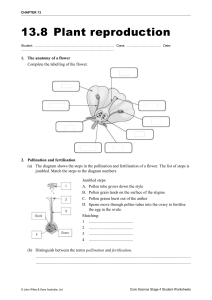
CHAPTER 1 What is photosynthesis? - It is the process of producing food in order to keep a plant alive What is starch? - features - It is a source of energy, it is a carbohydrate that forms colourless grains in the cytoplasm of leaf cells. What is a destarched plant? - A plant that had its starch removed Construct to word equation for photosynthesis and explain how it is constructed light - Water + carbon dioxide ----------→ glucose + oxygen chlorophyll What does soda-lime do? What mixture is it? - Soda-lime is a mixture of sodium hydroxide and calcium hydroxide, it absorbs the carbon dioxide from the air which is very useful in testing carbon dioxide and starch production What is the sodium hydrogen carbonate solution? - It releases carbon dioxide to the air With the two examples of mixtures above explain how you can test starch production in relation with carbon dioxide? 1. Two exact same plants are covered with plastic bags 2. A dish of soda lime will be placed in one of the plants 3. A dish of sodium hydrogencarbonate solution will be placed in another 4. The plants are left to sit under the sun 5. Leaves from both plants will be tested for starch using iodine solution How do we test light and starch production? 1. A leaf of a destarched plant is covered with aluminium 2. Another leaf of the same destarched plant is covered with transparent plastic 3. The plant is left under the sun 4. Presence of starch is tested using iodine solution What are variegated plants? - Plants with leaves that have white parts that show the absence of chlorophyll What does chlorophyll do? - Absorbs sunlight and gives leaves the green color What color is the iodine solution? - Yellowish-Brown What happens when you drop iodine solution on to a piece of the leaf? Explain the different colors shown - Presence of starch → blue-black - No starch → remains brown How do we test oxygen production? - By using the Canadian pondweed What does nitrogen do? - Nitrogen helps with the development of leaves, without it the leaves turn yellow and shows poor growth. It also needed for the production of chlorophyll as well as making proteins What does phosphorus do? - Needed for development of roots, without it, the plants will show poor growth. What does potassium do? - Development of flowers and fruits, without it it would be yellow and grow abnormally. What does biodegradable mean? - It can be decomposed/ broken down to simple substances CHAPTER 2 What is pollination? - The transfer of pollen from the male part of a flower to the female part of a flower. Fill in their functions and names ( Insect Pollinated flowers) Female parts (Carpel/Pistil) Male parts (Stamen) Stigma Anther Style Filament Ovary ------------- Compare and contrast these two types of flowers Insect pollinated Wind pollinated Flower is large and brightly colored in order to Often green or dull because it has no need to attract insects. attract insects. Some produce nectar in order to attract insects, could also have scents No scent or nectar because it has no need to attract insects. Spreads pollen by insects Spreads pollen by using the wind to transport the pollen Sticky or spiky - pollen grains can attach onto them Lightweight pollen grains What is a sepal? - Small tough, leaf like structure that protects the flower. What is a corolla? - Corolla is another word for petal What is a calyx? - A calyx is a ring of sepals What is a stalk? - A stalk is the main stem of a plant Name the parts of a wind pollinated flower - Stigma, Anther, Long filament, Ovary What are the sex cells of living things called? Give examples. - Gametes; Ovules, pollen grains (for plants) What happens when the pollen grains are fully formed? - The anther splits open to release them What is self pollination? - Self pollination is when the pollen grains are transported from one part of the flower to another part of the same flower What is cross pollination? - Cross pollination is when the pollen grains of one flower are transported to another flower How do flowers prevent self- pollination? 