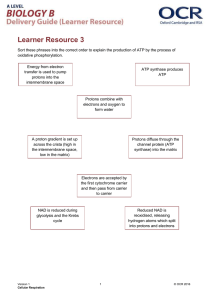
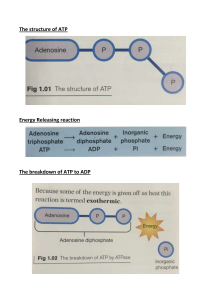
Describe how ATP is made in mitochondria (6 marks) ATP is produced in the krebs cycle. This cycle also produces reduced NAD, the hydrogen from this can be split into protons and electrons. These electrons pass along the ETC and the energy released is used to move protons into the intermembrane space. They then move through ATP synthase via chemiosmosis forming ATP from ADP and Pi. ATP is produced via the enzyme ATP synthase from ADP and Pi. In mitochondria it is also made in the calvin cycle. One turn of the calvin cycle produces 1 molecule of ATP. For each glucose molecule that is broken down, 32 molecules of ATP are formed. The ADP is phosphorylated in the matrix of the mitochondria as it passes there from the intermembrane space. The krebs cycle produces the coenzymes NADH and FADH which provide the electrons required for the electron transport chain. In a series of redox reactions, energy is released and protons move into the matrix of the mitochondria. Once here ATP synthase generates ATP molecules. Oxygen is the final electron acceptor in the ETC and the electrons join with oxygen and protons to form water. Describe how ATP is made in mitochondria (6 marks) ATP is produced in the krebs cycle. This cycle also produces reduced NAD, the hydrogen from this can be split into protons and electrons. These electrons pass along the ETC and the energy released is used to move protons into the intermembrane space. They then move through ATP synthase via chemiosmosis forming ATP from ADP and Pi. ATP is produced via the enzyme ATP synthase from ADP and Pi. In mitochondria it is also made in the calvin cycle. One turn of the calvin cycle produces 1 molecule of ATP. For each glucose molecule that is broken down, 32 molecules of ATP are formed. The ADP is phosphorylated in the matrix of the mitochondria as it passes there from the intermembrane space. The krebs cycle produces the coenzymes NADH and FADH which provide the electrons required for the electron transport chain. In a series of redox reactions, energy is released and protons move into the matrix of the mitochondria. Once here ATP synthase generates ATP molecules. Oxygen is the final electron acceptor in the ETC and the electrons join with oxygen and protons to form water.