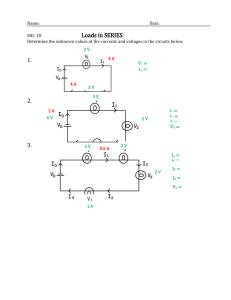
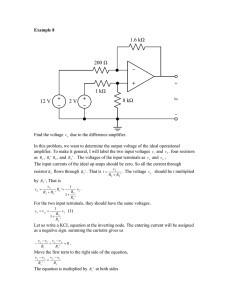
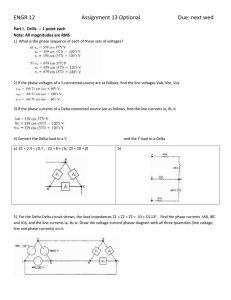
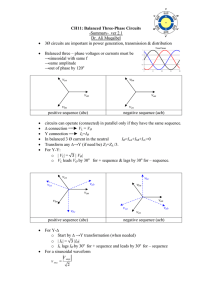
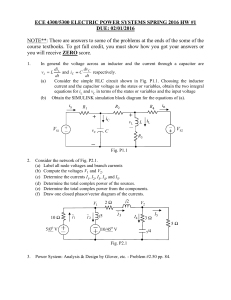
Introduction to Electrical Engineering Lecture #11 AC CIRCUIT ELEMENTS AND LAWS Dr. ARIUNBOLOR Purvee 11/28/2019 German-Mongolian Institute for Resources and Technology 1 POLYPHASE SYSTEM • Circuit or system in which AC sources operate at the same frequency but different phases are known as poly-phase. • Three phase is the most economical poly-phase system. • Melting purposes need 48 phases supply. POLYPHASE SYSTEM • Three Phase System: • A generator consists of three coils placed 120 apart. • The voltage generated are equal in magnitude but, out of phase by 120. 11/28/2019 ¾ Cycle ½ Cycle ¼ Cycle Start Three-phase Voltage Sources German-Mongolian Institute for Resources and Technology 4 Three phase vs single phase circuits 11/28/2019 German-Mongolian Institute for Resources and Technology 5 FARADAYS LAW • Three things must be present in order to produce electrical current: a) Magnetic field b) Conductor c) Relative motion • • Conductor cuts lines of magnetic flux, a voltage is induced in the conductor Direction and Speed are important THREE PHASE GENERATOR Video: Three phase generation (7:52) • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4oRT7PoXSS0&t=53s 8 GENERATOR WORK • The generator consists of a rotating magnet (rotor) surrounded by a stationary winding (stator). • Three separate windings or coils with terminals a-a’, b-b’, and c-c’ are physically placed 120 apart around the stator. • As the rotor rotates, its magnetic field cuts the flux from the three coils and induces voltages in the coils. • The induced voltage have equal magnitude but out of phase by 120. PHASE SEQUENCE van (t ) VM cos t vbn (t ) VM cost 120 vcn (t ) VM cost 120 Van VM 0 Van VM 0 Vbn VM 120 Vbn VM 120 Vcn VM 120 Vcn VM 120 POSITIVE SEQUENCE NEGATIVE SEQUENCE Balanced Y-connected Voltage Source • Balanced phase voltages are equal in magnitude and are out of phase with one another by 120 degrees. • Phase voltages sum up to zero. • Two possible combinations: abc or (+) sequence acb or () sequence Balanced Y-connected Voltage Source • Balanced line voltages are equal in magnitude and are out of phase with one another by 120 degrees. • Line voltages sum up to zero. • The magnitude of line voltages is 1.732 times the magnitude of the phase voltages • Line Voltages lead their corresponding phase voltages by 30 degrees Three-phase Voltage Sources Y-connected Source D-connected Source Balanced Three-phase Load Configurations A balanced load is one in which the phase impedances are equal in magnitude and in phase. Y-connected Load D-connected Load Balanced Three-phase Load Configurations Reminder: A Y-connected load consists of three impedances connected to a neutral node, while a –connected load consists of three impedances connected around a loop. The load is balanced when the three impedances are equal in either case. 11/28/2019 German-Mongolian Institute for Resources and Technology 15 THREE PHASE QUANTITIES QUANTITY SYMBOL Phase current I Line current IL Phase voltage V Line voltage VL PHASE VOLTAGES and LINE VOLTAGES • Phase voltage is measured between the neutral and any line: line to neutral voltage • Line voltage is measured between any two of the three lines: line to line voltage. PHASE CURRENTS and LINE CURRENTS • Line current (IL) is the current in each line of the source or load. • Phase current (I) is the current in each phase of the source or load. LINE VOLTAGES, VL Vab Van Vbn Vbc Vbn Vcn Vca Vca Van Vab 3VM 30 Vbc 3VM 90 Vca 3VM 150 Van VM 0 volt Vbn VM 120 volt Vcn VM 120 volt LINE VOLTAGE (VL) PHASE VOLTAGE (V) Vab 3 VM 30 volt Vbc 3 VM 90 volt Vca 3 VM 150 volt PHASE DIAGRAM OF V L AND V Vca Vcn Vab 30° 120° Vbn Vbc -Vbn Van PROPERTIES OF PHASE VOLTAGE • All phase voltages have the same magnitude, Vca Vcn Vab V = lVanl = lVbnl = lVcnl 30° 120° • Out of phase with each other by 120 Vbn Vbc -Vbn