International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD)
Volume 4 Issue 6, September-October 2020 Available Online: www.ijtsrd.com e-ISSN: 2456 – 6470
Performance Analysis of Sensor Node Energy in
Wireless Sensor Networks: A Perspective Analysis
Pramod Gujre1, Prof. Avinash Sharma2
1PG
Scholar, 2Head and Associate Professor,
1,2Department of CSE, MITS, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, India
How to cite this paper: Pramod Gujre |
Prof. Avinash Sharma "Performance
Analysis of Sensor Node Energy in
Wireless Sensor Networks: A Perspective
Analysis" Published
in
International
Journal of Trend in
Scientific Research
and
Development
(ijtsrd), ISSN: 24566470, Volume-4 |
IJTSRD33681
Issue-6,
October
2020,
pp.1308-1312,
URL:
www.ijtsrd.com/papers/ijtsrd33681.pdf
ABSTRACT
Theoretical In the previous many years, Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) has
become a wide territory of exploration. In WSN, various sensor hubs are
arbitrarily arrangement with various energy level. Energy goes about as force
source and is accessible to every sensor hub in restricted amount. The
restricting element is that sensor hubs are energy compelled and reviving or
supplanting battery is exorbitant and complex cycle. This paper investigates
the distinctive energy utilization factors which impact the lifetime and
execution of the WSN's. The primary variables which impact the energy
utilization in WSN's are versatility, load adjusting, dependability,
correspondence, crash, over-hearing, ideal posting and inactivity. Specialists
have demonstrated that the hub close to sink hub release fastly. Aside from
these, a large portion of the energy is expended during the exchange of
information from sender to recipient. In this paper exertion is made to dissect
the impact of various variables on energy utilization in WSN's.
Copyright © 2020 by author(s) and
International Journal of Trend in Scientific
Research and Development Journal. This
is an Open Access article distributed
under the terms of
the
Creative
Commons Attribution
License
(CC
BY
4.0)
KEYWORDS: Wireless Sensor Networks, Energy efficiency, Scalability, Load
balancing, Reliability, Over-hearing, Latency
(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0)
I.
INTRODUCTION
Remote Sensor Networks(WSN's) is an organization
comprising of various sensor hubs. A sensor node(SN) is a
multifunctional, low-force and ease minuscule size gadget.
SNs are arbitrarily conveyed over a zone to gauge different
marvels like stickiness, dampness, vibrations and some more.
By improving the capacities of sensor hubs, acknowledgment
of WSNs dependent on the synergistic exertion of sensor
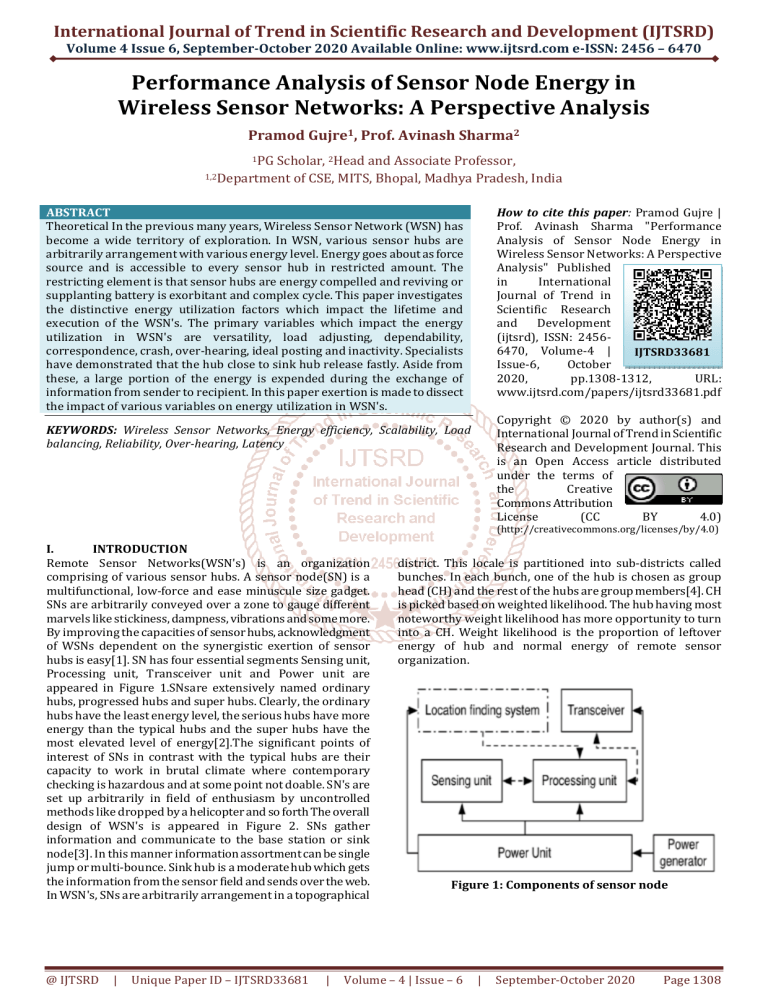
hubs is easy[1]. SN has four essential segments Sensing unit,
Processing unit, Transceiver unit and Power unit are
appeared in Figure 1.SNsare extensively named ordinary
hubs, progressed hubs and super hubs. Clearly, the ordinary
hubs have the least energy level, the serious hubs have more
energy than the typical hubs and the super hubs have the
most elevated level of energy[2].The significant points of
interest of SNs in contrast with the typical hubs are their
capacity to work in brutal climate where contemporary
