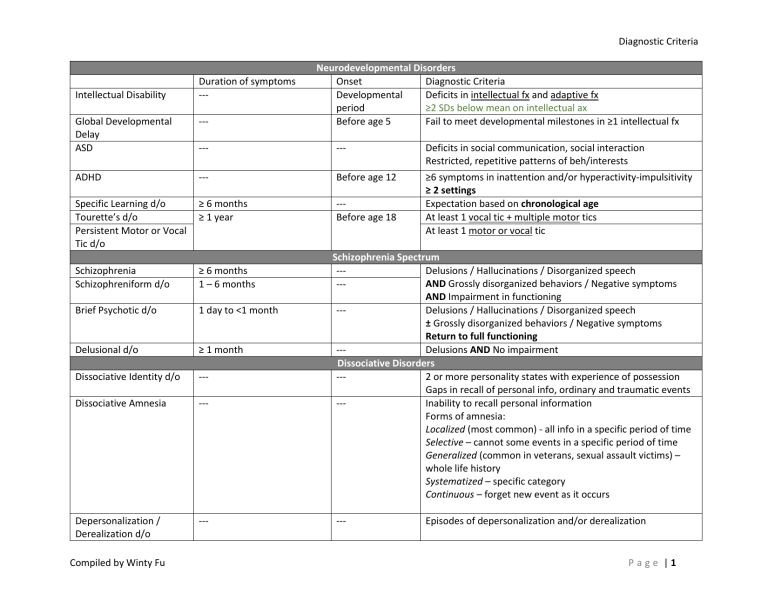
Diagnostic Criteria Intellectual Disability Duration of symptoms --- Neurodevelopmental Disorders Onset Diagnostic Criteria Developmental Deficits in intellectual fx and adaptive fx period ≥2 SDs below mean on intellectual ax Before age 5 Fail to meet developmental milestones in ≥1 intellectual fx Global Developmental Delay ASD ----- --- ADHD --- Before age 12 Specific Learning d/o Tourette’s d/o Persistent Motor or Vocal Tic d/o ≥ 6 months ≥ 1 year --Before age 18 Schizophrenia Schizophreniform d/o ≥ 6 months 1 – 6 months Brief Psychotic d/o 1 day to <1 month Delusional d/o ≥ 1 month Dissociative Identity d/o --- Dissociative Amnesia --- Depersonalization / Derealization d/o --- Compiled by Winty Fu Deficits in social communication, social interaction Restricted, repetitive patterns of beh/interests ≥6 symptoms in inattention and/or hyperactivity-impulsitivity ≥ 2 settings Expectation based on chronological age At least 1 vocal tic + multiple motor tics At least 1 motor or vocal tic Schizophrenia Spectrum --Delusions / Hallucinations / Disorganized speech AND Grossly disorganized behaviors / Negative symptoms --AND Impairment in functioning --Delusions / Hallucinations / Disorganized speech ± Grossly disorganized behaviors / Negative symptoms Return to full functioning --Delusions AND No impairment Dissociative Disorders --2 or more personality states with experience of possession Gaps in recall of personal info, ordinary and traumatic events --Inability to recall personal information Forms of amnesia: Localized (most common) - all info in a specific period of time Selective – cannot some events in a specific period of time Generalized (common in veterans, sexual assault victims) – whole life history Systematized – specific category Continuous – forget new event as it occurs --- Episodes of depersonalization and/or derealization Page |1 Diagnostic Criteria Bipolar I Bipolar II Cyclothymic d/o Disruptive Mood Dysregulation d/o Major Depressive d/o Persistent Depressive d/o Premenstrual Dysphoric d/o Separation Anxiety d/o Specific Phobia Social Anxiety d/o Panic d/o Duration of Symptoms Manic – 1 week Hypomanic – 4 days Depressive – 2 weeks ≥ 2 years for adults ≥ 1 year for children & adol Duration of symptoms ≥ 12 months 2 weeks Adults: ≥ 2 years Children & Adol: ≥ 1 year ≥ 2 symptomatic cycles Duration of Symptoms Adults: ≥ 6 months Children & Adol: ≥ 4 weeks ≥ 6 months --- Agoraphobia OCD Body Dysmorphic d/o Hoarding d/o Compiled by Winty Fu --- Symptoms of hypomanic AND depressive symptoms Present for over half of the time Not symptom free for ≥ 2 months Depressive Disorders Onset Diagnostic Criteria Before age 10 Dx after age 6 and before age 18 Recurrent temper outbursts at least 3 times per week --≥ 5 symptoms ----Anxiety Disorders Onset Diagnostic Criteria ----------- ≥ 6 months GAD Bipolar Disorders Onset Diagnostic Criteria --Manic ± Hypomanic / Major Depressive episode --Hypomanic episode AND Major Depressive episode Fear of being embarrassed/humiliated in ≥1 social situations Panic attacks Related maladaptive changes ≥ 1 month after panic attacks Fear/Anxiety in ≥2 situations Escape will be difficult / Help is unavailable --Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders Duration of Symptoms Onset Diagnostic Criteria ----Obsessions + Compulsions + ≥ 1 hour/day --------- Page |2 Diagnostic Criteria Reactive Attachment d/o Disinhibited Social Engagement d/o PTSD Acute Stress d/o Adjustment d/o Somatic Symptom d/o Illness Anxiety d/o Conversion d/o Factitious d/o Compiled by Winty Fu Trauma- and Stress-Related Disorders Onset Diagnostic Criteria Before age 5 Dx after 9+ months old Inhibited and socially withdrawn towards adult caregivers Social and emotional disturbance Extreme insufficient care as cause of disturbed behavior ----Dx after 9+ months old Child actively approaches and interacts with unfamiliar adults. Extreme insufficient care as cause >1 month --Exposure to