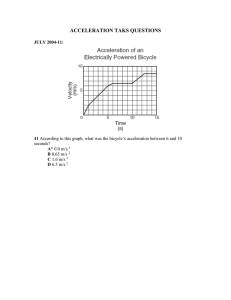
Describing motion Displacement is distance moved in a specific direction 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Steady speed Steady speed Stationary Decreasing speed Increasing speed Stationary Note: gradient of a distance time graph gives you the speed 1. Constant acceleration 2. Constant deceleration 3. Steady speed 4. Decreasing acceleration 5. Increasing acceleration 6. Stationary Note: Gradient of a velocity time graph gives you the acceleration Speed-time graphs To get the distance covered from a velocity-time graph we calculate the area under the graph. Common shapes include rectangle, triangle and trapezium. Area of rectangle = Area of triangle = Area of a trapezium = For curved graphs we use the method of counting the squares to estimate the distance covered. Calculate the deceleration of the vehicle Deceleration = ………………………….………………………. [2] a) Calculate the total distance covered by the vehicle. b) Find the average speed of the car. VECTORS AND SCALARS Vector quantities are described by magnitude and direction Scalar quantities have only magnitude. List five vector quantities you know RESULTANT OF A VECTOR Vector addition Parallelogram law (scale drawing) List five scalar quantities you know Force is a pull or push. Measured in newton using a force meter Forces can cause things to change shape, volume, direction of motion, speed or state of motion. Newton’s laws of motion Example: A body of mass 5kg is acted upon by a force and its speed increases from 10m/s to 30m/s in 4s. calculate the resultant force acting on the body. FALLING OBJECTS Bodies experiencing free fall have acceleration due to gravity. Downwards this value is 10m/s2 on earth and upwards it has a value of -10m/s2. Terminal speed = 40m/s At terminal velocity, the air resistance equals to the weight meaning resultant force equals zero. From A to B the body is having a decreasing acceleration At point B a parachute is opened and the air resistance is greater than the weight which makes the body to decelerate downwards. The new terminal speed is 5m/s and at that speed the air resistance and the weight are once again equal. MOVING IN CIRCLES When an object is moving in a circular track, a force directed towards the centre of the path keeps it in the track. This force is the centripetal force. Speed is constant Velocity is changing –observe the direction changing The centripetal force is the resultant force Acceleration is directed towards the centre of the path. The centripetal force is given by the relation Mean it is proportional to the square of the velocity and the mass The force is also inversely proportional to the radius of the orbit. Momentum and collision Momentum is the product of mass and velocity Unit: kgm/s and it’s a vector quantity. HOOKE’S LAW It states that the extension in a spring is directly proportional to the force provided the elastic limit of the spring is not exceeded. Extension force Where F = force/load force constant X= extension where new length original length The point where the spring stops to obey Hooke’s law is the proportional limit or elastic limit. A. Springs are connected in series. The total extension is the sum of the extensions B. Springs connected in parallel. The total extension is found by Question A spring of length 12cm is loaded with a load of 15N and its length increases to 12.5cm. a) Calculate the force constant of the spring b) Find the new length if the spring is loaded with a force of 17.5N c) What force will stretch the spring to a new length of 14.8cm? State any assumption you made. THE LAW OF MOMENTS It states that the sum of clockwise moments about a point is equal to the sum of anticlockwise moments about the same point. Clockwise moments = Anticlockwise moments = ) For equilibrium the following two conditions must be satisfied 1. Resultant moment must be equal to zero. (clockwise moments is equal to the anticlockwise 2. The resultant force must be equal to zero. ( sum of upward forces = sum of downward forces) There are three types of equilibrium: stable, unstable, and neutral Stable equilibrium- object returns to its original shape after slight displacement Unstable equilibrium- object moves away from its original position after slight displacement Neutral equilibrium- object is independent of displacements from its original position. Write brief notes on the following types of forces a) Gravity force b) Electrostatic force c) Magnetic force d) Centripetal force e) Friction force f) Tension forces g) Compression forces PRESSURE Is the force acting normally per unit area Unit = Pascal (Pa) 1Pa = 1N/m2 Generally, REMEMBER: FORCE =WEIGHT(W) = Show working here… Explain your reasoning here Pressure in liquids Pressure in liquids depends on density of the liquid, depth and the acceleration due to gravity. Generally, liquid pressure = density gravity depth Or Also note the following additional properties of liquid pressure a) Pressure at the same level is equal b) Pressure in liquids distributes equally in all directions. This is because liquids are incompressible. This property is applied in hydraulic machines. PRESSURE IN GASES a) Atmospheric pressure Defined as the pressure exerted due to the weight of air in the atmosphere Atmospheric pressure has a value of 76cmHg or 760mmHg and is measured using a mercury barometer at sea level. 1 atmosphere (atm) =76cmHg = 100,000 Pa (approx) The mercury barometer The atmospheric pressure will be equal to the height of the mercury in the capillary tube above that in the bulk liquid or beaker. It will be 760mmHg at sea level. Question Change 88cm of mercury to Pascals. B) Measuring pressure of a gas trapped in a container The U tube manometer The gas is connected to one end of the tube and the other end is left open to atmospheric pressure. The pressure of the gas will be measure in comparison with the atmospheric pressure. If the difference in height, h is due to the gas pushing the mercury more than the atmospheric pressure pushes the mercury, then the gas pressure is in excess of the atmospheric pressure by h cmHg. Implying gas pressure = (76cm + h ) cmHg But if the atmospheric pressure pushes more by a difference in hcmHg, then The gas pressure = (76-h) cmHg