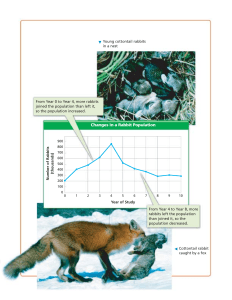
Stem 1 ______ Stem 2 ______ Stem 3 ______ Stem 4 ______ Wolves vs. Rabbits Name: ___________ Predator Prey Relationship Game HR: _______ Date:__________ Objective: To investigate how populations are affected by predator-prey relationships over several generations. Materials: 60, 6 x 6cm squares cut from red paper – the WOLVES 400, 2 x 2cm squares cut from yellow paper – the RABBITS One sheet of green paper (approx.. 43 x 28cm) – the MEADOW Graph paper Procedure: The rabbit managers add active rabbits by spreading them evenly in the meadow and remove rabbits when they are caught. The wolf managers throw active wolf cards and add or remove wolves from the meadow. All animals that are removed from the meadow are placed back into the reserve stacks. The Rules: 1. To start the game, the rabbit managers distribute THREE rabbits evenly on the meadow. 2. The wolf managers toss ONE active wolf square into the meadow in an effort to catch rabbits. The wolf must leave the managers hand outside the meadow area. 3. If the wolf square lands on or touches a rabbit square, the rabbit is considered “caught” (dead), and the rabbit manager removes the caught rabbit. 4. After the caught rabbits are removed, the remaining rabbits get to reproduce (double). 5. Any wolf that catches less than three rabbits has starved to death and is removed by the wolf manager. 6. If there are no surviving wolves, a new round is begun with a new wolf, which immigrates into the meadow, and double the number of rabbits left at the end of the last round. 7. If a wolf catches three rabbits, the wolf is allowed to reproduce (Add another wolf). 8. For every three rabbits a wolf catches it is allowed to have one pup. It will rarely reproduce more than one pup. Data: Record the number of wolves and rabbits for each generation. Once you see the rabbit population have a huge increase, and a huge decrease (down to almost nothing), YOU MAY STOP. Generation 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Wolves Rabbits Generation 15 Wolves Rabbits 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 Results: Use the data table above to make a ***GRAPH*** of the data. What kind of graph is best for showing changes over time? Use different colours to show the wolf and rabbit populations (you will need a legend!). Observations: 1. How do you explain what happened in the first round? 2. Look at your graph for the two populations. How are the wolf and rabbit populations related to each other? 3. What do you think would happen if you introduced another predator, such as a coyote? What would happen to the rabbits? What would happen to the wolves? Applications: 4. How does this simulation relate to the human population and its interaction with its environment? Are there any predator-prey relationships? 5. What predator-prey relationships have you observed in your neighbourhood? 6. If a population biologist visited your classroom, what are some questions you might ask? (Hint: do you think humans would impact other populations? What about our population?)