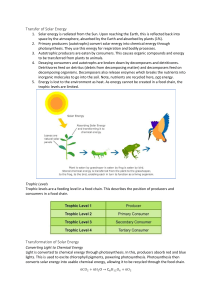
Energy flow in ecosystems paragraph 1. How is energy stored in producers? 2. How is energy transforming in the photosynthesis process? (talk about the transformation between types of energy) 3 How energy is stored in a primary consumer. 4. How is energy used by consumers? (talk about the 10% rule) 5. What happens with the rest of the energy that is not used? 6. How is energy transforming with the primary consumer? (talk about the transformation between types of energy) 7. What happens with the energy in a secondary consumer? Producers are autotrophic organisms or self-sufficient organisms, which use carbon dioxide to make their own organic molecules. Like plants, autotrophs use light energy to extract sugars from carbon dioxide. Energy is stored in the chemical bonds of molecules and is used by plants as fuel and building materials. Photosynthesis in plants converts solar energy into chemical energy using electrons and protons from water. ... In the energy-transduction reactions, solar energy is converted into chemical energy in the form of two energy-transporting molecules, ATP and NADPH. When organic molecules in one organism are swallowed by another organism, energy can be transferred from one trophic level to another. ...On average, in only one trophic layer, about 10% of the energy is stored as biomass level— e.g., primary producers—gets stored as biomass in the next trophic level—e.g., primary consumers. Primary consumers only obtain a fraction of the total solar energy—about 10%—captured by the producers they eat. ... Secondary consumers are eaten by tertiary consumers. Cats that eat birds that eat bugs that eat leaves, for instance. At each level, called a trophic level, about 90% of the energy is lost.