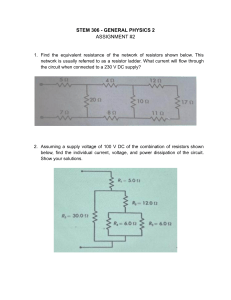
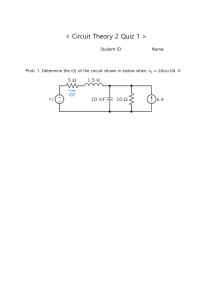
TEACHING METHODOLOGY GENERAL OBJECTIVE After this lesson the students will be able to Know about resistance and voltage Develop the ability to work cooperatively SPECIFIC OBJECTIVE After this lesson students will be able to To know about voltage and resistance graphic To develop the ability to identify metal, non metal PREVIOUS KNOWLEDGE I will ask some questions about previous knowledge related to my topic. What is current.? What is opposition to flow of current? Which parameter change when current flow in different materials? DECLARATION On the basis of the three question I will declare my topic that today out topic is “Relationship between resistance and voltage” 1 PRESENTATION CURRENT An electric current is the rate of flow of electric charge past a point or region. The SI unit of electric current is the ampere, or amp, which is the flow of electric charge across a surface at the rate of one coulomb per second. The ampere (symbol: A) is an SI base unit Electric current is measured using a device called an ammeter. VOLTAGE Voltage, electric potential difference, electric pressure or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points, which (in a static electric field) is defined as the work needed per unit of charge to move a test charge between the two points. In the International System of Units, the derived unit for voltage (potential difference) is named volt. In SI units, work per unit charge is expressed as joules per coulomb, where 1 volt = 1 joule (of work) per 1 coulomb (of charge)s. RESISTANCE Resistance is a measure of the opposition to current flow in an electrical circuit. Resistance is measured in ohms, symbolized by the Greek letter omega (Ω). 2 METAL Metal is a solid material which conduct heat & electricity ,hard, shiny, malleable, fusible, and ductile. Nonmetal is a substance that do not exhibit properties of metals such as hardness, luster, malleability, ductility and the ability to conduct electricity. NON METAL Nonmetal is a chemical element that mostly lacks the characteristics of a metal. Physically, a nonmetal tends to have a relatively low melting point, boiling point, and density. A nonmetal is typically brittle when solid and usually has poor thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity. 3 AV AIDS Marker Textbook Whiteboard Duster Pictures Models Charts Multimedia 4 p Circuit What is Electronic Circuit? An electronic circuit is a path, in which electric current can flow. A basic circuit is the combination of electrical components, which are wired together. The electronic circuit is made to do a certain job out of electricity. o Schematic The drawing of an electric circuit is called schematic. It is used to simplify the electronic circuit so that we can understand how the components are connected together. All the electrical components are represented by their symbols, called schematic symbol. Some schematic symbols used in circuits 5 o Series Circuit Series resistors circuit When the electronic components are connected in series with each other and power source, they are called to be connected in series. In a series connection, the components are connected in head-to-tail fashion. Consider the following example of a series circuit, in which resistors are connected in series. In a series circuit the current in the all components is same, but the voltage is divided among them. o Parallel Circuit  Parallel resistors circuit A parallel circuit is the combination of electrical components in parallel with each other and the power source. In parallel circuits, components are connected in headwith-head and tail-with-tail fashion. Consider the following schematic of the parallel circuit, in which resistors are connected in parallel. In a parallel circuit, the current is divided into each branch. But, the voltage of each branch is same. 6 o Series-Parallel circuit  Series-parallel resistors circuit This circuit has both kinds of connections. Some components are connected in series and some components are connected in parallel. To deal with the series-parallel circuit, each branch of the circuit is considered separately for understanding the behavior of the circuit. Consider the following circuit, in which the resistors are connected in series and parallel combination. o Ground of the Circuit A ground is the reference point in a circuit. This point works as a return path for the electrical current back to the source. Every circuit has at least one ground. However, a circuit can have more than one ground. The voltage across each electronic component is measured with respect to ground. The schematic symbol of the ground is:  circuit ground symbol 7 Interesting Facts The processor of a computer is a very complex circuit, which contains billions of transistors. Digital circuit carries the signal, that represents only zeros or ones. Analog circuits have a signal which varies in a continuous manner. Relationship between voltage and resistance Definition of Ohm’s law Ohm’s Law is the mathematical relationship between electric current, resistance and voltage. Ohm’s law states that the current through a conductor, between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points. The principle is named after the German scientist Georg Simon Ohm. Ohm’s Law formula The formula for Ohm’s Law is as follows: V = IR where V is Voltage I is Current R is Resistance 8 SUMMARY & EVALUATION SUMMARY I will summarize my topic with short words in short time EVALUATION I will ask some questions about my today topic. What is voltage ? What is resistance ? What is the relationship between voltage and resistance.... ? 9 SELF REFLECTION Q.1: Which teaching strategy I have used in my classroom to teach their concept? Answer: I used three strategies of reading pre and post reading to help my students and brain storming topic and think creatively. I also observed how these strategies motivate to ask questions seek answers apply these answers to their personal experience. Q.2: How did it go? Answer: All three strategies went well, because in this method of teaching the students learned more about voltage and resistance and their relationship. Q.3: What was their experience. Answer: According to my experience all the activities designed to help students to improve their learning skills. The students group activities went very well. Needed more A.V aids to improve learning process. Q.4: What was the response of students? Answer: The response of my students was excellent because in activities the student were active. the were more engaged in teaching learning process. They were also happy to memorized voltage and resistance relationship. Q.5: What problem did I face and how did it go? Answer: I faced two problems. 1. In this method of teaching A.V Aids are very important but unfortunately it was not available. 2. The Second problem was lack of time the topic were lengthy and road. Allhamdullilah! I tackle it by using various charts and group activities. 10 HOME WORK & DEPARTURE HOME WORK I will give home work related to my topic. "relationship between resistance and voltage". DEPARTURE At the end of the class, I will handover my class to class monitor or another Teacher. 11