Biomolecules Review: Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, Nucleic Acids
advertisement

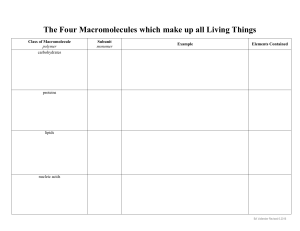
Unit 2 Review Biomolecules Monomer VS Polymer • Monomers: • Molecules that may react with similar molecules to form a chain • Polymers: • A chain of many monomers that are chemically bonded together Carbohydrates • • • • • Monomer - monosaccharides Function - main source of energy Structure - Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio; most often in a ring shape Examples - sugars and starches, cellulose, fructose, glucose, lactose Mneumonic - CHO CARBOHYDRATE Monosaccharide CARBOHYDRATE Disaccharide CARBOHYDRATE Polysaccharide Proteins • Monomer - amino acids • Function - proteins have specific jobs and carry out many different functions • Structure - amino acids connected by peptide bonds; very large molecules • Examples - hemoglobin, collagen, antibodies, enzymes • Mneumonic - CHON PROTEIN Lipids • • • • • Monomer - fatty acids Function - STORE energy Structure - 2 or 3 fatty acids with glycerol Examples - fats, oils , waxes, triglycerides Mneumonic - CH LIPID Nucleic Acids • • • • • Monomer - nucleotides Function - store and transmit genetic information Structure - each nucleotide composed of a 5 carbon sugar, a nitrogen base, and a phosphate group Example - DNA and RNA Mneumonic - CHOPN NUCLEIC ACID Overview Biomolecule Name Monomer Function Structure Examples Carbon, Hydrogen, Sugars, starches Main SOURCE of Oxygen Carbohydrates Monosaccharides Cellulose, 1:2:1 ratio C6H12O6 energy Fructose, Sucrose Ring shape Proteins Amino Acids Specific jobs Many different functions Lipids Fatty Acids STORES energy Nucleic Acids Nucleotides Mneumonic CHO Amino acids connected by peptide bonds Very large molecules Hemoglobin, collagen, antibodies, ENZYMES CHON 2 or 3 fatty acids with a glycerol Fats, Oils, Waxes Triglycerides CH DNA and RNA CHOPN Each nucleotide Store and contains a sugar, a transmit genetic phosphate, and information nitrogen base ENZYMES • Enzymes are PROTEINS • Enzymes are catalysts = speed up chemical reactions • Speed up reactions by LOWERING the amount of activation energy needed Enzymes • Enzyme-Substrate Complex – example: digestion of food you’ve eaten Enzymes •Factors that affect enzyme activity (could slow them down, or stop them) •Temperature •pH •Inhibitors