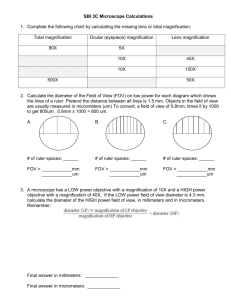
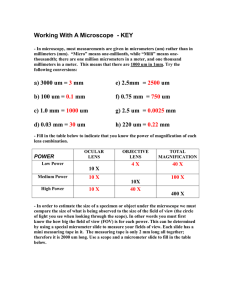
Microscopy Formulas This Photo by Unknown Author is licensed under CC BY-NC Magnification Magnification = Magnification of Eyepiece lens X Magnification of Objective lens If the eyepiece has a magnification of 10X, and the objective lenses are 4X, 10X, and 40X, what are the magnifications at low, medium, and high power? Low Power = 10 x 4 = 40X Medium Power = 10 x 10 = 100X High Power = 40 x 10 = 400X Example: Field of View at Low Power Computing FOV of other objectives If the diameter of field of view (FOV) is KNOWN for low power, you can compute for the FOV for the medium and high power FOV(low) x magnification (low) = FOV(med) x magnification (med) 5 mm x 40X = FOV(med) x 100X FOV(med) = (5 mm x 40X ) / 100X FOV(med) = 200 / 100 = 0.2 mm You often need to compute FOV into µm Magnification FOV (mm) FOV (µm) Low power (4X) 40X 5 5,000 Medium power (10X) 100X 2 2000 High power (40X) 400X 0.5 500 • 1 mm = 1,000 µm Computing Object Size (1) 1. Estimate how many times the specimen fits across the FOV 2. Example on the left: specimen fits across the high power FOV approx. 2.25 times times the object 3. Object size = FOV (in µm) / #fitsofacross FOV 4. Object size = 500 µm / 2.25 = 220 µm Computing Object Size (2) Example: • The average size of an onion skin cell was given at 0.25 mm • Magnification = Image size Actual size • The image printed on a worksheet measures 2 cm • What is the magnification of the image? = 20 mm/ 0.25 mm = 80 mm • = 80,000 µm Compute for Drawing Magnification Drawing magnification = Drawing size / Object Size Example: Drawing of an onion skin cell was measured at 4 cm Actual size of an onion skin cell was given at 0.25 mm Drawing magnification = 40 mm / 0.25 mm = (40,000 µm / 250 µm) = 160 times