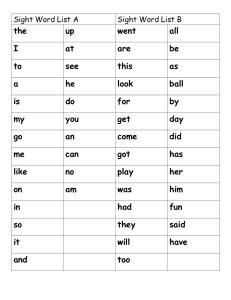
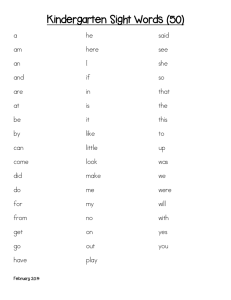
APPROACHES TO TEACH READING 1. Azrina 2. Naziha 3. Khavitraa APPROACHES TO TEACH READING LANGUAGE EXPERIENCE LANGUAGE EXPERIENCE APPROACH Language experience approach is suitable for all levels of learners. By using the Language Experience Approach (LEA) to teach beginning readers how to read, pupils can connect their life experiences with learning written words. The unique factor about this approach is that the pupils own words are recorded or used as they describe the event or activity. This allows them to interact with the text and gain knowledge and understanding through their experience. The LEA can be used with individual pupils or group. While it is most commonly used with young emerging readers, it is also effective for teaching struggling readers Language-Experience Approach It is an approach to reading in which the child’s own language and experiences is used to create reading material. Students dictate a story based on an experience they have had. The teacher writes the dictated story. Through discussion, the teacher can help students organize and reflect on their experiences. Language-Experience for ELL Accept the child’s language and show that it is valued. If the teacher edits it, it becomes the teacher’s language, not the child’s. However, if mispronounced, the teacher should spell correctly. As children grow in language, they will have opportunities to develop fuller knowledge of verbs, contractions, and pronunciation. Advantages It integrates the four language processes. It is child centred which brings new reader to the text rather than the other way around. Aids comprehension: the reader and composer are one and the same person. The child understands that text carries meaning It is enjoyable and allows the child and his or her life to become known. Highly motivating. Boosts self esteem Incorporates emotion and fun Can be used to develop sight vocabulary and comprehension via cloze exercises. How to conduct a LA approach in class? PROCEDURES Present the topic for discussion. This might be based on a previous field trip, as story that was read to the class, a video, or some other experience shared by the class. Write down the title on large lined chart paper with a marker. The whole class reads what you have written. Individual readings, using a pointer to indicate the words as the Encourage careful observations . Elicit and extend oral language relating to the students' thoughts and observations. Encourage students to listen and respond to their peers' observations. Read what you have written. the process and making note of the speaker's name. Make sure the students attend to this process. As the discussion occurs write down students' statements on the chart paper, repeating what you write in Follow-up activities. Develop basic skills through word banks. APPROACHES TO TEACH READING PHONICS APPROACH Phonics Approach Teaches the relation of the letters (graphemes) to the sounds (phonemes) they represent. The theory behind the phonics approach is based on two assumptions: most languages have consistent phonemes (sound) to grapheme (letter) correlation. Once children have learned the relationships of the letters to the sounds, they can pronounce printed words by blending the sounds together. Knowing these relationships help early readers recognizes familiar words accurately and automatically "decode" new words. TSL3106 Module Utilizes explicit, teacher-directed instruction to introduce skills and strategies. Provides distributed practice and cumulative review. Emphasis to reinforce phonic elements or linguistic patterns. Tightly controlled vocabulary and are used primarily for struggling readers. Selections are unnatural so it is difficult to use context clues. Program Goals Increase students’ phonemic awareness. Strengthen letter-sound associations. Increase decoding skills for single syllable and multi-syllabic words. Increase instant recognition of high frequency words. Improve spelling of single syllable and multi-syllabic words. Promote passage reading fluency and related comprehension APPROACHES TO TEACH READING SIGHT WORD APPROACH Sight Word Approach Sight words are words that are recognized instantly and without any analysis. Many sight words can’t be sounded out because they don’t follow decoding rules. Sight words are high frequency words – the words most frequently occurring in reading materials. Why do we teach sight words? Students who learn sight words have a good base for beginning reading instruction. When do we teach sight words? Sight word instruction usually begins in kindergarten and continues into primary and secondary school, although struggling readers continue learning sight words beyond secondary school. Approaches Language Experience Phonics Sight Words Definition the child’s own language and experiences is used to create reading material. Teaches the relation of the letters (graphemes) to the sounds (phonemes) they represent. words that are recognized instantly and without any analysis. Target Group individual pupils group (struggling readers) Young learner (initial stages of developing reading ) Adult learner (lack of reading proficiency) struggling readers Characteristics Language Experience Phonics Sight Word develop fuller knowledge of verbs, contractions, and pronunciation. -help early readers recognizes familiar words accurately and automatically "decode" new words. -can pronounce printed words by blending the sounds together. -high frequency words -can’t be sounded out (don’t follow decoding rules) -a good base for beginning reading instruction. Approaches Language Experience Phonics Sight Word Activity •Word Or Letter •Video & Songs •Antonyms •Picture Match •Phonic Stories •Synonyms •Listening Activity •Homophones •Parts of speech •Same double consonant words •Word family words •Beginning sounds and vowel sounds ACTIVITY FOR LANGUAGE EXPERIENCE APPROACH (LEA) Word or letter “hunts”: Teacher prepare word or letter (and sound) that he/she would like the students to recognize. Teacher then ask the students to find it in other chart story. Then, students will circle, box in, underline or etc. on the words/letters that are the same. Picture Match A few sentence strips pasted on the board. Teacher will prepare a few pictures and distribute it to the students. Then, the students need to match between the picture that already distributed with the sentence strips pasted on the board. They will be asked to read aloud the sentence. ACTIVITY FOR SIGHT WORD Use the poems and lessons to: Integrate language skills Antonyms Synonyms Homophones Parts of speech Same double consonant words Word family words Beginning sounds and vowel sounds Benefits 1. Easy to Use Lessons Minimal preparation Few outside resources required Sight words are identified in boldface type in poems Enjoyable, hands-on activities Benefits 2. Versatility of Use Can be used to introduce, practice, review and/or assess Can be used for whole-class or small-group instruction We Are Opposites We are opposites, And I’ll tell you more! I say after, And you say before. I look up, And you look down. I like to walk, You run to tow I think it’s hot, You think it’s cold. I say it’s new, You say it’s old. We are opposites It’s like I said before. Think of your own. If you want any more! I come in, And you go out. We are opposites, Let’s give a shout! Opposites Pyramid Objective to identify and read the antonym of a given sight word Video ACTIVITY FOR PHONICS Songs and Chants Blending Phonics Stories, http://www.kizphonics.com/phonics/mousecow/ Video Video. http://www.slideshare.net/cindyjbj79/teachingreading-through-phonics http://eslmethods.wikispaces.com/file/view/LANGUAG E+EXPERIENCE+APPROACH.pdf http://www.education.com/reference/article/Ref _Phonics_Language/