1. Releasing pollen before the stigma is ready to receive it 2. Having the stigmas of other plants ready first Give the two main ways of cross pollination - Insect pollination - Wind pollination Explain the relationship between bees and flowers - Bees get the nectar they need to make honey by traveling between flowers. The bee brings pollen from one plant to another, resulting in pollination. What is the process of fertilization? - The process of fertilization is when the male gamete fuses with the female gamete What happens after fertilization? - Zygote splits into multiple cells to create an embryo What is dispersion? - Seed dispersal is the movement, spread or transport of seeds away from the parent plant. What is the impact of dispersion? - Dispersion helps the seeds spread out away from each other so when in the process of growing the plants don’t compete against each other for nutrients. This means the plant will not fight for the water intake and the sunlight. CHAPTER 6 What are the main groups of living things? - Fungi, Monera, Protoctista, Viruses, Plants What is the monera kingdom→ give examples - One cell body with no nucleus, blue-green algae, bacteria What is the Fungi kingdom→ give examples - Spores, feeding threads called hyphae; Mushrooms, yeast What is the Virus kingdom→ give examples - No cell structure, Influenza, AIDS What is the protoctista kingdom→ give examples - One cell body with nucleus; amoeba, ciliates The Plant kingdom Group Features Examples Algae No stem, leaves, roots Green slime. seaweed Liverworts, mosses No true roots, spores moss Conifers Cones, Woody stem, seeds, roots Fiddle head ferns ferns Fronds, stems, spores, roots Fir, pine Flowering plants Everything Sunflower, daisy Group Features Examples Jellyfish Soft body, tentacles at on end Box jellyfish, sea anemone, round the mouth coral Flatworms Very thin, flat body Flukes, tapeworms Annelid worms Cylindrical bodies divided into rings Earthworm, leech, ragworm Nematode worms Small cylindrical bodies not divided into rings Hookworm, pinworm Arthropods Jointed legs Insects, spiders, scorpions Molluscs Soft body with shell Snails, slugs, octopus The Animal kingdom Invertebrates: Echinoderms Spiny skin, arms or globe shaped Brittle star, sea cucumber, sea lily Group Features Examples Fish Scales, fins Shark, guppy Amphibians Smooth or warty skin, tadpole stage Frogs, toads Reptiles Skin covered in dry scales Snakes, lizards Birds Feathers, beaks Penguin, eagle Mammals Fur, give milk to young Mouse, lion Vertebrates: Compare and contrast the differences between a spider key and a numbered key? What is internal and external skeleton? By using the information below create a type of key that is most suitable on your notebook. A) Kangaroo, Cow, Bee, Fish, Snail B) The image shown above What are inherited characteristics? - Features of living things that are passed down through different generations Name all the parts of a cell? Explain the functions - Cytoplasm - Nucleus - Cell membrane What is cell division? What happens? - The nucleus divides and each pair of threads separates. Each thread then enters one of the nuclei and forms new cells. For each cell formed every thread becomes a chromosome What long strands of material appear during cell division? - Chromosomes Why can we see the chromosomes? - Cell division Do we see chromosomes before, after or during cell division? - During It is known that chromosomes are like messages, what is each message called? - Genes What's their function? - Provide information on how the cell grows, develops and behaves as well as the body too What is the link between chromosomes and gametes? - Each organism has a pair of 23 chromosomes from their parents. What happens during the formation of gametes? - Parts of the chromosomes swap positions, this doesn't allow the exact copy of the genetic code to pass down, leading to variation. What are the bases in a DNA? - Thymine, cytosine, guanine, adenine What is selective breeding? - Selecting organisms with desired features to create variation What are mutations? - A change occurred in the DNA What are genetically modified crops? - Changing parts of the genes to create a new organism. What are clones? - An exact copy of its parent What is natural selection? - Selection that happens naturally (nature). Scenario: *Choose the best type of breeding for each* Scenario Type of breeding An apple tree the produces fresh apples and an apple tree that doesn’t produce as fresh apples Selective breeding Goat with wings Mutation Edible vegan meat to help the environment Genetically modified Hydra clone Parents having children Natural selection