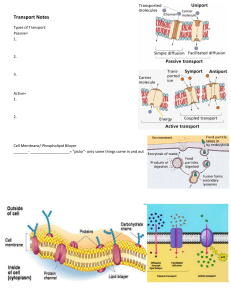
The Cell Membrane •All cells are separated from the external environment by a Plasma Membrane • Membrane is pliable and semipermiable only allowing certain materials in/out of cells. •It is composed of many components. –Phospholipids –Cholsterol –Proteins • Phospholipids –Very similar to triglycerides however, one of the fatty acid chains has been replaced by a very polar Phosphate group Phospholipids & Water • • • This poses a problem for the molecule since the molecule is both polar and non-polar simultaneously. It is therefore very unstable in water, polar end is attracted to it, non polar tails are repelled by it. This forces the phospholipids to take an arrangement such that their tails face each other. This accomplishes 2 things.. – The polar heads can be adjacent to polar water molecules – The non-polar tails can be adjacent to each other. The Lipid Bilayer • As the layer enlarges it forms a bubble shape formed of a lipid bilayer which is the foundation of the plasma membrane • More Membrane Components • The membrane requires a few more components to make it complete: • Cholesterol • Functions to hold the membrane together like glue. Adds strength to the membrane. • Proteins (2 types) • Intrinsic Proteins – Extend into or through lipid bilayer – Often are channel proteins allowing large molecules in/out • Extrinsic Proteins – Exist only on surfaces of the bilayer – Often serve as receptor molecules – Glycoproteins serve as cellular markers (nametags) The Fluid Mosaic Model • Entire model is referred to as the Fluid Mosaic model of the plasma membrane