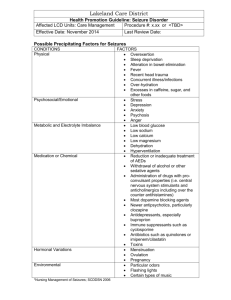
Psychology 359 Developmental Disabilities Test Review #3 DSM-5 identifies all of the following as domains of adaptive functions Conceptual (money skills, being able to tell time, math problems, etc.) Social (making friends, etc.) Practical (being able to do tasks) Intellectual Disability is defined by low intellectual functioning and by adaptive behavior deficit. What are the severities of Intellectual Disability? Mild Moderate Severe Profound Children with mild Intellectual Disability who behave in ways consistent with teachers’ expectations of students with Intellectual Disability in school, yet behave differently and function well outside of school are said to have 6-hour retardation. The term mental retardation was replaced with the term intellectual disability in all federal documents enacted on October 5, 2010 by Rosa’s Law. I Q test scores have a mean of 100. I Q test scores have a Standard Deviation of 15. Intellectual Disability is indicated when IQ scores are: 2 standard deviation below the mean (IQ<70) What do IQ tests measure? Cognitive ability: memory, reasoning, numerical calculation, problem solving, general information and comprehension. The most frequently used intelligence test for children and adolescents from 6 to 16 years of age is Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children - Fifth Edition (WISC-V). Normal curve is a symmetrical distribution in which large majority of cases fall around the middle of distribution. Half of the cases fall above, while half the cases fall below the middle (mean/average). IQ Distribution mean of 100, SD of 15. IQ range of: About 75 percent of ID population fall in mild ID and are identified once they start school. Mild ID → 55-75 - About 10 percent of ID population fall in moderate ID. Moderate ID → 35-49 I.e. Down syndrome - About 10 percent of ID population fall in severe/profound ID. Severe ID, Profound ID → 25-35 Lowest level of cognitive functioning, i.e. spina bifida, or anencephaly What is Cultural-familial intellectual disability? Children of mild ID parents (or MMR) raised in a deprived social and economic environment and will probably share their parents genetically determined limits of intelligence. What is the Active Socialization Hypothesis? Infers that without realization people in society such as parents or teachers may help create and maintain deficits that impedes the individual with ID. Social positions are defined in terms of occupation, a person’s attributes (age, gender), the characteristic behavior of people (sexual orientation, religion, etc.), and the behavior of others towards a person. High positive status: University president, U.S. senators, famous basketball players Lowest status: immigrant and farm laborers, farmer, homeless, criminal, mental illness, ID Modest positive status: teachers, nurse, parents, pastor In what social position does society view intellectual disability? Deviance position (lowest status) It is an assumption that research and training programs for caregivers of individuals with ID can help modify the child’s self- identity and improve the functioning of individuals with ID. Who first termed Autism Spectrum Disorder as early infantile autism in 1943? Leo Kanner According to the DSM-5, what are the diagnostic criteria for autism spectrum disorder? 1. Persistent deficits in social communication/social interaction 2. 3. Restrictive, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, and activities Symptoms present early in developmental period The DSM-5 provides a rating scale to describe severity levels for ASD in social communication and restricted, repetitive behavior based upon requirements of support. There are three levels of requirements of support. Level 3: very substantial support Level 2: substantial support Level 1: support What is - a Ritualistic behavior? More common in older children with ASD and among individuals with higher intellectual functioning. Children spend hours each day sorting and arranging toys, clothes, or collectibles Other children have food rituals (may insist on eating foods in a certain order according to color or texture) Some children show compulsive behaviors such as ritualistic patterns of walking around the room or turning light switches on and off What is a Stereotyped behavior? Common stereotypes behaviors in functioning ASD children are: Rocking Hand flapping Whirling Making unusual repetitive mannerisms with hands and fingers Stereotypes are most common among the younger children with ASD and also those with lower intellectual functioning What is Echolalia? Echolalia is the repetition of words that a child hears as others speak or over hear on television and radio These words are usually taken out of context or repeated at inappropriate times, so they seem nonsensical to others Approximately 85% of children with ASD and ID show echolalia. According to ADDM Network, what is the prevalence of ASD in 2016? 1 in 68 youths (14.6 per 1000 children) What is the best outcome for prognosis of youth with ASD of youth? Prognosis for youth with ASD is variable. Best outcomes seen in children with: Higher intellectual ability Kids to show interest in range of play, engage with others, and begin showing ability for symbolic play tend to fare well Better language skills Children with ASD who have functional language skills by age 5 tend to have much better outcomes than their counterparts who lack functional language Greater social engagement Young children with ASD who shows some capacity for shared attention, imitation, and social engagement tend to have better outcomes Who wrote The Empty Fortress and blamed cold, emotionally distant “refrigerator mothers” as the cause of children with ASD to retreat into themselves in response too dismissive parenting practices? Bruno Bettelheim What are the average concordance rates in ASD for monozygotic (MZ) twins? 