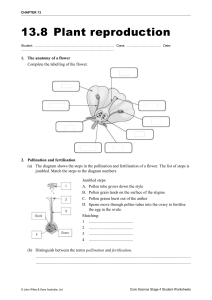
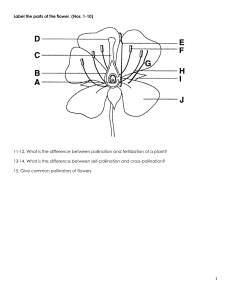
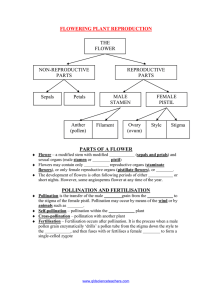
POLLINATION M RS. G. BRYAN OBJECTIVES Define pollination. Distinguish between self-pollination and cross-pollination. Describe the agents of pollination. Describe fertilization and seed production in plants. POLLINATION POLLINATION For reproduction in plants to occur the male sex cells in the pollen must meet the female sex cells inside the ovule. The transfer of pollen from anther to stigma is called pollination. SELF POLLINATION Self pollination is he ability of a plant to pollinate itself without the help of any agent. Pollen is transferred from the anther of a flower to the stigma of the same flower or to another flower on the same plant. CROSS POLLINATION Cross-Pollination occurs when pollen is transferred from the anther of a flower on one plant to the stigma of a flower on another plant. Pollination will only occur if the two plants are from the same species. Self pollination – A and B Cross pollination – C AGENTS OF POLLINATION Pollen is transferred in various ways by: • Animals • Wind • Water ANIMAL POLLINATION Pollination with the help of animals. Brightly coloured petals attract insects for pollination. • Bees • Birds • Bats ANIMAL POLLINATION How it works As animals feed on the nectar inside the flower, the pollen sticks to their legs and body. When the insect moves to a neighbouring flower to feed on more nectar, the pollen is transferred to the stigma. ANIMAL POLLINATION WIND POLLINATION Some plants do not need insects for pollination. Some plants grow long, feathery stamen with lots of light pollen grains. The wind blows the pollen grains to the stigma on the same plant or other plants. WIND POLLINATION WATER POLLINATION The transfer of pollen with the help of water. Aquatic flowering plants release pollen into the water and the water currents move the pollen to other plants. WATER POLLINATION FERTILIZATION Fertilization The fusion of the male and female cells. The fertilized cell produces a seed and the ovary matures into a fruit. The Process of Fertilization The pollen grain lands on the stigma. The pollen grain then grows a pollen tube down the style into the ovary. The male gamete (sperm cells) passes down the tube and into the ovule. Fertilization in a tomato The fertilized ovules become the seeds and the ovary grows to form the fleshy part.