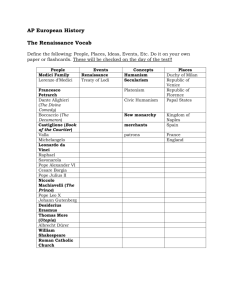
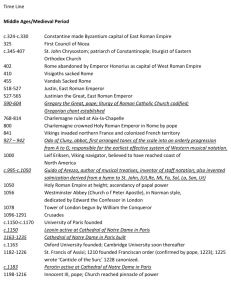
Florence Review Sheet: Test Renaissance- rebirth Quattrocento- Renaissance era in Italian Papacy/Religion Peter- one of twelve apostles, travels to Rome, becomes bishop, popes are from the direct line of Peter, Petrine Doctrine Paul- Jewish, believes in one male god, that is the creator and that all creatures are subordinate to him, does not believe in the gnostic believes, but did believe that Jesus had a closer connection with God, believes that God works through Jesus Rome- age of faith, Christianity, before plague, ruling city Gregory VII- “papacy over secular rulers”, rules of the Pope, pope of excommunicated Henry gave forgiveness after three days in the snow Excommunication- cuts the leader off from the Church and Sacraments, gives the people the power to disobey the leader Great Schism- the Church is split, there are two popes and at one point three popes, Italian and French popes Martin V- once he is elected, the Great Schism ends Savanarola- Bonfire of the Vanities, wanted to make God’s city, damned Lorenzo de Medici on death bed, worked with Charles VIII to gain power in Florence Julius II- pope, commissioned many works of art, Michelangelo, Raphael Politics and Economics Frederick Barbarossa- Germanic king, tries to claim the title of Holy Roman Emperor and unite all of Christianity Holy Roman Empire- tried to get power back into Rome after the fall Battle of Legano- Roman army (Frederick Barbarossa) and the Lombard League (Northern Italy and Pope’s forces), battle to prevent the dominance of Barbarossa over Italy Plague/Black Death- 1347 plague in Messina, went to China on boats, then went to Europe, 1349 Europe is full of plague until 1350, carrier is the flea, explanations were God’s wrath, witchcraft and polluted water by the Jews, ½ of Europes population, 25 million people, consequences is cheap labor is rare, individualism, people leading away from the church, rise of the middle class, revolts from lower class, rise of towns Textiles/wool making- Medici family was first involved in this before banking Banking- Medici’s were in this line, Albizzi, very competitive everyone wants the business, support popes Guilds- a group of people who work in the same occupation, there are regulated goods and prices Giovanni (di Bicci) Medici- godfather of the Medici’s, humble beginnings, bank and wool guild, supported pope, “God’s banker”, supported minuto populo, supported Pirate Cossa who became pope, funded the Ghiberti baptistery doors, gave Cosimo and Lorenzo a good humanist education, believed in civic humanism, loyalty (picked customers), be rich but not too rich, take no more than is legal, be humble, never show pride, avoid the public eye, give back to the city Cosimo de Medici- son of Giovanni, had a large library, Brunelleschi’s patron, commissioned the Dome, humanist, banker, grandfather of Lorenzo, wore cardinal colors, loyalty, exiled by the Albizzi family, build up power with rich foreign families, bribes the government to return, kills and exiles the Albizzi family, civil humanist, supported the minuto populo, tried to unite the Catholic and Orthodox Churches Albizzi family- another banking family, got Cosimo put in prison and exiled, Cosimo came back and killed and exiled the Albizzi family Exile- not able to return to the city/place, in Cosimo’s exile he built his power with his recourses and came back to Florence to regain his power and take out the Albizzi family Lorenzo (“the magnificent”) de Medici- Pericles of Florence, immature at first, then realized responsibilities and became more mature, target of Pazzi Conspiracy, stole money from the public, betrayed the public trust, patron of arts, hosted festivals, supported public buildings, opened doors for people, people paid with whatever they had to get his help, when he got sick he tried to turn to the church, Savonarola backlash Pazzi family/Pazzi Conspiracy- rivals of the Medici family, they gave the loan to the Pope that the Medici’s turned down, went against the Medici’s with plans of murder, pope said it was okay, they went against them during High Mass, planned to stab Lorenzo to death and kill Giuliano his brother, Giuliano died while Lorenzo escapes, all of the conspirators were killed in a gruesome fashion Charles VIII, France- takes over Florence, deals with Savonarola, Piero doesn’t stand up against him Piero de Medici- doesn’t stand up against Charles VIII, fled to Medici palace Lucrezia Borgia- duchess of Ferra, daughter of Cardinal Rodrigo Borgia later Pope Alexander VI, sister of Cesare Borgia, not many talents, engaged many times by her father in order to gain more political power, married Alphonso the duke of Ferra Structure of Florence Republican government- government