checking is hazardous and at some point not doable. SN's are
set up arbitrarily in field of enthusiasm by uncontrolled
methods like dropped by a helicopter and so forth The overall
design of WSN's is appeared in Figure 2. SNs gather
information and communicate to the base station or sink
node[3]. In this manner information assortment can be single
jump or multi-bounce. Sink hub is a moderate hub which gets
the information from the sensor field and sends over the web.
In WSN's, SNs are arbitrarily arrangement in a topographical
@ IJTSRD
|
Unique Paper ID – IJTSRD33681
|
district. This locale is partitioned into sub-districts called
bunches. In each bunch, one of the hub is chosen as group
head (CH) and the rest of the hubs are group members[4]. CH
is picked based on weighted likelihood. The hub having most
noteworthy weight likelihood has more opportunity to turn
into a CH. Weight likelihood is the proportion of leftover
energy of hub and normal energy of remote sensor
organization.
Figure 1: Components of sensor node
Volume – 4 | Issue – 6
|
September-October 2020
Page 1308
International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD) @ www.ijtsrd.com eISSN: 2456-6470
channel quality pointer for the multi-jump between bunch
information transmission. Finally, an inconsistent group size
procedure dependent on bunch head leftover energy and
good ways from the base station is used. This strategy
adjusts the energy among groups and keeps away from early
organization apportioning. This work further presents the
investigative execution model for energy utilization and
postponement of the proposed correspondence system. The
exhibition estimates utilized for assessment are energy
utilization, postponement, and organization lifetime. The
outcomes demonstrate that joining directing and MAC plans
preserves energy better than using MAC conspire
alone.(Maria Sefuba, Tom Walingo; 2018)
Figure 2: WSN’s architecture
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows. Areas II
presents the connected work on different parts of energy the
executives in WSNs. Conversation of different energy
utilization conventions is done in area III and Section IV
closes the paper.
II.
RELATED WORK
Web of thing (IoT) isn't just a promising exploration theme
yet in addition a sprouting mechanical pattern. Despite the
fact that the essential thought is to bring things or articles
into the Internet, there are different methodologies on the
grounds that an IoT framework is exceptionally application
situated. Notwithstanding the plan of a tweaked equipment
for range expansion, another synchronization conspire and a
burst transmission highlight are additionally introduced to
support the organization limit and diminish the energy
squander. Accordingly, the proposed stage can satisfy the
high throughput necessity for high-rate applications and the
prerequisite of long battery life for low-rate applications
simultaneously. We have built up a proving ground in our
grounds to approve the proposed system.(Yaw-Wen Kuo,
Cho-Long Li, Jheng-Han Jhang and Sam Lin; 2020)
In remote sensors organizations, the sensor hubs are thickly
sent. Attributable to this inordinate arrangement of sensor
hubs, each target is secured by different sensors all at once.
