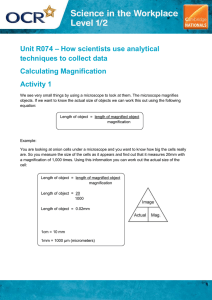
Contents Unit 1. Cell Structure and Microscopy 1. History of Cells………………………………………………………………….... 2 2. Why cells?..................................................................................................... 3 3. Cell Biology and Microscopy…………………………………………………..... 4 4. Animal and Plant cells have features in common…………………………….. 5 5. Differences between animal and Plant cells……………………………………5 6. Units of measurements………………………………………………………….. 6 7. Electron Microscopy……………………………………………………………… 11 8. Ultrastructure of an Animal Cell…………………………………………………. 13 9. Ultrastructure of a Plant Cell…………………………………………………….. 19 10. Two fundamentally different types of cells……………………………………… 21 11. Summary…………………………………………………………………………… 22 12. End of Chapter Questions……………………………………………………….. 23 Guided Worksheet for Calculating Linear Magnification 1. Magnification, Size, and Scale Bars………………………………………………. 27 2. Calculating Magnification of an Image Using it's Scale Bar…………………….. 28 3. Calculating Actual size of Specimen Using it's Scale Bar………………………. 29 4. Calculating specimen size using magnification of an image……………………. 30 More Practice on Calculating 1. Magnification…………………………………………………………………………. 32 2. Actual Size……………………………………………………………………………. 34 Past Paper Questions on Linear magnification…………… 37-40 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 Magnification, Size, and Scale Bars Cells are extremely small but knowing the sizes of objects viewed under the microscope can be really useful. For example, a plant scientist might want to compare the relative sizes of pollen grains from plants in the same genus to identify to help identify different species. With a compound microscope, the magnification is the product of both lenses, so if microscope has a 10x eyepiece and an 40x objective, the total magnification is 400x. Magnification is defined as the ratio of the size of the image to the size of the object. Magnification = Image size Actual size Image Size The relationship between these three values can be shown using the equation triangle to the right, which offers a quick way of rearranging the values in order to derive related formulas. Actual Size Magnification We use micrometers for specimen size under the microscope. The conversion is: 1mm = 1000 μm (micrometers) Complete the following Chart: Actual Specimen Size Image (Drawing) Size 0.5 mm 2 cm 200 m 1 cm 40 m 2 cm 100 m 100m 200X 5 cm 100X 4 cm 50X 10mm 4mm 3X 10cm 27 Magnification 25X Calculating Magnification of an Image Using it's Scale Bar Magnification= 320x 1. Calculate the magnification the cell. (show work) Answer____________________ 2. Calculate the magnification of the cilia base. (show work) Answer___________________ 2 28 3. Calculate the magnification of the plant cell. (show work) Answer_________________ Calculating the Size of a Specimen Using it's Scale Bar 4. Calculate the size of the mitochondria. (show work) Answer________________ 3 29 5. Calculate the size of a cilia. (show work) Answer____________________ 6. Calculate the size of the chloroplast. (show work) Answer__________________________ Calculating specimen size using magnification of an image 4 30 7. Calculate the size of the ant. (show work) 150x Answer_____________________ 8. Calculate the size of the nucleus. (show work) 15000x Answer___________________ 9. Calculate the size of the Golgi apparatus. (show work) 20000x Answer______________________ 5 31 Magnification Step 1) Measure the image size using a ruler in millimetres (mm) Step 2) Convert the millimetres (mm) into micrometres (µm) Step 3) Divide your answer by the actual size Question 1 This is a fly. Its actual eye size is 1,000µm. What is the magnification? 1) Length of eye is ________ mm 2) _______ mm x1000 = _________ µm 3) Image size = _________ µm 4) Magnification = Image ÷ Actual Magnification = _____ µm ÷ _____ µm Magnification = ________ The picture shows the eye magnified (zoomed in) by ________ times. Question 2 This is a red blood cell. Its actual size is 300µm. What is the magnification? 