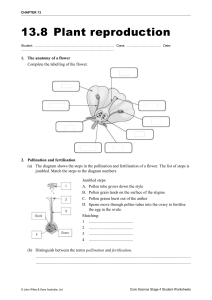
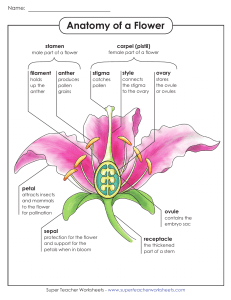
Remember that the flower has both male and female parts. Lets revise what the different parts are called. The Carpel The female part of the flower is called the Carpel. The Stamen The male parts of the flower are called Stamens. Now lets look more closely at the Stamens (male parts). Anther The top of the Stamen is called the Anther. Filament The Filament acts in the same way as a stem and holds up the Anther. What is the yellow powder on the Anther? Now lets look more closely at the Carpel (female parts). Stigma The top of the Carpel is called the Stigma. What do you notice when you touch it? Style The Style acts in the same way as a stem and holds up the Stigma. Ovary The ovary contains the eggs. Learning Objectives To understand how new seeds are formed. To understand the terms pollination and fertilisation. With your talk partner discuss what you think the term pollination might mean? Pollination occurs when the pollen from the anther (male part) is transferred onto the stigma (female part) pollen What do you remember about the stigma? stigma With your talk partner discuss ways in which the pollen might be moved from the anther to the stigma? Pollen sticks to insects and as they move around the pollen sticks to the stigma. How do flowers ensure that insects land on them? Flowers are scented and have attractive petals to attract insects. During windy days the pollen ay get blown from the anther to the stigma. What happens next? The style is hollow so the pollen travels down into the ovary (female part) where it mixes with the eggs to produce new seeds. pollen seed stigma eggs When the pollen mixes with the eggs to produce a new seed this process is called Fertilisation. Your Task Draw the diagram in your book Label the important parts in Pollination and Fertilisation Explain what is happening at each of the five stages 1 2 3 4 5