To drag out the organization lifetime, the creators can plan
the sensor action so that lone a subset of sensor hubs, called
spread set, is sufficiently adequate to cover all the objectives.
In this examination, they propose an energy-effective
planning calculation dependent on learning automata for
target inclusion issue. The learning automata-based method
encourages a sensor hub to choose its fitting state (either
dynamic or rest). To demonstrate the adequacy of their
proposed booking strategy, they lead a definite arrangement
of recreations and contrast the exhibition of their calculation
and the current algorithms.(Manju, Satish Chand, Bijender
Kumar; 2018)
This work presents a consolidated energy-effective medium
access control (MAC) and directing convention for huge
scope remote sensor networks that plans to limit energy
utilization and draw out the organization lifetime. The
proposed correspondence structure utilizes the
accompanying measures to improve the organization energy
productivity. Initially, it gives a versatile intra-bunch
timetable to referee media access of sensor hubs inside a
group, limiting inactive tuning in on sensor hubs, prompting
improved energy execution. Furthermore, it proposes an onrequest source cross-layer steering convention guaranteeing
choice of best courses dependent on energy level and
@ IJTSRD
|
Unique Paper ID – IJTSRD33681
|
3-pivot accelerometer is a broadly embraced gadget for
applications, for example, fall identification of the older folks,
kinematic investigation, building/connect/avalanche
checking, etc. To recover the detecting information
progressively, one may utilize a remote module to advance
those information to a door or worker. For outside
applications, Zigbee/IEEE 802.15.4 innovation is frequently
the competitor since it is financially savvy and simple to be
bought in the market. Be that as it may, transmission range,
energy utilization and organization limit are key elements in
planning an outside framework. (Yaw-Wen Kuo and ChoLong Li; 2017).
Time-synchronized channel jumping (TSCH) is right now the
most productive answer for crash free, obstruction staying
away from correspondences in specially appointed remote
organizations, for example, remote sensor organizations,
vehicular organizations, and organizations of robots or
automatons. Notwithstanding, all variations of TSCH require
some type of brought together coordination to keep up the
time-recurrence opening instrument. This prompts
moderate intermingling to consistent state and moderate
time-recurrence space usage, particularly under hub agitate
or versatility. We propose decentralized timesynchronized
channel trading (DT-SCS), a novel convention for medium
access control (MAC) in specially appointed remote
organizations. Under the proposed convention, hubs initially
unite to simultaneous guide bundle transmissions over all
accessible channels at the physical layer, with adjusted
number of hubs in each channel. (George Smart, Nikos
Deligiannis, Rosario Surace, Valeria Loscri, Giancarlo Fortino
and Yiannis Andreopoulos; 2016).
We have seen the Fixed Internet developing with practically
every PC being associated today; we are at present seeing
the rise of the Mobile Internet with the exponential blast of
advanced cells, tablets and net-books. Nonetheless, both will
be predominated by the foreseen development of the
Internet of Things (IoT), where ordinary articles can
interface with the Internet, tweet or be questioned. While
the effect onto economies and social orders the world over is
undisputed, the advances encouraging such a pervasive
network have battled up until now and as of late started to
come to fruition. To this end, this paper presents in an
opportune way the foundations of an in fact and industrially
reasonable IoT which remembers a definite conversation for
the specific norm of decision at every convention layer. This
stack is appeared to meet the significant measures of
intensity effectiveness, dependability and Internet network.
Modern applications have been the early adopters of this
stack, which has become the true norm, accordingly
Volume – 4 | Issue – 6
|
September-October 2020
Page 1309
International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD) @ www.ijtsrd.com eISSN: 2456-6470
bootstraping early IoT improvements. Certified all through
this paper and by rising industry partnerships, we accept
that a normalized approach, utilizing most recent
improvements in the IEEE 802.15.4 and IETF working
gatherings, is the main path forward. (Maria Rita Palattella,
Nicola Accettura, Xavier Vilajosana, Thomas Watteyne, Luigi
Alfredo Grieco, Gennaro Boggia and Mischa Dohler; 2016)
The principle worry in Wireless Sensor Networks is the way
to deal with their restricted energy assets. The exhibition of
Wireless Sensor Networks firmly relies upon their lifetime.
