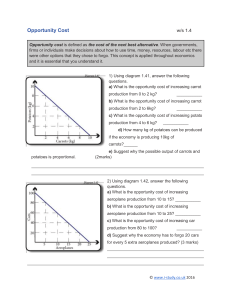
Opportunity Cost w/s 1.4 Opportunity cost is defined as the cost of the next best alternative. When governments, firms or individuals make decisions about how to use time, money, resources, labour etc there were other options that they chose to forgo. This concept is applied throughout economics and it is essential that you understand it. 1) Using diagram 1.41, answer the following questions. a) What is the opportunity cost of increasing carrot production from 0 to 2 kg? ___________ b) What is the opportunity cost of increasing carrot production from 2 to 6kg? ___________ c) What is the opportunity cost of increasing potato production from 4 to 6 kg? ___________ d) How many kg of potatoes can be produced if the economy is producing 10kg of carrots?______ potatoes is proportional. e) Suggest why the possible output of carrots and (2marks) 2) Using diagram 1.42, answer the following questions. a) What is the opportunity cost of increasing aeroplane production from 10 to 15? ___________ b) What is the opportunity cost of increasing aeroplane production from 10 to 25? ___________ c) What is the opportunity cost of increasing car production from 80 to 100? ___________ d) Suggest why the economy has to forgo 20 cars for every 5 extra aeroplanes produced? (3 marks) © www.i-study.co.uk 2016 3) A government decides to increase its spending on healthcare. Define opportunity cost and state how it applies to this decision. (4 marks) 4) Choosing to study IGCSE Economics has an opportunity cost. Explain this statement. (2 marks) © www.i-study.co.uk 2016