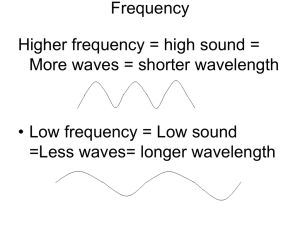
COMMUNICATION 1. Introduction 2. AM and FM 3. Analogue versus Digital transmission. 4. Channels of Communication. 5. Satellite communication. Welcome Enjoy Physics lesson. 1st objective understand the term modulation and be able to distinguish between amplitude modulation (AM) and frequency modulation (FM). 2nd objective Welcome know and describe the relative advantages of AM and FM transmissions Our lesson begins: Slide 1 Slide 1 MODULATION Modulation is the process where audio signal is added onto a carrier signal. In our case, we use the radio waves and microwaves as the carrier. The carrier is of sinusoidal form and hence carries the function, x = x0sint where x0 is its amplitude and its angular frequency both of which can be altered. 1 Shorter aerial required. 2 Less distortion 3 4 5 Longer transmission range. Less attenuation(signal power loss). Allows more than one station in a region. Types of Modulation The signals that we receive are either amplitude modulated (AM) Or frequency modulated (FM) Amplitude Modulation (AM) (i) The amplitude of the carrier wave is made to vary in synchrony with the displacement of the information signal. (ii) The amplitude variations of the carrier wave is at the signal frequency fs. (iii) The frequency of the amplitude modulated wave remains the same i.e. carrier frequency fc. Sideband Frequencies in AM Wave 1. The AM wave contains three frequencies viz fc, fc + fs and fc − fs. 2. The first frequency fc is the carrier frequency. The process of modulation does not change the original carrier frequency but produces two new frequencies (fc + fs) and (fc − fs) which are called sideband frequencies. 3. The sum of carrier frequency and signal frequency i.e. (fc + fs) is called upper sideband frequency. 4. The lower sideband frequency is fc − fs i.e. the difference between carrier and signal frequencies. 5. The signal frequency fs is contained in the sideband frequencies. Bandwidth In an AM wave, the bandwidth is from (fc − fs) to (fc + fs) i.e., 2 fs. Bandwidth . Example 1. An audio signal of 1 kHz is used to modulate a carrier of 500 kHz. Determine: (i) sideband frequencies (ii) bandwidth required. Solution. Carrier frequency, fc = 500 kHz Signal frequency, fs = 1 kHz The AM wave has sideband frequencies of ( fc + fs) and ( fc − fs ). (i) Sideband frequencies = (500 + 1) kHz and (500 − 1) kHz = 501 kHz and 499 kHz (ii) Bandwidth required = 499 kHz to 501 kHz = 2 kHz Frequency Modulation POINTS TO NOTE: 1. Definition: In frequency modulation (FM) frequency of the carrier wave is made to vary in synchrony with the displacement of the information signal. 2. the amplitude of the modulated wave remains the same i.e. carrier wave amplitude. 3.The rate at which the carrier wave frequency is made to vary is equal to the frequency of the information signal. Comparison of AM and FM Amplitude Modulation AM Advantages Disadvantages 1. Smaller bandwidth so more stations available 1. Requires a high power transmitter. in frequency range. 2. Susceptible to noise and intereference. 2. Greater area covered by one transmitter. 3. Cheaper radio sets. Frequency Modulation FM Advantages Disadvantages 1. Less electrical noise and interference. 2. Greater bandwidth produces better quality sound. 1. Shorter range 2. More complex circuitry. 3. More expensive