Therefore, Dynamic Power Management approaches with
the end goal of decrease of energy utilization in sensor hubs,
after organization and planning of the organization. As of
late, there have been a solid enthusiasm to utilize clever
instruments particularly Neural Networks in energy
proficient methodologies of Wireless Sensor Networks,
because of their straightforward equal circulated calculation,
dispersed capacity, information power, auto characterization
of sensor hubs and sensor perusing. This paper presents
another brought together versatile Energy Based Clustering
convention through the use of Self sorting out guide neural
organizations (called EBC-S) which can bunch sensor hubs,
in light of multi boundaries; energy level and arranges of
sensor hubs. We applied some greatest energy hubs as loads
of SOM map units; so the hubs with higher energy draw in
the closest hubs with lower energy levels. Thusly, framed
bunches may not really contain contiguous hubs. The new
calculation empowers us to frame energy adjusted bunches
and similarly disperse energy utilization. Recreation results
and correlation with past conventions( LEACH and LEA2C)
demonstrate that our new calculation can broaden the
lifetime of the network.(Mohammad Ali Azimi kashani and
Hassan Ziafat; 2016)
The expanding multifaceted nature of Wireless Sensor
Networks (WSNs) is driving towards the arrangement of
complex organized frameworks and the ideal plan of WSNs
can be an exceptionally troublesome errand in light of the
fact that few imperatives and prerequisites must be thought
of, among all the force utilization. This paper proposes a
novel fluffy rationale based instrument that as indicated by
the battery level and to the proportion of Throughput to
Workload decides the dozing season of sensor gadgets in a
Wireless Sensor Network for natural observing dependent
on the IEEE 802.15.4 convention. The primary point here is
to locate a compelling arrangement that accomplishes the
objective while dodging complex and computationally costly
arrangements, which would not be proper for the current
issue and would disable the down to earth appropriateness
of the methodology in genuine situations. The aftereffects of
a few genuine proving ground situations show that the
proposed framework beats different arrangements,
essentially diminishing the entire force utilization while
keeping up great execution as far as the proportion of
throughput to outstanding burden. An execution on off-therack gadgets demonstrates that the proposed regulator
doesn't need ground-breaking equipment and can be
effortlessly actualized on an ease gadget, accordingly
preparing for broad use in practice.(Giovanni Pau, "Force
Consumption Reduction for Wireless Sensor Networks Using
A Fuzzy Approach", International Journal of Engineering and
Technology Innovation, vol. 6, no. 1, 2016)
@ IJTSRD
|
Unique Paper ID – IJTSRD33681
|
Energy the board in Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) is of
fundamental significance for the distantly conveyed energy
rigid sensor hubs. These hubs are ordinarily controlled by
appended batteries. A few battery-driven energy
preservation plans are proposed to guarantee energy
productive organization activity. The limitations related to
the restricted battery limit moved the examination pattern
towards discovering substitute sources by reaping
surrounding energy. This study presents an elevated level
scientific classification of energy the board in WSNs. We
examine distinctive battery-driven energy utilization based
plans and energy gathering based energy arrangement plans.
We likewise feature the ongoing achievement of remote
energy transaction to a sensor hub as an option in contrast
to average batteries. We suggest consider late energy
provisioning progressions in corresponding with the
conventional energy preservation approaches for a sensor
organization
while
planning
energy
effective
schemes.(Junaid Ahmed Khan, Hassaan Khaliq Qureshi and
Adnan Iqbal, "Energy the executives in Wireless Sensor
Networks: A study", https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal01283728, 2015)
III.
