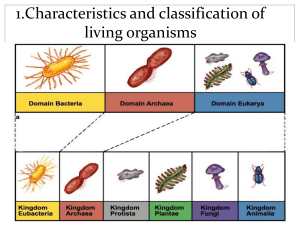
1.Characteristics and classification of living organisms Characteristics of living things 1. Movement 2. Respiration 3.Sensitivity 4. Growth 5. Reproduction Sexual - two sex cells required (sperm and egg) Asexual - only one parent cell is needed 6. Excretion 7. Nutrition Autotrophs - get energy from sun Heterotrophs - get energy by consuming nutrients from their environment Concept and use of a classification system WHY DO WE CLASSIFY THINGS? List some places where organization/ classification takes place What is classification? Classification: arranging organisms into orderly groups based on similar characteristics Taxonomy: the science of describing, naming, and classifying organisms Scientists use both genetic (the DNA makeup of a living thing) and physical evidence (how it looks) to classifying living things. Natural classification The hierarchical classification system described above is based on a natural classification system that uses common features shared by organisms. Natural classification is based on two ideas: • similar structures- (Morphology & anatomy) • evolutionary relationships Early classification Aristotle grouped everything into simple groups such as animals or plants He then grouped animals according to if they had blood or didn’t have blood, and if they had live young or laid eggs, and so on… Therefore Organisms can be classified into groups by the features that they share They were classified based on morphology and anatomy Concerned with the identification and description of the body structures of living things Binomial Nomenclature Developed by Carolus Linnaeus Swedish Biologist 1700’s Two-name system Genus and species named using Latin or Greek words The Binomial System Rules used to write scientific names The scientific name Species: group of individualslook alike, live in same habitat, breed together producing fertile offspring Genus: group of individuals closely related, but cannot interbreed Task Write down the scientific name of the following organisms e.g. • Dog • cat, • Cow • Rat • Monkey • Red rose. Classification systems aim to reflect evolutionary relationships Classification and cladistics Sequence of bases in DNA and of amino acids in proteins is a more accurate means of classification. The organisms may be different morphologically, however, their DNA and amino acid sequences may be similar. e.g mice and humans were found to share virtually the same set of genes after studying their base sequences. However, they are physically different. Cladistics also allows to to determine evolutionary relationship of organisms. By sequencing the DNA and amino acid bases of organism, similar base sequences can be determined. More recent ancestors (more closely related ones) have base sequences that are more similar than those that share only a distant ancestor. From the diagram above: Determine The most recent ancestorsThe distant ancestors- Classification systems aim to reflect evolutionary relationships 1.3 Features of Organisms The modern system of classification has 8 levels: Domain Order Kingdom Family Phylum Genus Class Species Now, let’s play with the words and see if we can think of any rhymes to help us remember each classification word. Kingdom– Phylum – Class – Order – Family – Genus – Species – - King, kings, kids, any k words.... - play, Phillip, party - chess, checkers, cooks, came - on, over - for, fine, fun - glass, great - spaghetti, sets Obviously, different people may come up with different sentences or rhymes that help them. For today, let’s go with: KINGS PLAY CHESS ON FINE GLASS SET Helpful way to remember the 7 levels Kids playing catch on freeways get squashed Or…make up your own… KPCOFGS The five Kingdoms Characteristics of different kingdoms Kingdom Animalia Plantae Fungi Protoctista Prokaryotes Characteristics and Examples Vertebrates Feature 1. Body 2. Habitat 3. Feeding habits 4. Fertilisation 5. Breathing 6. Blood 7. Movement 8. Examples Fish Amphibians Reptiles Birds Mammals Invertebrates-Arthropods Feature 1. Body 2. Habitat 3. Feeding habits 4. Eyes 5. Breathing 6. Movement 7. Examples Fish Amphibians Reptiles Birds Mammals Structure of a virus Scientists do not classify a virus as a living thing. This is because: •it does not show all seven processes for life •when it enters a cell it changes the way a cell works so it can make copies of the virus. Classification of plants M Types of seeds Dicotyledon Monocotyledon Artificial classification-Dichotomous key With artificial classification you can use any grouping you like. You could put all the animals that fly in the same group. This group would then include birds, bats and many insects. You could put all animals that live in water and have streamlined, fish-like bodies in the same group. This group would then include fish and whales. Artificial classification systems are also used as the basis for dichotomous keys that biologists use to identify organisms. A dichotomous key is an organized set of pairs of mutually exclusive characteristics of biological organisms. Taxonomic Key 1a Fruits occur singly ................................................. Go to 3 1b Fruits occur in clusters of two or more ................ Go to 2 2a Fruits are round ................................................... Grapes 2b Fruits are elongate ............................................... Bananas 3a Thick skin that separates easily from flesh .........Oranges 3b Thin skin that adheres to flesh .............................. Go to 4 4a More than one seed per fruit ............................ Apples 4b One seed per fruit ............................................ Go to 5 5a Skin covered with fuzz.................... Peaches 5b Skin smooth, without fuzz........................... Plums What steps would you use to identify an apple?