actual/threatened death, serious injury or sex violence. Intrusion. Persistent avoidance of event-associated stimuli. Negative alterations in cognitions and mood. Marked alterations in arousal and reactivity 3 days to 1 month after --Exposure to actual/threatened death, serious injury or sex trauma violence. Intrusion. Avoidance. Dissociative symptoms. Negative mood. Arousal symptoms. Remit within 6 months after Within 3 months termination of stressor of onset of stressor Somatic Symptoms and Related Disorders Duration of Symptom Onset Diagnostic Criteria --Somatic symptoms cause distress/disruptions in daily life Excessive thoughts/feelings/behs related to symptoms --Preoccupations with having serious illness ≥ 6 months Absence/mild somatic symptoms High anxiety about health Excessive health-related beh/Maladaptive avoidance ----Disturbance of voluntary motor or sensory functioning Incompatibility between symptoms and medical conditions ----Falsify physical/psychological symptoms Present to others as ill/impaired ***Without obvious external rewards (vs Malingering) Imposed on either self or others Duration of Symptoms --- Page |3 Diagnostic Criteria Pica Anorexia Nervosa (elevated serotonin) Duration of Symptoms ≥ 1 month --- Bulimia Nervosa (low serotonin) (low endorphin) ≥ 3 months Binge-eating d/o Duration of Symptoms Enuresis ≥ 3 months Encopresis Compiled by Winty Fu Feeding and Eating Disorders Onset Diagnostic Criteria --Dx after age 2 Persistent eating of non-nutritive, non-food substance Inappropriate to developmental level Not part of culturally sanctioned practice --Restriction of energy intake results in sig. low body weight Intense fear of gaining weight Disturbed body image --Recurrent episodes of binge eating Inappropriate compensatory behaviors to prevent weight gain Self-evaluation influenced by body weight and shape Binge eating + compensatory beh at least once a week --Recurrent episodes of binge eating Distress about binge eating Binge eating at least once a week Elimination Disorders Onset Diagnostic Criteria --Dx after age 5 Repeated voiding of urine into bed/clothes At least twice a week Nocturnal subtype – nREM, slow-wave sleep; more common in boys --Dx after age 4 Repeated involuntary/intentional passage of faeces into inappropriate places at least once a week Page |4 Diagnostic Criteria Obstructive Sleep Apnea Hypopnea --- Sleep-wake Disorders Onset Diagnostic Criteria --Dissatisfaction with sleep quality or quantity At least 3 nights a week --Excessive sleepiness despite a main sleep period of over 7 hrs At least 3 times a week --Sleep attacks at least 3 times a week Cataplexy/Hypocretin deficiency/REM sleep latency ≤15mins --Obstructive apnea / Hypopnea NREM Sleep Arousal d/o --- --- REM Sleep Behavior d/o --- Nightmare d/o --- Duration of Symptoms Insomnia d/o Hypersomnolence d/o ≥ 3 months Narcolepsy Duration of Symptoms Erectile d/o Genito-Pelvic Pain/Penetration d/o Premature / Early Ejaculation Gender Dysphoria ≥ 6 months --- Duration of Symptoms ≥ 6 months Duration of Symptoms Frotteuristic d/o Compiled by Winty Fu Incomplete awakening from sleep (first 1/3 of major sleep) Sleepwalking / sleep terrors No recall on dream + Amnesia for the episode --Arousal during sleep AND vocalization ± complex motor beh During REM sleep (>90 mins after sleep onset) Alert and oriented on awakening --Well-remembered dreams inv. threats to survival/security During REM sleep (2nd half of major sleep) Fully alert on awakening Sexual Dysfunctions Onset Diagnostic Criteria --Difficulty in obtaining and maintaining an erection Reduced erectile rigidity --- ≥ 6 months Ejaculation within 1 minute of vaginal penetration or before the person desires it low serotonin Gender Dysphoria Onset Diagnostic Criteria --Marked incongruence between one’s experienced/expressed gender and assigned gender Children: ≥ 6 symptoms Adolescents & adults: ≥ 2 symptoms Paraphilic Disorders Onset Diagnostic Criteria --Intense and recurrent sex arousal from