is public, power isn’t passed down Grandi- rich and noble families, weren’t allowed to have representation in the government Signoria- 9 people, governing body of Florence, in office for two months, six people from the guilds, two from the minor and the last was the Gonfalioniere Gonfalioniere- chairman/spokesperson of the government Quartieri- four quarters of Florence Priori- elected officials that made up the Signoria Minuto Populo- people who weren’t allowed in guilds; weavers, spinners, dyers, boatmen, laborers, peddlers, people who didn’t have a permanent workshop Consiglio del Commune/Consiglio del Populo- 500 members, six month term, from all over Florence, voted on laws but couldn’t enact legislation “The Seventy”- Lorenzo de Medici put these people in the government to be in favor of his ideas Theocracy- government based on religion Ciompi revolt- a revolt to try and increase the power of minor guilds Artists/Thinkers Giotto- created first idea of perspective painting, painter of fresco Fresco- painting on wet plaster Perspective/Vanishing Pt- makes things seem three-dimensional Brunelleschi- architect, Cathedral of Florence, lost contest of baptistery doors, also worked on perspective, made ties with Medici family, genus Donatello- sculptor, worked in Ghiberti’s workshop, made David the 1st free standing nude since Greek and Roman times Masaccio- painter, finished Giotto’s work and created perspective, made “The Healing of the Cripple and the Resurrection of the Tabitha” Leonardo da Vinci- painter, inventor, architect, weapons designer, military engineer Michelangelo- painter, sculptor, Sistine chapel, David Raphael- painter, School of Athens, La Disputa, Madonna and the Gold Finch Botticelli- painter, Birth of Venus, Prima Verra Ghiberti- goldsmith, bronze doors for the baptistery Machiavelli- wrote The Prince, taught about a powerful way to rule, not necessarily the moral way, wrote a lot about politics My Vocab Vernacular- writing in your own land’s language Romanesque- huge doors, colored walls, round arches, heavy roofs pressing on thick walls, thick pillars Gothic- designed to be towards God and light and Heaven Flying buttress- helped support church, brought weight outwards Canon law- law of the Church Tithe- tax by the Church, ¼ to sick and poor Heresy- groups that had differing opinions on religion, sometimes whole villages were killed Simony- buying and selling church offices? Lay investiture- appointment of church officials by rulers not the church Fallow- a field that was not farmed that year Three field system- one field was fallow, one was winter and one was summer Burgher- people who lived in walled towns Bourgeoisie- burgh dwellers in France Church Christianity- higher power on earth (rituals, traditions, priests and sacraments), extensive influence over all types of Christianity Biblical Christianity- higher power in the Bible, came from Church Christianity Christendom- a Christian society that was ruled by the pope and the Church and protected by leaders who respected the Roman Empire Top down Evangelization- the spread of Christianity from the top down, for example a ruler would convert, then his household would convert and so on until churches would appear in the land Gospels- “good news”, written information about Jesus, propaganda aiming to hold up a certain glorified view of who/what is described Canonical- “New Testament”, gospels of Mathew, Mark, Luke and John, earlier writing, authoritative Apocryphal- Gospel of Thomas, not as important as canonical gospels, any Christian group could write these, later writings, being of questionable authenticity Renaissance Values Individualism: Economic vs. feudal inheritance Self-expression Self-promotion Free will, free thought Materialism- care about items/objects, show wealth through attainable things Humanism: Human beings are worth study Roman, Greek thought Civic Humanism Secularism- people moving away from the church Analytical Paragraphs: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Rise and Fall- the end of the plague, people wanted a change to their lives, “to live a little”, the fall was that Lorenzo dies, Piero gets money but leaves when Charles VIII comes, Savonarola has the Bonfire of the Vanities, symbolizes the end of luxuries and Renaissance ideas Geography Economic Development- guilds, banking Technological Change- innovations by artists Gender- still bound by marriage, prosperity changed the lives of women, servants could do house hold jobs, women are now depicted realistically in paintings, though supposed to be look down upon, they were more equals than before Politics church vs. people, foreign powers Ideas- individualism, celebration of worldly pleasures, humanism, secularism Creative Arts- many innovations by Renaissance artists