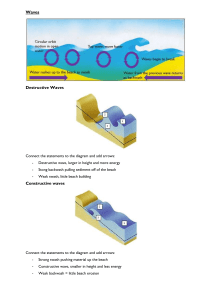
CONNECT Be READY TO LEARN Start thinking like a Geographer Make sure you have your book, write today’s date and title. Types of Waves GET THINKING! What’s going on in the photograph? Should we be concerned? Why might we be concerned? Do things change at this location? Do those waves do anything to the coastal environment? LO: To explore constructive and destructive waves and their characteristics. Be READY TO LEARN ACTIVATE Think like a Geographer Write the Learning Objective. LO: To explore constructive and destructive waves and their characteristics. SUCCESS CRITERIA: • I can describe how a wave forms and what happens as it approaches the coast. • I can draw diagrams of constructive and destructive waves. • I can compare the characteristics of constructive and destructive waves. Types of Waves ACTIVATE Be READY TO LEARN Think like a Geographer Teach each other. • First, you must complete the part of your worksheet that relates to your activate card. (5 minutes) • Then, you teach each other and complete remainder of your worksheet. (5 minutes) • A teaches B how waves form. • B teaches A what happens when waves reach the coast. LO: To explore constructive and destructive waves and their characteristics. ACTIVATE Be READY TO LEARN Think like a Geographer How do waves form? • Waves form when the wind blows over the sea. Friction with the surface of the water causes small ripples in the water, which develop in to waves. The distance the wind blows across the water is called the fetch. The longer the fetch, the more powerful the wave. • Waves can also be formed when earthquakes and volcanic eruptions shake the seabed. These waves are known as tsunami waves. LO: To explore constructive and destructive waves and their characteristics. ACTIVATE Be READY TO LEARN Think like a Geographer What happens when the waves reach the coast? • Despite the relatively wavy surface in the open sea, there is little horizontal movement of water. This only occurs when the waves break and surge up the beach as they approach the shore. • As the water gets shallower, the seabed interrupts the circular motion of the water making the waves more elliptical. This causes the crest of the wave to rise up and eventually collapse onto the beach. The water that rushes up the beach is called the swash and the water that flows back towards the sea is called the backwash. LO: To explore constructive and destructive waves and their characteristics. ACTIVATE Be READY TO LEARN Think like a Geographer Question Time What is need for a ripple to form and develop into a wave? A) Wind B) Hot air C) Distance What does fetch mean? A) The movement of water up the beach B) The distance the wind blows across the water C) Shallow water interrupting circular motion of waves. Which statement is true? A) The longer the fetch, the more powerful the wave. B) The shorter the fetch, the more powerful the wave. LO: To explore constructive and destructive waves and their characteristics. Be READY TO LEARN DEMONSTRATE What are the types of waves? Draw two diagrams in your book; one to show constructive waves and another to show destructive waves. You may use p93 in the text book or the diagrams on this slide. Think like a Geographer Constructive Wave Destructive Wave LO: To explore constructive and destructive waves and their characteristics. Be READY TO LEARN DEMONSTRATE Think like a Geographer Glue the table into your books and use your diagrams to compare the characteristics of constructive and destructive waves. Wave Characteristic Constructive Wave Destructive Wave Wave height Wave length Wave Frequency Type of wave break (spilling or plunging) Strength of Swash Strength of backwash Net beach sediment (gain or less) LO: To explore constructive and destructive waves and their characteristics. Be READY TO LEARN CONSOLIDATE Think like a Geographer Write the Learning Objective. Compare the characteristics of constructive and destructive waves (4 marks). SUCCESS CRITERIA: FOR FULL MARKS (4) Must give characteristics of both constructive and destructive waves. Must use comparative languages (whereas, however, in contrast, compared with) MAXIMUM OF (2) MARKS IF: No comparative language has been used. Only given characteristics of one type of wave. MODEL ANSWER: Destructive waves have a greater backwash than swash (1) compared to constructive waves due to their higher energy (1) meaning that they can erode beaches (1). Constructive waves have a lower frequency (1) as a result of their longer wavelength (1) Destructive waves are plunging whereas constructive are surging (1). Destructive waves are higher (>1m) compared with constructive (1). LO: To explore constructive and destructive waves and their characteristics.