1) Length of cell is ________ mm 2) _______ mm x1000 = _________ µm 3) Image size = _________ µm 4) Magnification = Image ÷ Actual Magnification = _____ µm ÷ _____ µm Magnification = ________ 32 The picture shows the cell magnified (zoomed in) by ________ times. Question 3 This is a snowflake. Its actual height is 700µm. What is the magnification? 1) Length of snowflake is ________ mm 2) _______ mm x1000 = _________ µm 3) Image size = _________ µm 4) Magnification = Image ÷ Actual Magnification = _____ µm ÷ _____ µm Magnification = ________ The picture shows the snowflake magnified (zoomed in) by ________ times. Question 4 This is an insect. Its wings are 2,500µm. What is the magnification? 1) Length of wing is ________ mm 2) _______ mm x1000 = _________ µm 3) Image size = _________ µm 4) Magnification = Image ÷ Actual Magnification = _____ µm ÷ _____ µm Magnification = ________ The picture shows the wing magnified (zoomed in) by ________ times. 33 Question 5 This is a chloroplast. Its actual length is 50µm. What is the magnification? 1) Length of chloroplast is ________ mm 2) _______ mm x1000 = _________ µm 3) Image size = _________ µm 4) Magnification = Image ÷ Actual Magnification = _____ µm ÷ _____ µm Magnification = ________ The picture shows the chloroplast magnified (zoomed in) by ________ times. Actual Size Step 1) Measure the image size using a ruler in millimetres (mm) Step 2) Convert the millimetres (mm) into micrometres (µm) Step 3) Divide your answer by the magnification Question 1 This is a mosquito stinger. The magnification is x4. What is the actual size? 1) Length of stinger is ________ mm 2) _______ mm x1000 = _________ µm 3) Image size = _________ µm 4) Actual size = Image ÷ Magnification Actual size = ______ µm ÷ _____ 34 Actual size = ________ The actual size of this stinger is _____ µm. We can see it because it has been magnified. Question 2 This is shark skin. It is made of teeth. The magnification is x50. What is the actual size of 1 tooth? 1) Length of tooth is ________ mm 2) _______ mm x1000 = _________ µm 3) Image size = _________ µm 4) Actual size = Image ÷ Magnification Actual size = ______ µm ÷ _____ Actual size = ________ The actual size of this tooth is _____ µm. We can see it because it has been magnified. Question 3 This is a grain of salt. The magnification is x100. What is the actual size of the salt? 1) Size of salt is ________ mm 2) _______ mm x1000 = _________ µm 3) Image size = _________ µm 4) Actual size = Image ÷ Magnification Actual size = ______ µm ÷ _____ Actual size = ________ The actual size of this salt is _____ µm. We can see it because it has been magnified. 35 Question 4 This is a needle and thread. The magnification is x4. What is the actual size of the needle? 1) Size of needle is ________ mm 2) _______ mm x1000 = _________ µm 3) Image size = _________ µm 4) Actual size = Image ÷ Magnification Actual size = ______ µm ÷ _____ Actual size = ________ The actual size of this needle is _____ µm. We can see it because it has been magnified. Question 5 This is a ballpoint pen. The magnification is x20. What is the actual size of the ballpoint pen? 1) Size of pen is ________ mm 2) _______ mm x1000 = _________ µm 3) Image size = _________ µm 4) Actual size = Image ÷ Magnification Actual size = ______ µm ÷ _____ Actual size = ________ The actual size of this ballpoint pen is _____ µm. We can see it because it has been magnified. 36 Theory (structured) Questions On Linear Magnification :1. (a) Name the structures A, B and C. [3] (b) State the function of structure C. [1] (c) Explain why structure C cannot be seen with a light microscope. [2] (d) State two disadvantages of the electron microscope compared to the light microscope for the study of cells. [2] (e) Calculate the magnification of the image in Fig.1.1 Show your working and calculate the answer to the nearest whole number. Answer= ……………………....[2] 37 2. 38 3. 39 4. The drawing below shows the structure of a chloroplast. a. Name structures labelled A to E, on the diagram. (5) (b) Describe three similarities in the structure of chloroplasts and mitochondria. (3) (c) The chloroplast shown in the drawing was magnified 8500 times. Calculate the actual length of the chloroplast along axis XY. Show your working a nd express your answer in micrometers. (2) 40 41