DISCUSSION
Different conventions examined in segment II are
investigated and their results/technique are introduced in
even structure as appeared in table I. WSN approaches talked
about in area II have been arranged into three fundamental
catagories: information driven directing convention, various
leveled conventions and collection based conventions. In the
field of WSN's, LEACH convention tackles the issue of energy
utilization due turn of group heads in arrangement period of
bunch formation[4]. In LEACH, information gathering issue
created doesn't arrive at an ideal arrangement. PEGASIS
convention was produced for tackling information gathering
issue. The central issue of PEGASIS is to make chain to closest
sensor hub with the goal that every hub can get and
communicate information to nearest SN[5]. PEGASIS gives
better execution in contrast with LEACH. In both LEACH and
PEGASIS network test systems are utilized to gauge the
proficiency of WSN's. Drain doesn't have the information
driven directing capacity. Another convention called REEP
was created for solid and energy productive information
driven routing[6]. In information driven directing, the BS
sends questions to specific districts and sits tight for
information from sent sensors, subsequently information is
gathered through inquiries. EEHCA was created to beat the
issue of burden adjusting. EEHCA is a various leveled and
information conglomeration based WSN convention. EEHCA
expanded the WSN's lifetime with the assistance of
reinforcement bunch heads. In EEHCA on the off chance that
the essential CH is exhausted of all its energy, at that point
auxiliary CH deals with the heap. EEHC was created for
energy productivity amplification based on weighted political
decision likelihood of their lingering energy.To satisfy the
goal of energy proficient and load adjusting plan, a
methodology called S-EECP and M-EECP was created. In SEECP the single bounce correspondence is set up inside the
groups between non-CHs and CHs while multi-jump
correspondence is set up among CHs and BS by M-EECP[10].
The most recent convention for accomplishing the portability
and diminishing the postponement in transmission of
information is VELCT. VELCT build the DCT dependent on
group head area which helps in diminishing the start to finish
postponement of organization.
Volume – 4 | Issue – 6
|
September-October 2020
Page 1310
International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD) @ www.ijtsrd.com eISSN: 2456-6470
Table 1: Comparative analysis of different algorithms and protocol
Further inside and out investigation the impact of various boundary, for example, load adjusting, dependability, ideal tuning in
and dormancy in information transmission. The principal factor, load adjusting is the appropriation of energy load all through
the WSN's for augmenting the organization lifetime. The essential target of convention recorded in Table 2 is adjusting the
energy load and giving a dependable correspondence between SNs[9]. Dependability implies convention is working as per their
usefulness or particular with no disappointment. Ideal-listening happens when a hub isn't getting any message yet at the same
time in a functioning state for approaching messages, consequently the energy is expended. So as to decrease the energy
utilization because of inert tuning in WSN a convention called Sparse Topology and Energy Management (STEM) has been
created. STEM effectively awakens hubs from a rest state to dynamic state when there is any message to get. Anyway the hubs
don't experience the ill effects of inert tuning in. Dormancy implies delay in parcel transmission; thus more energy is expended if
bundle takes a long course. REEP, S-EECP, M-EECP and VLECT convention endure with issue of ideal-tuning in.
Table 2: Effect of various techniques over selected parameters
@ IJTSRD
|
Unique Paper ID – IJTSRD33681
|
Volume – 4 | Issue – 6
|
September-October 2020
Page 1311
International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD) @ www.ijtsrd.com eISSN: 2456-6470
On examination of WSN conventions we have discovered some exploration expands. In EEHCA the information transmission
capacity and entomb group correspondence can be improved. The REEP convention has been intended for static hubs just so it
can likewise be plan for versatile hub which will supportive for following moving gadgets. In REEP loads of energy is squander
when the hub in dynamic mode so it's likewise plan for rest or dynamic mode activity for sparing energy and lifetime of WSN is
increments.
Another fascinating issue with regards to energy utilization conventions is the determination of bunch head among accessible
sensor hubs. A bunch head perform information collection and transmition to BS. Numerous scientists have been done in WSNs
to manufacture advanced bunches with proficient and dependable information assortment procedures, yet at the same time
there are research holes in group development and CH choice. The majority of the convention accepts that sink hub is fixed.
Anyway there are a few circumstances where the sink hub is versatile like a war zone where the data of foe and war vessels
current area are often communicated to the control rooms consequently the sensors energy depletes quickly. So new
conventions are required for dealing with the adjustments in geography and portability overhead.
IV.
CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORKS
At present, WSNs is a rising exploration territory. In this
paper we have summed up the WSNs conventions and
proposed a near report dependent on the information driven
directing, progressive and conglomeration based convention.