Van PROPERTIES OF LINE VOLTAGE • All line voltages have the same magnitude, VL = lVabl = lVbcl = lVcal Vca Vcn • Out of phase with each other by 120 Vab 30° 120° Vbn Vbc -Vbn Van RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN V and VL 1. Magnitude VL 3 V 2. Phase Vca Vcn Vab - VL LEAD their corresponding 30° V by 30 VL V 30 120° Vbn Vbc -Vbn Van Three phase connections In three phase circuit, star and delta connection can be arranged in four different ways• • • • Star-Star connection Star-Delta connection Delta-Star connection Delta-Delta connection 11/28/2019 German-Mongolian Institute for Resources and Technology 25 Balanced Y-Y Connection ZY = ZS + Zl + ZL IL = I Balanced Y-Y Connection 𝑉𝑎𝑛 = 𝑉𝑝00 𝑉𝑏𝑛 = 𝑉𝑝 − 1200 𝑉𝑐𝑛 = 𝑉𝑝1200 𝑉𝑎𝑏 = 𝑉𝑎𝑛 +𝑉𝑛𝑏 = 𝑉𝑎𝑛-𝑉𝑏𝑛 = 3𝑉𝑝 300 𝑉𝑏𝑐 = 𝑉𝑏𝑛 − 𝑉𝑐𝑛 = 3𝑉𝑝 − 900 𝑉𝑐𝑎 = 𝑉𝑐𝑛 − 𝑉𝑎𝑛 = 3𝑉𝑝 − 2100 Balanced Y-Y Connection • Thus, the magnitude of the line voltages is times the magnitude of the phase voltages 𝑉𝑝 , or 𝑉𝐿 = 𝑉𝑝 3 𝑉𝑝 = 𝑉𝑎𝑛 = 𝑉𝑏𝑛 = 𝑉𝑐𝑛 𝑉𝐿 = 𝑉𝑎𝑏 = 𝑉𝑏𝑐 = 𝑉𝑐 • Also the line voltages lead their corresponding phase voltages by 300 11/28/2019 German-Mongolian Institute for Resources and Technology 28 Problem: Calculate the line currents in the three-wire Y-Y system as shown. n Van Ia ZY 1100 Ia 6.81 21.8 16.15521.8 I b I a 120 6.81 141.8A I c I a 240 6.81 261.8 6.8198.2A PHASE VOLTAGE AND LINE VOLTAGE • In D-D system, line voltages equal to phase voltages: VL Vφ PROPERTIES OF PHASE CURRENT • All phase currents have the same magnitude, Iφ I AB I BC ICA Vφ ZΔ • phase shifts are by 120 with each other PROPERTIES OF LINE CURRENT • All line currents have the same magnitude, I L Ia I b Ic • Out of phase with each other by 120 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN I and I L 1. Magnitude IL 3 IF 2. Phase - VL LAG their corresponding V by 30 IL IF 30 PHASE DIAGRAM OF IL AND I Conclusions 1. Line voltage and phase voltage 11/28/2019 German-Mongolian Institute for Resources and Technology 36 Conclusions 2. Peak voltage, rms 11/28/2019 German-Mongolian Institute for Resources and Technology 37 Conclusions 3. Vector Diagram 11/28/2019 German-Mongolian Institute for Resources and Technology 38 Problem: A balanced delta connected load having an impedance 20-j15 is connected to a delta connected, positive sequence generator having Vab = 3300 V. Calculate the phase currents of the load and the line currents. Balanced ∆ − ∆ Connection Given Quantities ZΔ 20 j15 25 36.87 Vab 3300 Phase Currents VAB 3300 I AB 13.236.87A ZΔ 25 38.87 I BC I AB 120 13.2 - 83.13A I CA I AB 120 13.2156.87A Line Currents I a I AB 3 30 13.236.87 3 30 A 22.866.87 I b I a 120 22.86 - 113.13A I c I a 120 22.86126.87A Balanced Y-D Connection Problem: A balanced abc-sequence Y-connected source withVan 10010 V is connected to a delta-connected balanced load of 8+j4 per phase. Calculate the phase and the line currents. Solution: Given Quantities • Balanced WYE source • Van= 10010 V • Balanced DELTA load • ZD= 8+j4 Phase Currents VAB I AB ZΔ VAB= voltage across ZD = Vab= source line voltage VAB 3 Van 30 VAB 173.240 V 173.240 I AB 19.3613.43 8 j4 Phase Currents I AB 19.3613.43 I BC I AB13.43 120 I BC 19.36 106.57 A I CA 19.3613.43 120 I CA 19.36133.43 A Line Currents I a 3 I AB 30 3 (19.36) 13.43 30 I a 33.53 16.57 A I b I a 120 33.53 136.57 A I c I a 120 33.53 103.43 A Balanced D-Y Connection Balanced D-Y Connection 11/28/2019 German-Mongolian Institute for Resources and Technology 51 Example A balanced Y-connected load with a phase impedance of 40+j 25 is connected to a balanced, positive sequence D-connected source with a line voltage of 210 V. Calculate the phase currents. Use Vab as reference. 𝑍𝑌 = 40 + 𝑗25 = 47.17 320 𝑉𝑎𝑛 = 𝑉𝑎𝑏 = 21000 𝑉𝑎𝑏 3 300 = 121.2 − 620 𝑉𝑎𝑛 121.2 − 620 0 = = 2.57 − 62 𝐼𝑎 = 47.17320 𝑍𝑌 𝐼𝑏 = 𝐼𝑎 1200 = 2.57 −1780 𝐼𝑐 = 𝐼𝑎 1200 = 2.57 −1780 11/28/2019 ¾ Cycle ½ Cycle ¼ Cycle Start Three-phase Voltage Sources German-Mongolian Institute for Resources and Technology 53 Three phase vs single phase circuits 11/28/2019 German-Mongolian Institute for Resources and Technology 54