60 - 90% What are the average concordance rates in ASD for dizygotic (DZ) twins? 5-20% At what age do the American Academy of pediatrics recommends that physicians routinely screen all infants for ASD? 18 months old What are treatments for Autism Spectrum Disorder with limited empirical research? Holding therapy, pet therapy, equine therapy, megavitamin/diet therapy, facilitated communication, auditory integration training, Irlen lenses training Parents seek these therapies when they’re desperate for help for their kids, the places they live may not have the empirically based effective services. Or the empirically based services may not have helped their child so they are seeking other routes. What is the communication system developed to help children with ASD to communicate? Augmentative and alternative communication systems (AAC) PECS (picture exchange communication system) is a low-tech AAC system in which children communicate by pointing to or exchanging cards with symbols or pictures that represent actions, feelings, ideas, or objects Speech generating devices What is an Aura? Prior to a seizure an individual may feel of anxiety, unease,or discomforting sensations such as flickering lights, pre conditioned feeling that a seizure is about to happen, or visual “sunburst” What is a Seizure threshold? A theoretical concept concerning the amount of stimulation that is minimally necessary to trigger seizure activity. Individuals have different seizure thresholds. What are Partial seizures? Occur in one specified area of the brain Generalized partial seizure partial seizures sometimes developed into second phase of generalized tonic-clonicseizures in which person loses consciousness, Falls down, and has convulsions. Simple partial seizure no loss of consciousness, typically involves the arms or legs, starting at periphery and going up the limb, person is aware of the seizure but unable to control the movement Complex partial seizure person loses awareness during seizure, repetitive behavior may occur such as picking at clothing, hand rubbing, or walking about in a daze, seizure is fairly brief about 1 to 2 minutes, recovery may take longer than person may feel confusion irritable and angry, more common in adults and adolescents than children (2/3 of all cases of known epilepsy) What are Generalized seizures? Occur throughout the brain Absence seizure usually occurs in children from 4 to 12 years old, absence seizures are brief, lasting a few seconds, Child is unaware of what is happening like in a fog, staring, daydreaming and not paying attention sometimes there is rapid eye blinking, mouthing motions or arm waving Atonic seizure Sudden loss of muscle tone so severe that the person falls down, injury may occur when the person falls, no tonic-clonic movement involved Generalized tonic-clonic the entire brain and body are affected in immediate loss of consciousness occurs often no warning of the coming seizure Person becomes rigid(tonic phase), Falls down, and the body stiffens and relaxes (clonic face) and has violent convulsions lasting 1 to 2 minutes physical injury can occur during fall during recovery there is confusion, fatigue, and muscle soreness and no awareness or memory of the seizure What are some causes of seizures? Head trauma-head injuries in car accidents, falls, child abuse, sports injury Strokes, brain tumors, and Alzheimer’s disease-inolder people Misuse of medications and other drugs- High doses or sudden withdrawal of drugs Infections and high fever-febrile seizures most common in young children Environmental triggers-flickering and fluorescent lights, pattern of lights in movement on television and computer screen, extreme heat Toxins-lead poisoning, exposure to insecticides and other chemicals can trigger seizures Emotions and fatigue-Extreme excitement or fear, being overtired, lacking sufficient sleep can all trigger seizures in some people - **What causes some people to have them normally low seizure threshold and experience repeated seizures? In symptomatic epilepsy the presumed causes known such as head injury that leave permanent brain damage and the epilepsy can be accounted for.However in the majority of cases because cannot be specified but many risk factors have been identified.** Be familiar with different seizure disorder treatments. Drug therapy medication reduces and controls the seizures/ 80 to 85% achieve good control over seizures with medication Surgery About 15 to 20% do not respond well to drug therapy/ Surgery is recommended if the seizures if a specific focal point in the brain is identified; most are temporal lobe seizures therefore required temporal lobe surgery Risk of surgery could lead to death or further damage or complications including brain hemorrhage and rural deterioration Psychological treatment Behavior modification can alleviate seizures associated with emotions, thoughts, sounds, smells, lights, and temperature extremes - These thoughts and emotions can be associated with seizures/ Creating a behavior intervention plan can alleviate these symptoms/Behavior modification offers therapeutic procedure for long-term management The ketogenic diet Very high in fat and low in protein and carbohydrate and requires very careful monitoring to maintain seizure control/Works well with children who do not respond to medication due to negative side effects What is - Status Epilepticus? A serious emergency situation usually are occurring in young children It involves seizures that continue for at least 15 to 30 minutes or more or recur at short intervals Immediate emergency treatment is necessary