Besides, the convention is ordered dependent on the energy
utilization factors like dormancy, load adjusting and energy
effectiveness. Albeit a large number of WSN convention look
encouraging yet there are numerous provokes that should be
unraveled in WSNs. We feature those difficulties and bringing
up future examination toward the path to take care of energy
utilization issue to be understood in WSNs. We feature those
difficulties and calling attention to future exploration toward
the path to tackle energy utilization issue.
REFERENCES
[1] Yaw-Wen Kuo, Cho-Long Li, Jheng-Han Jhang and Sam
Lin, “Design of a wireless sensor network based IoT
platform for wide area and heterogeneous
applications”, IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018.
[2]
[3]
Manju, Satish Chand, Bijender Kumar, “Target
coverage heuristic based on learning automata in
wireless sensor networks”, IET Wirel. Sens. Syst.,
2018.
Maria Sefuba, Tom Walingo, “Energy-efficient
medium access control and routing protocol for
multihop wireless sensor networks”, IET Wireless
Sensor Systems, 2018.
[4]
Yaw-Wen Kuo and Cho-Long Li, “Design of a long
range wireless 3-axis accelerometer module for
environmental monitoring”, IEEE Journal of WSN,
2017.
[5]
Arvind Kumar, Damanpreet Singh, “Importance of
Energy in Wireless Sensor Networks: A Survey”, An
International Journal of Engineering Sciences, Vol. 17,
2016.
[6]
George Smart, Nikos Deligiannis, Rosario Surace,
Valeria Loscri, Giancarlo Fortino and Yiannis
Andreopoulos, “Decentralized Time-Synchronized
Channel Swapping for Ad Hoc Wireless Networks”,
IEEE Transaction of Wireless Network, 2016.
[7]
Maria Rita Palattella, Nicola Accettura, Xavier
Vilajosana, Thomas Watteyne, Luigi Alfredo Grieco,
@ IJTSRD
|
Unique Paper ID – IJTSRD33681
|
Gennaro Boggia and Mischa Dohler, “Standardized
Protocol Stack For The Internet Of (Important)
Things”, IEEE Conference of IoT, 2016.
[8]
Mohammad Ali Azimi kashani and Hassan Ziafat, “A
method for Reduction of Energy Consumption in
Wireless Sensor Network with using Neural
Networks”, IEEE Conference of Wireless Sensor
Network, 2016.
[9]
Giovanni Pau, “Power Consumption Reduction for
Wireless Sensor Networks Using A Fuzzy Approach”,
International Journal of Engineering and Technology
Innovation, vol. 6, no. 1, 2016.
[10]
Junaid Ahmed Khan, Hassaan Khaliq Qureshi and
Adnan Iqbal “Energy management in Wireless Sensor
Networks:
A
survey”,
https://hal.archivesouvertes.fr/hal-01283728, 2015.
[11]
Keshav Sood, Shui Yu and Yong Xiang, “Software
Defined Wireless Networking Opportunities and
Challenges for Internet of Things: A Review”, IEEE
internet of things journal, 2015.
[12]
Ala Al-Fuqaha, Mohsen Guizani, Mehdi Mohammadi,
Mohammed Aledhari and Moussa Ayyash, “Internet of
Things: A Survey on Enabling Technologies, Protocols,
and Applications”, IEEE communication surveys &
tutorials, vol. 17, no. 4, fourth quarter 2015.
[13]
Antonio Guerrieri, Giancarlo Fortino and Wilma
Russo, “An Evaluation Framework for Buildingsoriented Wireless Sensor Networks”, 14th IEEE/ACM
International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Grid
Computing, 2014.
[14]
B. Molina, C. E. Palau, G. Fortino, A. Guerrieri, C.
Savaglio, “Empowering smart cities through
interoperable Sensor Network Enablers”, IEEE
International Conference on Systems, Man, and
Cybernetics, 2014.
[15]
Mihai T. Lazarescu, “Design of a WSN Platform for
Long-Term Environmental Monitoring for IoT
Applications”, IEEE journal on emerging and selected
topics in circuits and systems, vol. 3, no. 1, march
2013.
Volume – 4 | Issue – 6
|
September-October 2020
Page 1312