touching/rubbing against a nonconsenting person Page |5 Diagnostic Criteria Transvestic d/o Pedophilic d/o ODD CD Intermittent Explosive d/o Delirium NCD due to Alzheimer’s Disease Vascular NCD NCD with Lewy Bodies (cortical area affected) Frontotemporal NCD Compiled by Winty Fu ----- Intense and recurrent sex arousal from cross-dressing Dx after age 16 ≥5years older than the children Disruptive, Impulse Control and Conduct Disorders Duration of Symptoms Onset Diagnostic Criteria ≥ 6 months --Angry/irritable mood, Argumentative/ Defiant behaviors, Vindictiveness At least 1 symptom in past 6 Persistent behaviors that violate the basic rights of others months and/or age-appropriate social norms or rules 4 features: Aggression to people and animal, Destruction to property, Deceitfulness/Theft, Serious violation of rules ----Dx after age 6 Inability to control aggressive impulses by Verbal / Physical aggressive at least twice a week for 3 months 3 behavioral outbursts inv. Damage to property and/or injury to people or animals within 12 months Neurocognitive Disorders ----Disturbance in attention and awareness Fluctuate in severity over a course of day ----Decline in learning and memory Steadily progressive and gradual decline in cognition ----Decline in complex attention and frontal executive functioning ----Fluctuating cognition with pronounced variations in attention and awareness Recurrent visual hallucinations Parkinson features with onset after cognitive decline REM sleep behavior d/o ----Behavior disinhibition, apathy or inertia, loss of empathy, preservative behavior, hyperorality and dietary change Decline in language ability Sparing of memory and learning, perceptual-motor fx Page |6 Diagnostic Criteria Paranoid PD Schizoid PD Schizotypal PD Antisocial PD Borderline PD Histrionic PD Narcissistic PD Avoidant PD Dependent PD Obsessive-Compulsive PD Compiled by Winty Fu Personality Disorders – Cluster A Core Features Distrust and suspiciousness Detachment from interpersonal relationship Neuroticism & Conscientiousness – Low Restricted range of emotional expressions in social settings Agreeableness – High Acute discomfort with and reduced capacity for close relationships Cognitive or perceptual distortions (odd beliefs and magical thinking) Eccentricities of behaviors Personality Disorders – Cluster B Core Features Big Five Personality Traits Dx after age 18 Neuroticism – High Disregard for and violations of the rights of others since age 15 Agreeableness & Conscientious – Low Code 49/94 (psychopathic-hypomania) on MMPI Instability in interpersonal relationship, self-image and affect Marked impulsivity Excessive emotionality and attention seeking Grandiosity Neuroticism & Conscientious – High Need for admiration Agreeableness – Low Lack of empathy Personality Disorders – Cluster C Social inhibition Feelings of inadequacy Hypersensitivity to negative emotions Need to be taken care of Submissive and clinging behaviors, fear of separation Preoccupation with orderliness, perfection, mental and Neuroticism & Conscientiousness – High interpersonal control Agreeableness – Low Severely limits flexibility, openness and efficiency Page |7 Diagnostic Criteria Etiologies Brain Abnormalities ASD ADHD Tourette’s d/o Childhood-onset Fluency d/o Schizophrenia Schizophreniform d/o MDD Seasonal Affective d/o Specific phobia OCD Compiled by Winty Fu Good Prognostic Indicators Neurodevelopmental Disorders Elevated serotonin Ability to speak by age 5 to 6 Abnormal dopamine Late onset of symptoms IQ ≥ 70 Smaller and lower activity level in caudate nucleus, globus pallidus, PFC Elevated dopamine Hypersensitive dopamine receptors in caudate nucleus Onset in age 2 to 7 Severity at age 8 as predictor Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders Good premorbid adjustment Females Acute and late onset Presence of precipitating events Enlarged ventricles Brief duration of active-phase symptoms Smaller hippocampus, amygdala, global pallidus Insight Elevated