants try to avoid self-pollination, because for sexual reproduction characteristics of two different parents are required. Fertilisation and seed dispersal ● Fertilisation - fuse of male gamete with female gamete. ● After the pollen tube has grown fertilisation happens. Egg cell and male gamete join together and their nuclei fuse into one. This forms zygote (fertilised egg cell). ● Seed dispersal - the spreading of seeds away from a parent plant. ● Fleshy fruits (such as tomato and apple) use animals for dispersal. When animals eat fruit, seeds pass through the digestive system. Then seeds are egested by animals in their faeces. Seed coat protects seed. ● Dry fruits use wind, water and explosions to spread their seed. For example: dandelion fruit is spreading its fruits by air. Germination and growth ● Germination - growth of a plant. ● The energy for growth comes from respiration. Below you can see the word equation. glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water ● Germination requires: - water. It is used in many chemical reactions. - warmth. It speeds up reactions. ● Dormant - if something is dormant its life processes are very slow. ● After germination plants make food by photosynthesis. It happens in chloroplasts. Word equation is given: Carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen ● Plant converts glucose into starch, to store it. Oxygen is a byproduct. ● Byproduct - a substance produced by the reaction, that is not the desired product of the reaction. ● Photosynthesis requires energy. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll which traps sunlight energy. ● Plants also need a small amount of mineral salts taken from the soil. Such as magnesium ions( for making chlorophyll), nitrates (for growth) and etc. ● Interdependence - when organisms depend on each other. ● Many plants depend on insects for pollination and the insects depend on the plants for food, such as nectar. They are interdependent. CHEMISTRY Physical Trends ❖ Melting point - the temperature at which solid turns liquid. ➢ Freezing point - the temperature at which liquid turns solid. ➢ Boiling point - the temperature at which liquid becomes gas. ❖ Rows in periodic table are called periods, and columns groups. ❖ Melting point of alkali metals decreases as you go down the group. ● Make sure you know the sequence of alkali metals (Group 1) and noble gases (Group 8). Below are the properties of metals and non-metals. Chemical Trends ● Elements in the same g roup have similar physical properties. For Example alkali metals are all soft with low melting point. Also elements in the same group have similar chemical properties. All the alkali metals must be stored under oil because they react quickly with water and oxygen. ● Look at the word equations below: Metal + water → metal hydroxide + hydrogen Metal + oxygen → metal oxide ● As you go down the group of alkali metals reactivity increases. Lithium is the least reactive metal in Group 1. Potassium Sodium Lithium _____________________________________________________________________________ Metal Properties ❖ Metal properties: ➢ Flexible (malleable and ductile) ➢ Good conductors of heat and insulators ➢ Strong ● We use different metals for a wide range of purposes. For example iron sole is made of metal, because it is a good conductor of heat. We use copper for making wires in electrical circuits, because copper is a good conductor of electricity. ● We decide which metal to use by comparing different criterias, such as cost, appearance and precise properties. ● We can’t use iron for making jewelry, because it reacts with water and air, and as a result rusts. Instead we use gold which is unreactive and stays shiny. ● Most metals react with oxygen and halogens (Group 7) and they produce other compounds. Below you can see examples. Iron + Oxygen → Iron oxide (rust) Zinc + fluorine → zinc fluoride ● Metals also can be used as catalysts. C atalyst is a substance which speeds up reaction PHYSICS Refraction ● Lens - a curved piece of glass or other transparent material that can change the direction of rays of light. Lenses are used everywhere. For example they are used in microscopes to make things look bigger. ● Refraction - change in direction when light goes from one transparent material to another. ● Converging lens - a lens that makes rays of light come together. Cameras and Eyes Colour Coloured light can be made using a filter. A red filter lets red light through, but absorbs all the other colours. We are able to see colours because objects do not reflect all the colours in light: White objects reflect all the colours. A red object only reflects red and all other colours are absorbed. This idea applies to all colours except black. Black objects absorb all colours. Temperature Changes ● Energy produced by the movement of particles is called an i nternal energy. ● Measurement unit for energy is joule. ● Temperature is measured in degrees C elsius (usually).