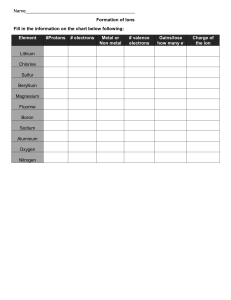
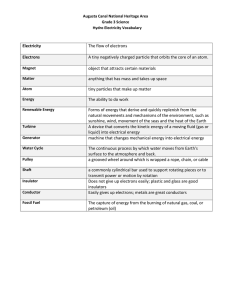
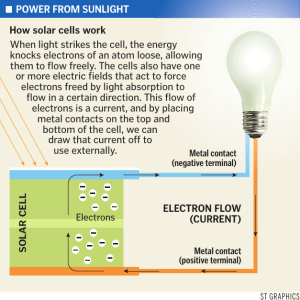
UNIT 10 LESSON 10.1 STATIC ELECTRICITY Let’s do some magic using the physics of electricity. LEARNING LADDER Starter: Observation, Analysis and conclusion Q1 ) Draw the structure of an atom (NOT Hydrogen and Helium) a) Which part of the atom is moving? Does this particle ever leave the atom, why? b) What happens to the over all charge of the atom when the particle leaves? KEY WORDS Electron, Proton Neutron Charges, Positive, Negative, Neutral, Attraction, Repulsion Q2) Watch the following video on an experiment and answer the following questions: (use the key words) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Dh8e1kWFZVI a) Why was the balloon rubbed with the straw? b) Why was the balloon moving away? MAIN TASK ( 15 MIN) Step 1 : Take a plastic ruler, rub against your jacket – Write down your observation in the shared slides. Step 2 : Inflate a balloon to an appropriate size. Rub it against hair of a volunteering partner. Write down your observation in the shared slides. Step 3 : Write a concluding statement for your two observations ( charge goes from where and is gained where) HINT :- Use the simulation link in GC to write up the conclusion for your observation EXT TASK Complete the following sentences using words from the list below. An electric current is a flow of …………….. carried by …………….. which move round the circuit from the …………….. terminal of the battery to the …………….. terminal. A metal contains …………….. that can move about freely inside the metal. A metal object can only hold …………….. if it is insulated from the ground. When two oppositely charged metal objects are brought into contact, electrons transfer from the …………….. object to the …………….. object. An …………….. can become charged with ……………. EXIT TICKET TASK Complete the following sentences using words from the list below. charge electrons positive negative Conductor insulator Friction An electric current is a flow of …………….. carried by …………….. which move round the circuit from the …………….. terminal of the battery to the …………….. terminal. A metal contains …………….. that can move about freely inside the metal. A metal object can only hold …………….. if it is insulated from the ground. When two oppositely charged metal objects are brought into contact, electrons transfer from the …………….. object to the …………….. object. An …………….. can become charged with ……………. Lesson 10.3 : Electrons on the move ( review of concept before term break 10.210.3) Starter question: 1) Write down three main characteristics of Static Electricity? 2) Differentiate between static electricity and the conventional current? 3) Can neutral objects be charged? How and explain? LESSON 10.4 CONDUCTORS AND INSULATORS Understanding the working of a characteristic difference between a conductor and an insulator. Learning about circuits and symbols of circuits. STARTER TASK MAIN TASK Go to GC and find the link to the simulation lab Define : Series circuit, parallel circuit What ammeter does? What voltmeter does? How cell makes current flow Why a lamp will light up? Lesson 10.3 : Electrons on the move ( review of concept before term break 10.210.3) Starter question: 1) Write down three main characteristics of Static Electricity? 2) Differentiate between static electricity and the conventional current? 3) Can neutral objects be charged? How and explain? LESSON 10.4 CONDUCTORS AND INSULATORS Understanding the working of a characteristic difference between a conductor and an insulator. Learning about circuits and symbols of circuits. STARTER TASK MAIN TASK Go to GC and find the link to the simulation lab Define : Series circuit, parallel circuit What ammeter does? What voltmeter does? How cell makes current flow Why a lamp will light up? LET’S ACHIEVE! WHAT ARE THE ENERGY TRANSFORMATIONS YOU SEE? ( START WITH THE FIRST ENERGY AND CONTINUE THE FLOW UNTIL THE FINAL OUTPUT ENERGY) MAIN TASK Complete the task assigned in manage back about the energy balance PLENARY ISA Questions