dopamine Family history of mood disorders Mesolimbic pathway +ve symptoms No family history of schizophrenia Mesocortical pathway -ve and cognitive symptoms Onset of prominent psychotic symptoms within 4 Hypofrontality Negative symptoms weeks of noticeable changes in behavior or functioning Confusion / Perplexity Good premorbid functioning No blunted / flat affect Depressive Disorders Catecholamine hypothesis – deficiency in norepinephrine Indolamine hypothesis – Low serotonin Elevated cortisol; Atrophy of neurons in hippocampus Faulty suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) in hypothalamus Anxiety Disorders Abnormal serotonin, norepinephrine, GABA levels Low serotonin (also in PTSD) ? Low GABA Overreactive right caudate nucleus, OFC, cingulate cortex Page |8 Diagnostic Criteria Anorexia Nervosa Bulimia Nervosa Substance Use d/o Severity depends on no. of symptoms Alzheimer’s Disease Parkinson’s Disease Huntington’s Disease Dominant autosomal gene disease AIDS Smaller subthalamic nucleus (part of basal ganglia) Feeding and Eating Disorders High serotonin Low serotonin Low endogenous opioid Beta-endorphin Substance-related Disorders Elevated dopamine in mesolimbic system Smoking cessation: Alcohol-primary effect on GABA Age 35+, male, college education, married or living Nicotine mimics Ach at nicotinic receptor sites with a partner, smoke-free home, non-smoking policy *Nicotine nasal spray as most effective replacement. at home, start smoking at later age, low nicotine Nicotine gum as the least effective. dependence level Neurocognitive Disorders Degeneration of acetylcholine (Ach) cells Stage 1 (1 to 3 years): Anterograde amnesia, anomia, Formation of amyloid-predominant neurotic plagues and sadness, deficits in visuospatial skills (wandering) tau-predominant neurofibrillary tangles in hippocampus, Stage 2 (2 to 10 years): Retrograde amnesia, amygdala and entrorhinal cortex indifference/irritability, fluent aphasia, restlessness, Excessive glutamate receptor activity ideomotor apraxia, acalculia APOE4 gene variant Stage 3 (8 to 12 years): Severely impaired intellectual fx, limb rigidity, apathy, urinary and fecal incontinence Degeneration of dopamine receptors in substantia nigra Imbalance between dopamine and acetylcholine Degeneration of GABA-secreting cells in basal ganglia Mental changes (e.g. irritability or anhedonia) before Excessive glutamate receptor activity motor disturbances Abnormal nigrostriatal pathway (a dopamine pathway) Mid-age onset (ages 35-40) HIV infection affects deep white matter in subcortical Stage 0: Normal; 0.5: Equivocal brain areas Stage 1: Mild – perform most but most demanding aspects of work ↓ dopamine receptors in putamen and ventral striatum Stage 2: Moderate - Cannot work, need assistance to (part of basal ganglia) walk Stage 3: Severe – Major intellectual incapacity, motor disability Stage 4: End Stage – Vegetative, mute, paraplegia/paraparesis Baumgartern’s 6 phases: Dx Post-dx turning point Immersion Post-immersion turning point Integration Disclosure Compiled by Winty Fu Page |9 Diagnostic Criteria Sleep Beta (fully awake) Alpha Stage 1 Depression (esp. endogenous) Alcohol-induced Sleep d/o Enuresis - nocturnal subtype Aging Theta (Sleep spindles & K Complex) Stage 2 Delta (Slow-wave sleep) REM Stage 3 & 4 Reduction in Increase in Sleep continuity REM density Slow-wave (nREM) sleep Sleep latency REM latency (i.e. earlier onset of REM sleep) Stage 3 & 4 sleep Intoxication: Immediate sedation Increase in Stage 3 & 4 sleep Reduced REM sleep + Increased wakefulness Increased REM Reduced Stage 3 & 4 sleep Withdrawal: Reduced sleep continuity Vivid dreams Occurs in slow-wave (nREM) sleep More common in boys nREM & REM sleep Awakenings Total sleep time Sleep patterns across lifespan Newborns REM precedes nREM + REM to 50% of total sleep time 3 months old nREM precedes REM 6 months old REM to 30% of total sleep time Adults REM to 20% of total sleep time Compiled by Winty Fu P a g e | 10



