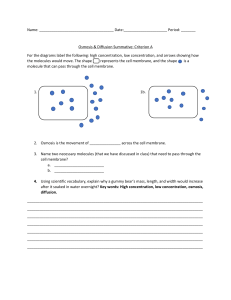
Cell Membranes are Gatekeepers PLASMA MEMBRANE • Functions: – Helps cells maintain balance (homeostasis) – Holds contents of the cell in place – Takes food and nutrients (glucose, amino acids, and lipids) PLASMA MEMBRANE • Selectively Permeable – Plasma membrane allows some molecules to pass in while keeping others out – Water: in and out freely PLASMA MEMBRANE Phospholipid molecule Hydrophilic Head = Glycerol backbone Hydrophobic Tail = 2 fatty acid chains Polar head (includes phosphate group) Love water Nonpolar tails (fatty acids) Fear Water Organization of Plasma Membrame PLASMA MEMBRANE • Cholesterol: – Stabilizes phospholipids by preventing fatty acid tails from sticking together Cholesterol Molecule Plasma membrane are made up of two layers that are filled with variety of pores, molecules, and channels Receptor Proteins: Trigger a set of cell responses when specific molecules bind to cell. Recognition Proteins ID tags and cell surface attachment sites “belongs” or “doesn’t belong” Enzymatic Proteins Accelerate chemical reactions on membrane surface Transport Proteins Allows needed large substances or waste materials to cross membrane CELLULAR TRANSPORT: OSMOSIS • Concentration gradient, areas of high and low concentrations • Salt, sugar, etc. too large to pass through a membrane • Diffusion: Movement From high to low concentration CELLULAR TRANSPORT: OSMOSIS • During osmosis, water diffuses across selectively permeable membrane. Notice number of sugar molecules did not change on each side of membrane but number of water molecules did. CELLULAR TRANSPORT: OSMOSIS • Hypertonic solution • water leaves cell by osmosis • Cell shrinks CELLULAR TRANSPORT: OSMOSIS • Hypertonic Solution: Concentration of dissolved substances (Ex: Salt) is higher outside of cell than inside • Water flows out of cell to balance out high concentration of dissolved particles outside of cell. CELLULAR TRANSPORT: OSMOSIS • Hypotonic Solution: Concentration of dissolved substances (Ex: Salt) is lower in the solution outside of cell than inside • Water flows into cell CELLULAR TRANSPORT: OSMOSIS • In hypotonic solution, water enters cell by osmosis causing cell to swell—could burst. Cell Membranes: Part 2 CELLULAR TRANSPORT: OSMOSIS • Isotonic Solution: Concentration of dissolved substances in the environment is same as concentration of dissolved substances inside cell. • Water molecules move into and out of cell at same rate • Cells maintain normal shape PASSIVE TRANSPORT • Simple Diffusion with concentration gradient • Requires no energy PASSIVE TRANSPORT • FACILITATED DIFFUSION: – Transport proteins help substances move through plasma membrane • Channel proteins • Diffusion = no energy used ACTIVE TRANSPORT • Against concentration gradient – From lower concentration to higher • Requires energy • Sodium-Potassium Pump: – transports sodium out of the cell and potassium into the cell against their concentration gradients. ACTIVE TRANSPORT • Carrier proteins used in active transport to pick up ions or molecules near cell membrane and carry them across membrane releasing them on other side. TRANSPORT OF LARGE PARTICLES TRANSPORT OF LARGE PARTICLES • Endocytosis: Cell surrounds and takes in material from environment – Material does not pass directly through membrane – Is engulfed and enclosed by portion of cell’s plasma membrane – Portion of membrane breaks away, leaving vesicle with contents which moves into cell TRANSPORT OF LARGE PARTICLES – Endocytosis: Ingest Food (Take In) • _phagocytosis________ Ingest liquid • __pinocytosis__________ – Exocytosis: Release of Wastes, Secretions TRANSPORT OF LARGE PARTICLES TRANSPORT OF LARGE PARTICLES • Exocytosis: Expulsion/Release of __large___ materials from cell – Used to excrete wastes – Also used to secrete hormones produced by cell Let’s break it down… Transport through the Cell Membrane Type of Transport Transport Protein Used? Direction of Movement Requires Energy Input from Cell? Classificatio n of Transport Simple Diffusion No With Concentration Gradient No Passive Facilitated Diffusion Yes—channel proteins or carrier proteins With concentration gradient No Passive Active Transport Yes—carrier proteins Against concentration gradient Yes Active